Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Microwave Photonics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
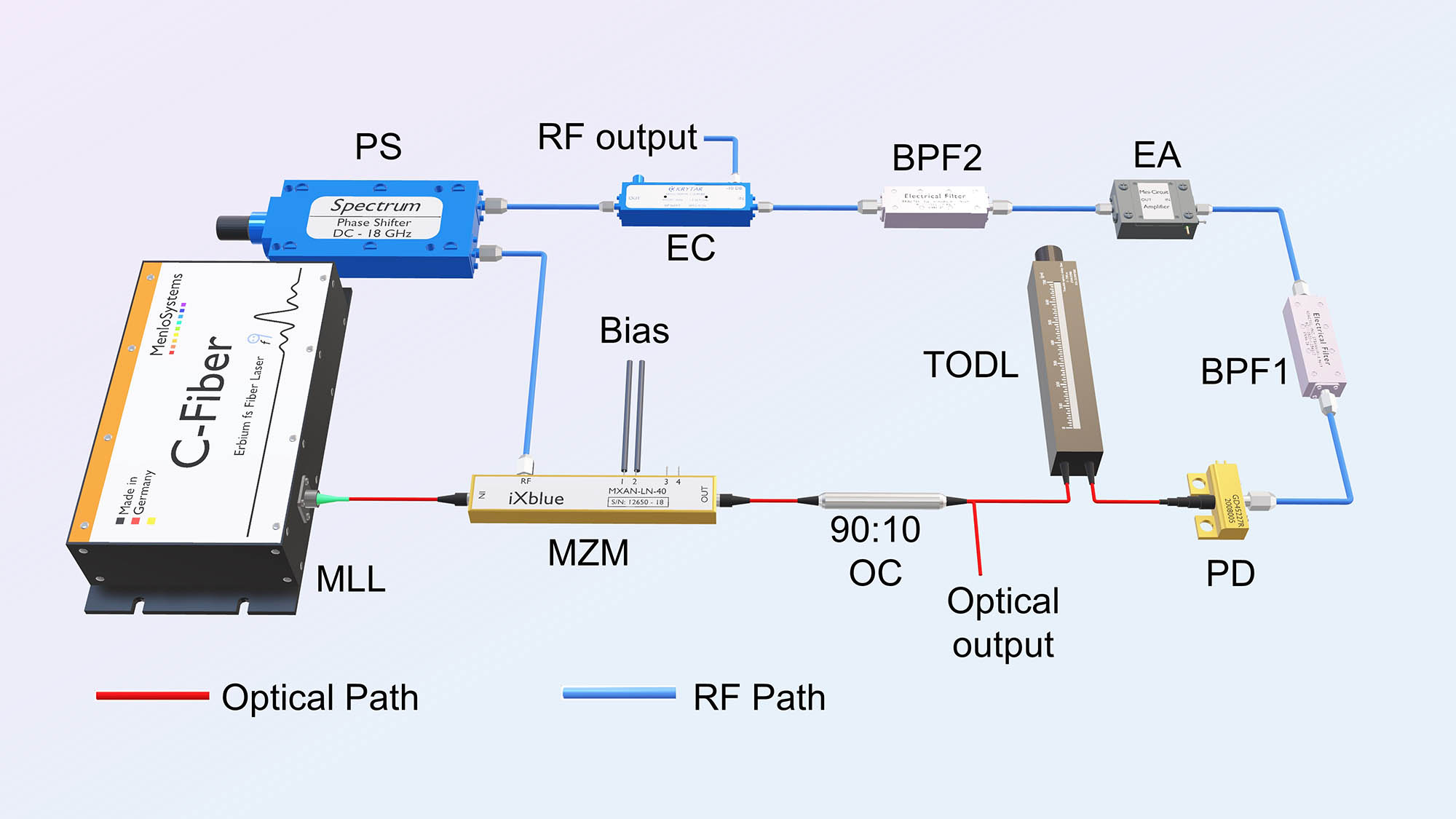
An approach for frequency division of an optical pulse train (OPT) based on an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. When the OPT is injected into the OEO, a microwave signal with a frequency equaling fractional multiples of the repetition rate of the OPT is generated. This signal is then fed back to the OEO, maintaining its oscillation, while simultaneously serving as the control signal of a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) in the OEO. The MZM acts as an optical switch, permitting specific pulses to pass through while blocking others. As a result, the repetition rate of the OPT is manipulated. A proof-of-concept experiment is carried out. Frequency division factors of 2 and 3 are successfully achieved. The phase noises of the OPT before and after the frequency division are investigated. Compared to previously reported systems, no external microwave source and sophisticated synchronization structure are needed.
frequency division optoelectronic oscillator mode-locked laser microwave photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043902
光电振荡器是一种采用光电结合方式的新型微波频率源,其利用光学长时储能,可以实现极低相位噪声的信号输出。文章研究了光纤中散射噪声对光电振荡器相位噪声的影响,重点介绍了基于相位调制等效展宽激光线宽,抑制布里渊散射噪声架构,通过理论公式推导以及实验验证,表明了上述架构可极大改善光电振荡器的相位噪声。实验中采用调制频率为50MHz、调制幅度为3.1的相位调制信号对激光线宽进行等效展宽,得到在10GHz频率下为-157.3dBc/Hz@10kHz的极低相位噪声信号输出。
相位调制 激光线宽 极低相噪 光电振荡器 phase modulation laser line-width ultra-low phase noise optoelectronic oscillator
南京师范大学计算机与电子信息学院,江苏省光电技术重点实验室,江苏 南京 210023
提出了一种基于双环光电振荡器(OEO)的频分复用光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)传感系统。在该传感系统中,从两个级联的FBG反射的光信号经马赫-曾德尔调制器调制后进入光路的双环结构,两路光信号经耦合后再通过波分复用分成两路,由光电探测器还原为电信号。该电信号分别通过两个不同中心频率的电带通滤波器后形成稳定的微波振荡,输出两路微波信号,分别对应两个FBG传感器。最后,通过对两路微波信号的频率漂移进行测量,最终实现传感解调。实验中对两个FBG分别施加应变和温度,结果表明:传感系统的应变灵敏度为0.100 kHz/μ?,最大频率偏移0.035 kHz,对应0.35 μ?的测量误差;温度灵敏度为1.135 kHz/℃,最大频率偏移0.072 kHz,对应0.06 ℃的测量误差。该系统借助双环OEO的结构,具有稳定性高、测量误差小的优点。
传感器 光电振荡器 微波光子学 频分复用 光纤光栅 光学学报
2023, 43(20): 2028002
南京邮电大学先进光子技术实验室,江苏 南京 210023
提出和研究了一种高信噪比(SNR)随机光电振荡器(ROEO)。该ROEO由随机光纤激光器与光电振荡器两部分组成,得益于随机光纤激光器中瑞利散射(RS)提供的随机分布反馈,实现了宽带随机微波信号的产生。通过在随机光纤激光器中加入另一个波分复用器(WDM),去除残余的拉曼泵浦光,提高了随机微波信号的信噪比。控制信号光的偏振态,抑制了随机腔中的受激布里渊散射(SBS)效应。实验中,获得了带宽为DC~30 GHz(DC代表直流0 Hz,表达的含义是从0 Hz到30 GHz)的随机微波信号。在DC~10 GHz范围内的信噪比约为40 dB,并且腔内的受激布里渊散射与随机微波信号的功率差达到约19.64 dB。高信噪比宽带随机微波信号在随机比特生成、雷达、安全通信等领域有重要的应用前景。
微波光子学 随机光电振荡器 瑞利散射 波分复用器 高信噪比 光学学报
2023, 43(20): 2023001
1 长春理工大学空间光电技术国家与地方联合工程研究中心,吉林 长春 130022
2 长春理工大学光电工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
如何获得频率高、相位噪声低和稳定性高的微波信号一直都是微波光子学领域的研究热点。基于此,提出一种基于受激布里渊散射(SBS)的可调谐光电振荡器(OEO)。实验中光载波和泵浦光来自同一可调谐激光器,利用泵浦光的SBS对光载波的相位调制边带进行放大,通过改变可调谐激光器的输出波长使布里渊频移量发生变化,从而实现输出微波信号的可调谐。实验结果表明,所设计的OEO可以实现频率范围为10.13~10.65 GHz的信号输出,可调谐范围为520 MHz。结构中仅使用了一个相位调制器,无偏压输入器件的引入,这使得所设计的OEO稳定性较高。在20 min内频率漂移小于1 MHz,功率变化小于1.15 dB。
光学器件 光电子学 微波光子学 受激布里渊散射 光电振荡器 频率可调谐 光学学报
2023, 43(11): 1123002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics and School of Optical and Electronic Information, Wuhan, China
2 China Information and Communication Technologies Group Corporation, State Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Technologies and Networks, Wuhan, China
3 National Information Optoelectronics Innovation Center, Wuhan, China
4 Optics Valley Laboratory, Wuhan, China
Parity‐time (PT) symmetry breaking offers mode selection capability for facilitating single‐mode oscillation in the optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) loop. However, most OEO implementations depend on discrete devices, which impedes proliferation due to size, weight, power consumption, and cost. In this work, we propose and experimentally demonstrate an on-chip tunable PT‐symmetric OEO. A tunable microwave photonic filter, a PT‐symmetric mode‐selective architecture, and two photodetectors are integrated on a silicon‐on‐insulator chip. By exploiting an on‐chip Mach–Zehnder interferometer to match the gain and loss of two mutually coupled optoelectronic loops, single‐mode oscillation can be obtained. In the experiment, the oscillation frequency of the on-chip tunable PT‐symmetric OEO can be tuned from 0 to 20 GHz. To emulate the integrated case, the OEO loop length is minimized, and no extra-long fiber is used in the experiment. When the oscillation frequency is 13.67 GHz, the single‐sideband phase noise at 10-kHz offset frequency is -80.96 dBc / Hz and the side mode suppression ratio is 46 dB. The proposed on-chip tunable PT‐symmetric OEO significantly reduces the footprint of the system and enhances mode selection.
silicon photonics optoelectronic oscillator parity-time symmetry Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(1): 016004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of The Gas Disaster Detecting, Preventing and Emergency Controlling, Chongqing 400037, China
2 China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Chongqing Research Institute, Chongqing 400039, China
3 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
A novel fiber-optic magnetic field sensor with high interrogation speed and resolution by using an etched fiber Bragg grating (FBG) in conjunction with a dual-loop optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. A commercial FBG is firstly dipped into mixed hydrofluoric acid solution to remove the cladding layer and then is embedded with the magnetic fluid (MF) as a sensing element. The central wavelength reflected from the FBG is related to the overall time delay of the dual-loop OEO, which determines the oscillating frequency of the OEO. Therefore, the magnetic field can be estimated by measuring the oscillating frequency shift of OEO. The experimental results show that the oscillating frequency linearly increases with the increment of the magnetic field, achieving the sensitivity of 16.3 Hz/Oe with an R-square of 0.991 in the range of 5 mT-10 mT. In addition, the maximum error is within ±0.05 mT in the range of 7 mT-8 mT, which offers potentials in many fields where the high-precision magnetic field measurement is required.
Etched fiber Bragg grating optoelectronic oscillator magnetic fluid magnetic field measurement Photonic Sensors
2022, 12(4): 220419
1 中国矿业大学信息与控制工程学院,江苏 徐州 221116
2 吉林大学电子科学与工程学院集成光电子学国家重点实验室,吉林 长春 130012
光电振荡器(OEO)作为微波信号源是微波光子学领域的研究热点,提出并理论分析了一种基于受激布里渊散射(SBS)效应和载波相移单边带调制的频率和相位均可调谐的五倍频OEO。在该结构中,利用级联调制器结构产生5个功率相等、频率间隔相同的光作为泵浦光,并通过布里渊增益损耗补偿原理得到五倍频OEO。利用布里渊波长依赖特性得到了频率可调谐的微波信号,通过调节双平行马赫-曾德尔调制器实现了输出微波信号的相位可调谐。所设计的OEO可以输出高频率微波信号,频率调谐范围为44.00~47.25 GHz,并在频率可调谐的基础上实现~的相位可调谐。
光电子学 微波光子学 光电振荡器 微波信号产生 受激布里渊散射效应 光学学报
2022, 42(22): 2225001





