
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information Materials and Intelligent Sensing Laboratory of Anhui Province, Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronic Information Acquisition and Manipulation of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Opto-electronics Engineering, Anhui University, Hefei 230601, China
2 School of Instrument Science and Opto-electronics Engineering, Laboratory of Optical Fibers and Micro-nano Photonics, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
3 School of Opto-electronic Engineering, Zaozhuang University, Zaozhuang 277160, China
Random lasers are a type of lasers that lack typical resonator structures, offering benefits such as easy integration, low cost, and low spatial coherence. These features make them popular for speckle-free imaging and random number generation. However, due to their high threshold and phase instability, the production of picosecond random lasers has still been a challenge. In this work, we have developed three dyes incorporating polymer optical fibers doped with various scattering nanoparticles to produce short-pulsed random fiber lasers. Notably, stable picosecond random laser emission lasting 600 ps is observed at a low pump energy of 50 µJ, indicating the gain-switching mechanism. Population inversion and gain undergo an abrupt surge as the intensity of the continuously pumped light nears the threshold level. When the intensity of the continuously pumped light reaches a specific value, the number of inversion populations in the “scattering cavity” surpasses the threshold rapidly. Simulation results based on a model that considers power-dependent gain saturation confirmed the above phenomenon. This research helps expand the understanding of the dynamics behind random medium-stimulated emission in random lasers and opens up possibilities for mode locking in these systems.
random laser polymer optical fiber gain-switched laser picosecond pulse Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 040603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Center for Humanoid Sensing, Zhejiang Lab, Hangzhou 311100, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
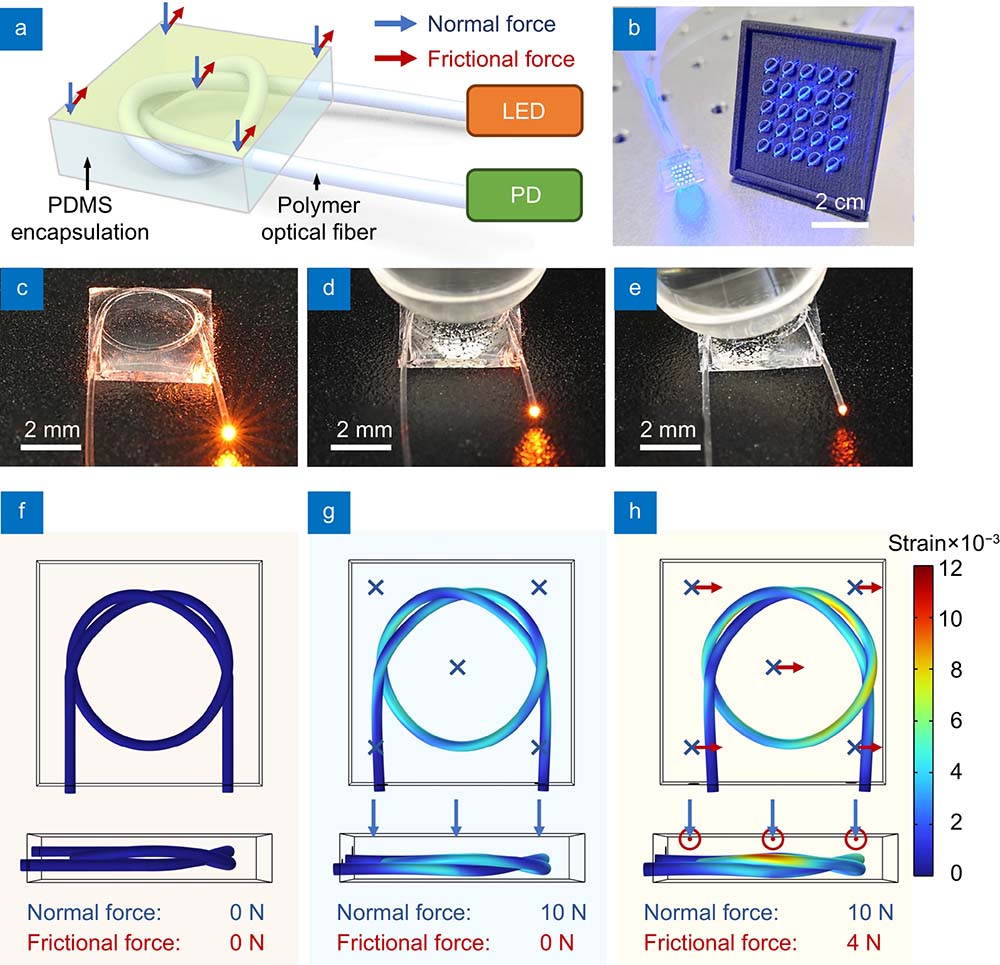
Friction plays a critical role in dexterous robotic manipulation. However, realizing friction sensing remains a challenge due to the difficulty in designing sensing structures to decouple multi-axial forces. Inspired by the topological mechanics of knots, we construct optical fiber knot (OFN) sensors for slip detection and friction measurement. By introducing localized self-contacts along the fiber, the knot structure enables anisotropic responses to normal and frictional forces. By employing OFNs and a change point detection algorithm, we demonstrate adaptive robotic grasping of slipping cups. We further develop a robotic finger that can measure tri-axial forces via a centrosymmetric architecture composed of five OFNs. Such a tactile finger allows a robotic hand to manipulate human tools dexterously. This work could provide a straightforward and cost-effective strategy for promoting adaptive grasping, dexterous manipulation, and human-robot interaction with tactile sensing.
robotic perception adaptive grasping slip detection force decoupling polymer optical fiber Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(10): 230076
1 浙江大学 光电科学与工程学院,极端光学技术与仪器全国重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310058
2 浙江大学 材料科学与工程学院,浙江 杭州 310058
随着人工智能、大数据、云计算、物联网、移动电子等的发展,传统的稀土离子掺杂单芯单模光纤放大器承载的光纤通信系统的传输容量已经逐渐接近香农极限,需要发展新型材料体系,以拓宽光纤通信系统的传输容量。相比于稀土离子,量子点具有较宽的发光带宽、可调波长的发光特性,且量子点的发光性质可以通过多种化学手段调控,在量子点光放大器上显示出了宽带光放大特性,受到学术界和产业界的广泛关注。在该背景下,本文提出将化学合成的PbS/CdS核壳量子点与低损耗聚合物集成,获得量子点掺杂光纤放大器,实现近红外通信波段可调波长、宽带光放大特性。文章研究并揭示了影响固化后的聚合物纤芯连续性的因素和影响机制,提出了降低固化胶前驱体液面附加压力、固化收缩力、聚合物前驱体与光纤内壁的摩擦力,并提高抽真空产生的牵引力以获得连续光纤,在此基础上获得了基于热固化聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)和光固化NOA61、NOA85固化胶的纤芯连续光纤,量子点光纤在1 530~1 630 nm获得了增益带宽达到100 nm以上的开关增益,最高增益达到6.5 dB。本文的研究结果将促进量子点光纤器件和宽带光通信技术的发展。
量子点 聚合物光纤 宽带光纤放大器 quantum dots polymer optical fiber broadband optical fiber amplifier
北京师范大学珠海校区认知神经科学与学习国家重点实验室认知神经工效研究中心,珠海 广东 519085
近年来,聚合物光纤因其体积小、质量小、柔软、成本低等诸多优点,以及不同于石英光纤的生物相容性等优良特性,在传感及通信等领域逐渐受到了重视。系统介绍了包括聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯、环烯烃共聚物、环烯烃均聚物以及聚碳酸酯等的聚合物光纤组成材料,基于不同波段的刻写激光源如248 nm、266 nm、325 nm等的光栅制备技术,以及包括相位掩模板刻写、飞秒激光直写技术以及飞秒激光双光子聚合刻写技术等的光栅刻写技术。最后,回顾了近些年聚合物光纤光栅在传感及通信领域的研究进展,并进行了总结和展望。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(13): 1306020
1 华侨大学信息科学与工程学院, 福建 厦门 361021
2 华侨大学工学院, 福建 泉州 362021
3 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
为了将光纤束端头发光应用于均匀照明场景,设计了一种基于光纤照明技术的光纤端头灯并制作了样灯模型。基于光纤导光特性设计LED光源与光纤束的耦合装置,通过公差分析得到代数多项式拟合配光曲线的最佳拟合阶次为10;并结合裁剪法设计光纤束端头的配光透镜,将光纤束与透镜进行装配得到灯具。仿真得到灯具在300 mm远接收平面上的光斑垂直照度均匀度为90.99%,水平照度均匀度为89.59%,耦合装置的耦合效率为87%。最后经过误差实验分析得到系统的最佳耦合距离为2 mm,透镜与发光端面的距离为50 mm,灯具的实际光斑照度均匀度为81.54%。理论和实验结果表明光学透镜明显改善了光纤端头光束的发散特性和均匀性,该光纤端头灯设计方案为将光纤端头发光应用于均匀照明设计提供了一种可行方案。
光学设计 光纤照明技术 耦合装置 光学透镜 塑料光纤 非成像光学 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(3): 032204
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院, 福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
研究了一种侧面均匀发光聚合物光纤(POF)的制备方法,采用激光打标技术在POF侧面制作变栅距(VLS)光栅型散射点,建立了激光打标VLS散射点模型,该模型由深度很浅的表面凹坑和纤芯内分布着散射颗粒的散射区组成。理论推导出散射点相对散射光功率和VLS栅距的计算公式,分析了散射点的散射光功率随凹坑深度和颗粒密度的变化规律,以及不同散射点凹坑深度和不同POF侧面发光相对出射度下VLS栅距的分布规律。结果表明散射点凹坑深度的微小变化(微米量级)对散射点的散射光功率和VLS栅距的影响很大。当散射颗粒密度N<10
5 mm
-3时,散射点散射光功率变化不大;但是当N>10
5 mm
-3时,散射光功率变化明显。理论计算了不同散射点凹坑深度和不同相对出射度的VLS栅距分布曲线,并且通过实验验证了理论结果的正确性。通过调节激光打标功率,实验得到了亮度均匀度高于90%的侧面发光POF。
光纤光学 聚合物光纤 侧面发光 激光打标技术 变栅距光栅 散射点 光学学报
2018, 38(12): 1206001
华侨大学信息科学与工程学院福建省光传输与变换重点实验室, 福建 厦门 361021
研究了以大功率发光二极管(LED)作为光源的聚合物光纤束(POFB)透镜耦合器的原理和设计方法,基于能量补偿和坐标迭代法设计了一种能量均匀分布自由曲面透镜耦合器。透镜耦合器由两个折射曲面和两个反射曲面以及一个环形柱透镜面组成,折射曲面将修正的朗伯型大功率LED光束中发散角度较小的光线均匀分配在POFB端面上;反射曲面将LED光束中发散角度较大的光线作为补偿光线进行能量重新分配以提高目标面的照度均匀性,并以光纤束端面的照度均匀性和有效光利用率为优化目标对透镜耦合器结构进行优化设计。光学仿真结果表明,当采用3535规格的LED作为光源时,设计的耦合器可使直径为0.5 mm的20×20根POFB端面照度均匀性达到92%,有效光利用率达到71%。
几何光学 发光二极管 聚合物光纤束 自由曲面 光学仿真
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Instrumentation Science & Dynamic Measurement (North University of China), Ministry of Education, Taiyuan, 030051, China
The macro-bending induced optical fiber cladding modes frustrated total internal reflection effect is used to realize the liquid level probe with a simple structure of single macro-bend polymer optical fiber loop. The test results show that the extinction ratio reaches 1.06 dB. “First bath” phenomenon is not obvious (about 0.8%). The robustness of the sensor is better, and the ability of anti-pollution is stronger compared with the conventional sensors. The process of making this sensing probe is extremely easy, and the cost is very low.
Water leakage measurement polymer optical fiber frustrated total internal reflection Photonic Sensors
2016, 6(4): 312
1 华东电子工程研究所, 安徽 合肥 230031
2 东南大学信息科学与工程学院, 江苏 南京 210096
针对未编码离散多音频调制(DMT)的阶跃折射率塑料光纤(SI-POF)通信系统传输容量的计算,采用均匀功率谱密度(PSD)注入的方法,对SI-POF 强度调制直接检测(IM/DD)的通信传输进行数学建模。借助一阶低通和高斯低通信道模型,推导出基于信噪比(SNR)间隔的信道容量和最佳使用带宽的数学计算模型。在不同使用带宽下对系统容量进行了理论分析与数值计算,并分别取不同长度的SI-POF 进行实物传输测试。理论计算和传输实验表明了该计算模型的准确性,且信道容量与等效信噪比呈正向分布,与传输距离呈反向变化;使用优化的传输带宽可以减小传输速率的损失。该模型可有效用于SI-POF 通信系统的容量计算和最优带宽预测。
光通信 调制技术 塑料光纤 最优带宽 信道容量 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(1): 010604





