Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Frontiers Science Center for Nano-optoelectronics & Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter & Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
4 Peking University Yangtze Delta Institute of Optoelectronics, Nantong 226010, China
5 Hefei National Laboratory, Hefei 230088, China
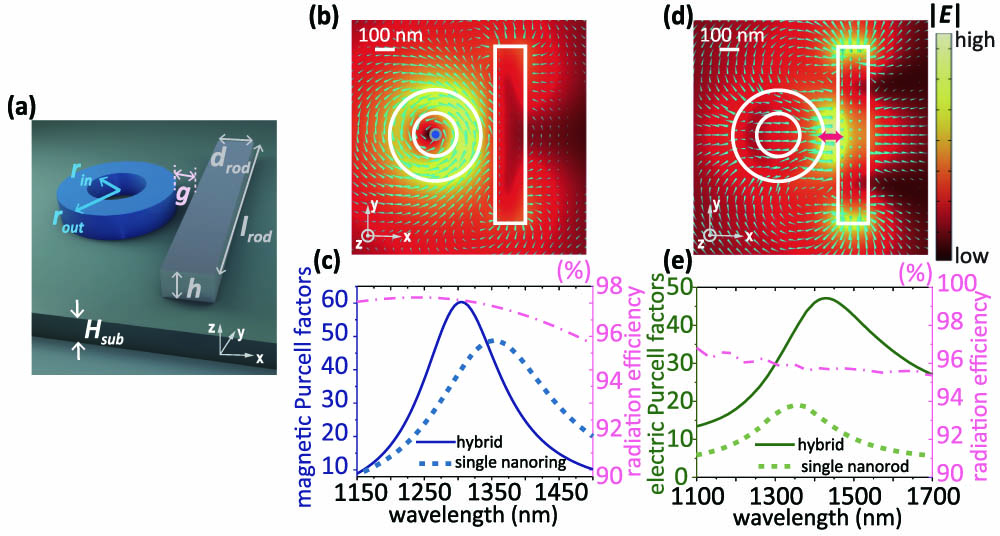
Hybrid metal-dielectric structures combine the advantages of both metal and dielectric materials, enabling high-confined but low-loss magnetic and electric resonances through deliberate arrangements. However, their potential for enhancing magnetic emission has yet to be fully explored. Here, we study the magnetic and electric Purcell enhancement supported by a hybrid structure composed of a dielectric nanoring and a silver nanorod. This structure enables low Ohmic loss and highly-confined field under the mode hybridization of magnetic resonances on a nanoring and electric resonances on a nanorod in the optical communication band. Thus, the 60-fold magnetic Purcell enhancement and 45-fold electric Purcell enhancement can be achieved. Over 90% of the radiation can be transmitted to the far field. For the sufficiently large Purcell enhancement, the position of emitter has a tolerance of several tens of nanometers, which brings convenience to experimental fabrications. Moreover, an array formed by this hybrid nanostructure can further enhance the magnetic Purcell factors. The system provides a feasible option to selectively excite magnetic and electric emission in integrated photonic circuits. It may also facilitate brighter magnetic emission sources and light-emitting metasurfaces with a more straightforward design.
Purcell effect magnetic emission hybrid structures Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 103602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
![]()
![]() The Purcell effect is commonly used to increase the spontaneous emission rate by modifying the local environment of a light emitter. Here, we propose a silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna for simultaneously enhancing electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD) and electric quadrupole (EQ) emission. We study the scattering cross section, polarization charge distribution, and electromagnetic field distribution for electromagnetic plane wave illuminating the silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna, from which we have identified simultaneous existence of ED, MD and EQ resonance modes in this nanoantenna. We have calculated the Purcell factor of ED, MD and EQ emitters with different moment orientations as a function of radiation wavelength by placing these point radiation source within the nanoantenna, respectively. We find that the resonances wavelengths of the Purcell factor spectrum are matching with the resonance modes in the nanoantenna. Moreover, the maximum Purcell factor of these ED, MD and EQ emitters is 18, 150 and 118 respectively, occurring at the resonance wavelength of 475, 750, and 562 nm, respectively, all within the visible range. The polarization charge distribution features allow us to clarify the excitation and radiation of these resonance modes as the physical origin of large Purcell factor simultaneously occurring in this silicon cuboid nanoantenna. Our theoretical results might help to deeply explore and design the dielectric nanoantenna as an ideal candidate to enhance ED, MD and EQ emission simultaneously with very small loss in the visible range, which is superior than the more popular scheme of plasmonic nanoantenna.
The Purcell effect is commonly used to increase the spontaneous emission rate by modifying the local environment of a light emitter. Here, we propose a silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna for simultaneously enhancing electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD) and electric quadrupole (EQ) emission. We study the scattering cross section, polarization charge distribution, and electromagnetic field distribution for electromagnetic plane wave illuminating the silicon dielectric cuboid nanoantenna, from which we have identified simultaneous existence of ED, MD and EQ resonance modes in this nanoantenna. We have calculated the Purcell factor of ED, MD and EQ emitters with different moment orientations as a function of radiation wavelength by placing these point radiation source within the nanoantenna, respectively. We find that the resonances wavelengths of the Purcell factor spectrum are matching with the resonance modes in the nanoantenna. Moreover, the maximum Purcell factor of these ED, MD and EQ emitters is 18, 150 and 118 respectively, occurring at the resonance wavelength of 475, 750, and 562 nm, respectively, all within the visible range. The polarization charge distribution features allow us to clarify the excitation and radiation of these resonance modes as the physical origin of large Purcell factor simultaneously occurring in this silicon cuboid nanoantenna. Our theoretical results might help to deeply explore and design the dielectric nanoantenna as an ideal candidate to enhance ED, MD and EQ emission simultaneously with very small loss in the visible range, which is superior than the more popular scheme of plasmonic nanoantenna.
dielectric nanostructure spontaneous emission resonance Purcell effect Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(2): 210024

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 DTU Fotonik-Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Ørsteds Plads 343, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
2 Institute of Spectroscopy RAS, Moscow 108840, Russia
3 Higher School of Economics, National Research University, Moscow 101000, Russia
Photoluminescence including fluorescence plays a great role in a wide variety of applications from biomedical sensing and imaging to optoelectronics. Therefore, the enhancement and control of photoluminescence has immense impact on both fundamental scientific research and aforementioned applications. Among various nanophotonic schemes and nanostructures to enhance the photoluminescence, we focus on a certain type of nanostructures, hyperbolic metamaterials (HMMs). HMMs are highly anisotropic metamaterials, which produce intense localized electric fields. Therefore, HMMs naturally boost photoluminescence from dye molecules, quantum dots, nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamonds, perovskites and transition metal dichalcogenides. We provide an overview of various configurations of HMMs, including metal-dielectric multilayers, trenches, metallic nanowires, and cavity structures fabricated with the use of noble metals, transparent conductive oxides, and refractory metals as plasmonic elements. We also discuss lasing action realized with HMMs.
fluorescence metamaterials metasurfaces Purcell effect nanophotonics hyperbolic metamaterials Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(8): 08210031
长春理工大学高功率半导体激光国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130022
主要研究了不同结构参数对金属纳米表面等离子激元辐射增强的影响,以提高入射电磁波与金属表面自由电子的耦合效率。对Au、Ag纳米颗粒进行了数值模拟,比较了不同形状金属纳米颗粒的局域场增强。与其他结构相比,球形金属纳米颗粒具有更显著的局域场增强效应。通过改变球形金属纳米颗粒的各个参数进行Purcell分析,结果表明:沿极化方向的长轴尺寸、垂直于极化方向的短轴尺寸、环境材料的折射率以及光源距纳米颗粒的距离都会极大地改变金属纳米表面等离子激元共振辐射增强的效果,且会对共振波长的位置产生极大影响。最后对具有椭球壳结构的金属纳米颗粒进行了模拟,发现随着椭球壳内填充介质的折射率和椭球壳厚度改变,辐射强度都表现出不同程度的增强。
物理光学 辐射增强 Purcell效应 表面等离子激元 金属纳米颗粒 局域场 核壳结构 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(4): 042601
聊城大学物理科学与信息工程学院山东省光通信科学与技术重点实验室,山东 聊城 252059
采用三维数值模拟方法研究了基于带状束的史密斯-帕塞尔自由电子激光(S-P FEL)的辐射输出特性。当一束相对论带状束紧贴着矩形光栅表面飞行时,可以激励起非相干的史密斯-帕塞尔(S-P)辐射,而全反馈谐振腔可以将各个方位角的S-P辐射反射回带状束,同时进行速度调制,使电子注发生群聚,进而获得相干的S-P辐射。通过数值模拟发现,带状束可以提高S-P FEL的功率和功率谱密度;随着带状束宽高比的增大,电子束的速度调制和群聚更为明显,S-P FEL的功率和功率谱密度也越大。
激光光学 史密斯-帕塞尔效应 全反馈谐振腔 带状束 宽高比 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(6): 061404
聊城大学 物理科学与信息工程学院,山东省光通信科学与技术重点实验室,山东 聊城 252059
提出了一种基于史密斯-帕赛尔效应的太赫兹振荡器,该器件由电子枪、调制腔、输出腔、收集极等部分构成。在器件调制腔中,电子注的速度调制通过史密斯-帕赛尔效应完成的,当群聚电子注通过输出腔时,群聚电子注会在输出腔的间隙处激励起高频电场,该高频电场会使电子注的一部分动能转换为高频能量,并完成太赫兹振荡.模拟发现:当金属光栅的空间周期为0.6 mm、电子注能量为100 keV时,利用史密斯-帕赛尔效应调制的太赫兹振荡器可以输出频率为349.017 GHz和346.324 GHz、功率谱密度接近4 kW/GHz、最大输出峰值功率超过2 kW的太赫兹波.
物理电子学 太赫兹 粒子模拟 振荡器 史密斯-帕赛尔效应 调制 群聚 Physical electronics Terahertz Particle-in-cell simulation Oscillator Smith-Purcell effect Modulation Bunching
聊城大学物理科学与信息工程学院, 山东省光通信科学与技术重点实验室, 山东 聊城 252059
研究了电介质在史密斯-帕塞尔自由电子激光中的作用。将电介质加载于电子注与光栅之间,所加电介质为电容率为4 的细玻璃管,电子注在玻璃管内的真空腔中运动,玻璃管外是金属光栅。对加载电介质的史密斯-帕塞尔自由电子激光和不加载电介质的史密斯-帕塞尔自由电子激光分别进行了3 维数值模拟,结果发现:如果在电子注与光栅间加载电介质,可以成功模拟出363.37 GHz 的相干太赫兹波,如果在电子注与光栅间不加载电介质,只能模拟出191.2 GHz 的慢波辐射场。这说明加载电介质可以提高史密斯-帕塞尔受激辐射的增益,强化史密斯-帕塞尔辐射对电子注的调制,使电子有效群聚。
激光器 太赫兹 史密斯-帕塞尔效应 全反馈谐振腔 电介质 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(3): 031405
State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2012, 5(1): 51
电子科技大学 物理电子学院, 大功率微波电真空器件技术重点实验室, 成都 610054
新型史密斯-帕塞尔互作用结构是一个同轴型系统, 它包括倒置的曲面镜和柱状光栅, 并且光栅的截面可以是任意形状。用粒子模拟软件MAGIC对新结构进行模拟分析和优化, 由于新结构采用倒置曲面镜, 改变了光栅位置, 大大增加了环状电子注半径, 在同样电子注密度和厚度情况下, 可以获得比改进前结构高几倍的电流, 且辐射功率可提高1个数量级。并给出了新结构及改进前两种互作用结构在3 mm甚至更短波段的粒子模拟分析和计算结果, 其输出功率达到数百MW以上。
准光学谐振腔 史密斯-帕塞尔效应 柱状光栅 倒梯形光栅 quasi-optical cavity Smith-Purcell effect cylindrical grating inverted trapezoidal grating
聊城大学 物理科学与信息工程学院,山东 聊城 252059
电子束沿多层膜表面运动时会产生自发辐射。分析自发辐射的精确波长公式、自发辐射中电子束品质的变化规律和电子自发辐射的功率后得出:电子束沿金属-介质多层膜表面运动时产生自发辐射,电子束内各种速度的电子数都按指数规律变化,实际电子束自发辐射的总辐射功率与金属-介质多层膜的空间周期成反比。
激光技术 史密斯-帕塞尔效应 金属-介质多层膜 光栅