
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Beijing Key Laboratory for Microwave Sensing and Security Applications, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
High-resolution frequency-domain spectroscopy (FDS) is set up using a coherent and continuous wave terahertz (THz) emitter and receiver. THz waves are generated and detected by two photomixers with two distributed feedback (DFB) lasers. Atmospheric water vapor with different relative humidity is systematically investigated by the FDS. A high-frequency resolution of ~14 MHz is obtained with the help of Hilbert transformation, leading to a well resolved and distinct transmittance characterization of water vapor. Compared with conventional THz time-domain spectroscopy, the high-resolution continuous wave THz spectrometer is one of the most practical systems in gas-phase molecular sensing, identification, and monitoring.
300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 010.7340 Water 010.0280 Remote sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 073001
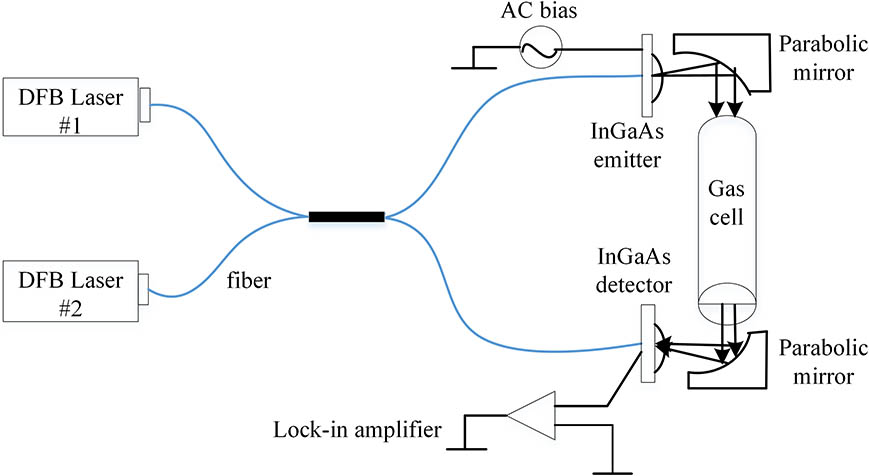
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Computer and Communication Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
2 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Industrial Spectrum Imaging, Beijing 100083, China
3 School of Automation and Electrical Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
We present a specific-window method to subtract the interference of water vapor on terahertz frequency-domain spectroscopy (THz-FDS) at ambient temperature and pressure. A continuous-wave spectrometer based on photomixing was utilized to obtain THz-FDS of methanol vapor in the range of 50–1200 GHz. The distinctly spaced absorption features in the neighborhood of atmospheric windows of transparency were selected to perform linear fitting versus the calculated absorption cross section and obtain the concentration of methanol. Furthermore, the gradually decreased methanol vapor was quantified to demonstrate the reliability of the method.
300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 300.6390 Spectroscopy, molecular 300.1030 Absorption Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(10): 103001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
In this work, we report a broadband terahertz wave modulator based on a top-gate graphene field effect transistor with polyimide as the gate dielectric on a PET substrate. The transmission of the terahertz wave is modulated by controlling the Fermi level of graphene via the polyimide as the top-gate dielectric material instead of the traditional dielectric materials. It is found that the terahertz modulator can achieve a modulation depth of ~20.9% with a small operating gate voltage of 3.5 V and a low insertion loss of 2.1 dB.
230.4110 Modulators 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 160.4236 Nanomaterials 310.6845 Thin film devices and applications Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(5): 052301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 School of Optical and Electronic information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
We design a plano-convex lens working in the terahertz (THz) frequency range and fabricate it using three-dimensional (3D) printing technology. A 3D field scanner is used to measure its focal properties, and the results agree well with the numerical simulations. The refractive index and absorption coefficient measurements via THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) reveal that the lens material is highly transparent at THz frequencies. It is expected that this inexpensive and rapid 3D printing technology holds promise for making various THz optical elements.
220.3630 Lenses 050.6875 Three-dimensional fabrication 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(2): 022201
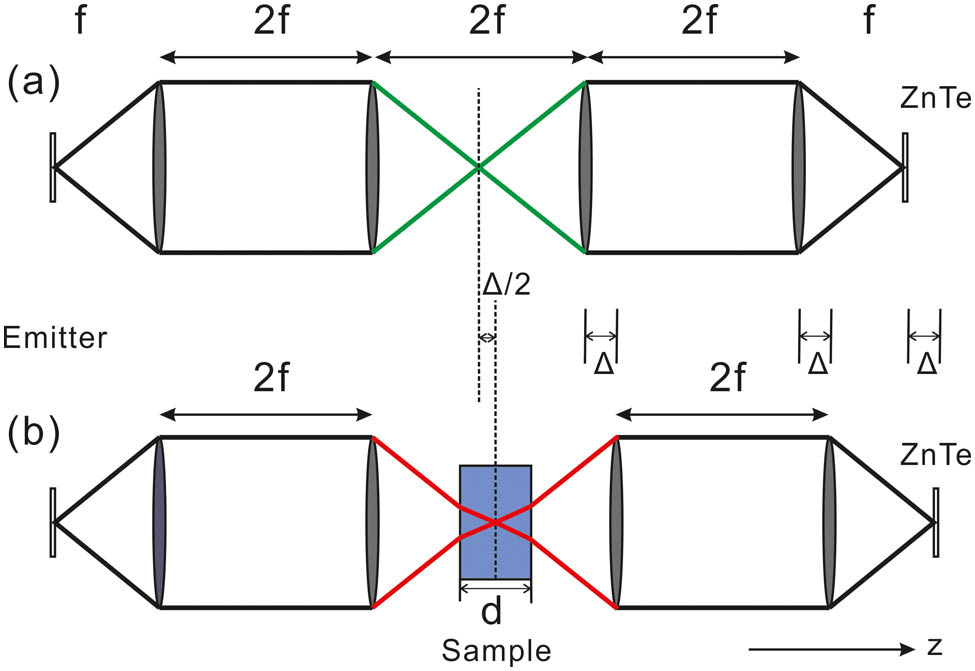
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics and Center for Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz, 78464 Konstanz, Germany
2 Laser Quantum GmbH, 78464 Konstanz, Germany
3 Faculty of Physics, National Taras Shevchenko University of Kyiv, 01601 Kyiv, Ukraine
We demonstrate theoretically and experimentally how changes of a terahertz (THz) beam induced by the sample affect the accuracy of the determination of THz dielectric properties in THz time-domain transmission spectroscopy (TDTS). We apply a Gaussian beam and the ABCD matrix formalism to describe the propagation of the THz beam in a focused beam setup. The insertion of the sample induces a focus displacement which is absent in the reference measurement without a sample. We show how the focus displacement can be corrected. The THz optical properties after focus displacement correction reported in this Letter are in quantitative agreement with those obtained using collimated beam THz–TDTS in previous work.
300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 160.4760 Optical properties 120.7000 Transmission Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(9): 093001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Modulation properties of terahertz waves going through a light excited high resistivity silicon wafer are analyzed and measured. Free carrier lifetime of the silicon wafer affects the modulation depth and speed of the terahertz wave. The lifetime is reduced to less than 1 μs by thermal processing for high speed modulation. Experimental results show that the response time and modulation depth of the proposed modulating structure are close to 1 μs and 51%, respectively.
250.4110 Modulators 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 160.6000 Semiconductor materials Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(8): 082501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The evolution of terahertz (THz) waveform in air plasma driven by low-energy few-cycle laser pulses is investigated to improve the accuracy of the carrier envelope phase (CEP) determination. Based on the transient photocurrent model, a balanced spatial distribution of the Kerr and free-electron effects in the plasma is found at 109 \mu J input energy. THz inversion occurs only once at the initial CEP of 0.5\pi, in which high-precision measurement of the CEP of few-cycle laser pulses is achieved.
300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 260.3060 Infrared 350.5400 Plasmas Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(12): 123002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
To suppress the fluctuation effect due to laser power instability and terahertz radiation fluctuation, a homomorphic filtering method is proposed to process the terahertz images obtained from a pulsed terahertz raster scanning imaging system. The physical model of homomorphic filtering for terahertz imaging is established. The mathematical expressions are given with the specific physical meaning in accordance with the imaging principle. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the method, a homomorphic filtering experiment based on two raw terahertz images selected from the literature using a continuous-wave (CW) terahertz source is also performed. The effect of the method is compared with those described in the literature, and the advantages of homomorphic filtering are discussed. The pulsed- and CW-terahertz image processing results both show that in addition to suppressing the fluctuation effect, the method can also enhance target imaging.
120.6200 Spectrometers and spectroscopic instrumentation 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz 100.2960 Image analysis 100.2980 Image enhancement Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(8): 081201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We present a review of terahertz plasmonic metamaterial devices that have functionalities and applications ranging from sensing, enhanced electromagnetic fields, and near field manipulation. Metamaterials allow the properties of light propagation to be manipulated at will by using a combination of appropriately designed geometry and suitable materials at the unit cell level. In this review, we first discuss the sensing aspect of a planar plasmonic metamaterial and how to overcome its limitations. Conventional symmetric metamaterials are limited by their low Q factor, thus we probed the symmetry broken plasmonic metamaterial structures in which the interference between a broad continuum mode and a narrow localized mode leads to the excitation of the sharp Fano resonances. We also discuss the near field mediated excitation of dark plasmonic modes in metamaterials that is caused by a strong coupling from the bright mode resonator. The near field coupling between the dark and bright mode resonances leads to classical analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency in plasmonic systems. Finally, we discuss active switching in terahertz metamaterials based on high temperature superconductors that holds the promise of reducing the resistive losses in these systems, though it fails to suppress the radiation loss in plasmonic metamaterial at terahertz frequencies.
160.3918 Metamaterials 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(1): 011602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The influence of varied water distribution in different locations of the mesophyll and mid-vein of the same leaf on the absorption and refraction coefficient is described. And the further comparisons between green leaf and yellow leaf reveal that the complex permittivity of leaf can provide important information about the water content and can characterize the changes of the water distribution of the leaf. So our measurements tend to demonstrate that the dielectric material parameters will be employed to determine the leaf water status in plant leaves.
300.0300 Spectroscopy 300.6270 Spectroscopy, far infrared 300.6495 Spectroscopy, teraherz Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s1): S13001





