Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Optical and Electronic Information-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, P. R. China
Light field microscopy (LFM), featured for high three-dimensional imaging speed and low phototoxicity, has emerged as a technique of choice for instantaneous volumetric imaging. In contrast with other scanning-based three-dimensional (3D) imaging approaches, LFM enables to encode 3D spatial information in a snapshot manner, permitting high-speed 3D imaging that is only limited by the frame rate of the camera. In this review, we first introduce the fundamental theory of LFM and current corresponding advanced approaches. Then, we summarize various applications of LFM in biological imaging.Light field microscopy (LFM), featured for high three-dimensional imaging speed and low phototoxicity, has emerged as a technique of choice for instantaneous volumetric imaging. In contrast with other scanning-based three-dimensional (3D) imaging approaches, LFM enables to encode 3D spatial information in a snapshot manner, permitting high-speed 3D imaging that is only limited by the frame rate of the camera. In this review, we first introduce the fundamental theory of LFM and current corresponding advanced approaches. Then, we summarize various applications of LFM in biological imaging.
Light field deep learning three-dimensional microscopy Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(1): 2230017
1 江南大学理学院, 江苏 无锡 214122
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
为了克服传统数字全息三维成像技术的扫描速度慢等诸多缺点,设计一种仅需单波长且可以一维扫描的透射式K空间变换数字全息三维成像技术。首先采用片状光束对样品进行照明并记录透射光的离轴全息图;然后利用传统的数字全息重建技术得到透射光的复振幅分布后去除其低频分量;最后在频谱空间进行坐标变换并对变换后的空间频谱进行傅里叶逆变换,便可得到被照明切片平面上的样品结构信息。在对工作原理和主要参数进行系统理论分析的基础上,利用数值模拟和光学实验对此技术的可行性进行实际验证。由于该技术能够使用透射光进行三维层析成像,因此很容易推广并应用于X光和其他短波长的辐射源成像,为研究样品高分辨三维结构提供新的工具。
全息 数字全息 三维显微成像 K空间变换 透射成像 中国激光
2021, 48(21): 2109001
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 上海 201800
2 上海科技大学, 上海 201210
3 中国科学院上海高等研究院上海光源, 上海 201204
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
同步辐射红外(SRIR)光具有光谱范围宽、发散角小、亮度高以及信噪比高等优点,结合传统红外谱学技术,采用SRIR谱学显微技术对样品进行红外谱学显微,可以获得样品微米级别的空间光谱信息。利用MiTeGen聚亚酰胺小环作为样品,以上海光源BL01B1线站的SRIR光为光源,通过点扫描采样方式进行同步辐射红外三维谱学显微实验研究。通过获得聚亚酰胺小环在不同角度下的SRIR二维显微光谱信息,选取波数范围为1495~1485 cm -1的显微光谱信息处理,用代数迭代算法对聚亚酰胺小环的化学组分酰胺Ⅱ进行SRIR三维显微重构,获得了完整的三维重构图。实验表明本文方法能够以较高的信噪比重构出样品化学组分的三维红外显微结构。
X射线光学 同步辐射 三维谱学显微 高分辨率光谱学 断层图像处理
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Modern Optics, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
Subtractive imaging is used to suppress the axial sidelobes and improve the axial resolution of 4pi microscopy with a higher-order radially polarized (RP) Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) beam. A solid-shaped point spread function (PSF) and a doughnut-shaped PSF with a dark spot along the optical axis are generated by tightly focusing a higher-order RP-LG beam and a modulated circularly polarized beam, respectively. By subtracting the two images obtained with those two different PSFs, the axial sidelobes of the subtracted PSF are reduced from 37% to about 10% of the main lobe, and the axial resolution is increased from 0.21 to 0.15.
110.0180 Microscopy 100.6640 Superresolution 170.0180 Microscopy 180.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 121103

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Information Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
2 Division of Physical Biology, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
The fluorescence from the out-of-focus region excited by the sidelobes of a Bessel beam is the major concern for light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) with Bessel beam plane illumination. Here, we propose a method of applying the subtractive imaging to overcome the limitation of the conventional LSFM with Bessel beam plane illumination. In the proposed method, the sample is imaged twice by line scanning using the extended solid Bessel beam and the ring-like Bessel beam. By subtracting between the two images with similar out-of-focus blur, the improved image quality with the suppression of the Bessel beam sidelobes and enhanced sectioning ability with improved contrast are demonstrated.
180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy 170.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy 100.2980 Image enhancement Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(11): 111801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Eberhard Karls University Tübingen, Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry, Tübingen 72076, Germany
2 University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, UKE Microscopy Imaging Facility, Hamburg 20246, Germany
We show the power of spirally polarized doughnut beams as a tool for tuning the field distribution in the focus of a high numerical aperture (NA) lens. Different and relevant states of polarization as well as field distributions can be created by the simple turning of a λ/2 retardation wave plate placed in the excitation path of a microscope. The realization of such a versatile excitation source can provide an essential tool for nanotechnology investigations and biomedical experiments.
180.1790 Confocal microscopy 170.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy 260.5430 Polarization Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(3): 030013
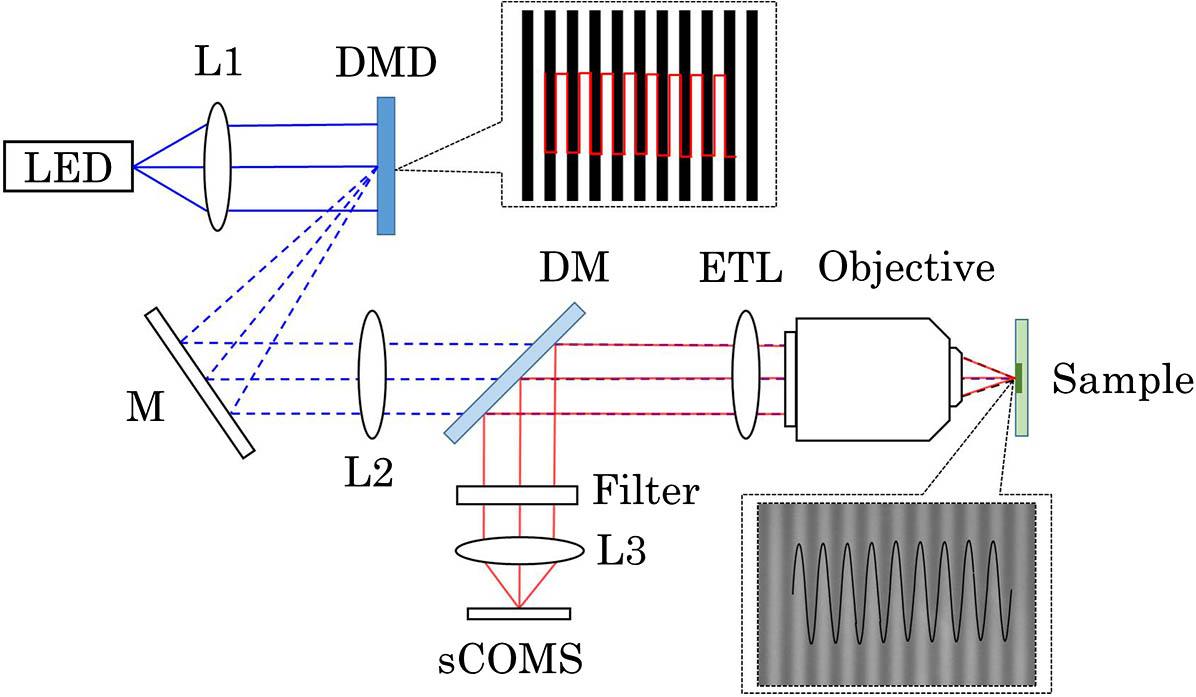
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, Hong Kong SAR, China
2 Shenzhen Research Institute, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen 518057, China
In this Letter, we present a high-speed volumetric imaging system based on structured illumination and an electrically tunable lens (ETL), where the ETL performs fast axial scanning at hundreds of Hz. In the system, a digital micro-mirror device (DMD) is utilized to rapidly generate structured images at the focal plane in synchronization with the axial scanning unit. The scanning characteristics of the ETL are investigated theoretically and experimentally. Imaging experiments on pollen samples are performed to verify the optical cross-sectioning and fast axial scanning capabilities. The results show that our system can perform fast axial scanning and three-dimensional (3D) imaging when paired with a high-speed camera, presenting an economic solution for advanced biological imaging applications.
180.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy 180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(9): 090004
1 复旦大学 上海超精密光学制造工程中心 光科学与工程系, 上海 200433
2 伊斯兰堡 巴基斯坦信息技术学院 物理系, 伊斯兰堡 45550
“衍射极限”实际上不是一个真正的障碍,除非处理远场和定位精度。这种衍射障碍并不是坚不可摧的,可以利用一些智能技术来突破光学衍射极限。讨论了四种技术,近场扫描光学显微镜(NSOM)法,受激发射损耗(STED)显微镜法,光激活定位显微镜(PALM)法或随机光学重建显微镜(STORM)法和结构照明显微镜(SIM)法,并且介绍了各自的基本原则与优劣。NSOM利用纳米级探测器检测通过光纤的极小汇聚光斑,从而获得单个像素的分辨率;PALM和STORM利用荧光探针,实现暗场和荧光的转换,从而观察到极小的荧光团;SIM则是利用栅格图案与样品叠加成像来实现。其中,STORM具有相对较高的潜力,能够更为有效地突破衍射极限。
衍射极限 近场显微镜 三维显微 diffraction limit near-field microscopy three-dimensional microscopy
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Academy of Opto-Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100094, China
Digital holographic microscopy using multiframe full-field heterodyne technology is discussed in which two acousto-optic modulators are applied to generate low-frequency heterodyne interference and a high-speed camera is applied to acquire multiframe full-field holograms. We use a temporal frequency spectrum analysis algorithm to extract the object’s information. The twin-image problem can be solved and the random noise can be significantly suppressed. The relationship between the frame number and the reconstruction accuracy is discussed. The typical objects of microlenses and biology cells are reconstructed well with 100-frame holograms for illustration.
090.1995 Digital holography 180.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy 110.1650 Coherence imaging 040.2840 Heterodyne Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(5): 050901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Control Engineering, Institute of Information Technology Convergence, Hankyong National University, 327 Chungang-ro, Anseong-si, Kyonggi-do 456-749, Korea
In this Letter, we propose a novel three-dimensional (3D) color microscopy for microorganisms under photon-starved conditions using photon counting integral imaging and Bayesian estimation with adaptive priori information. In photon counting integral imaging, 3D images can be visualized using maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). However, since MLE does not consider a priori information of objects, the visual quality of 3D images may not be accurate. In addition, the only grayscale image can be reconstructed. Therefore, to enhance the visual quality of 3D images, we propose photon counting microscopy using maximum a posteriori with adaptive priori information. In addition, we consider a wavelength of each basic color channel to reconstruct 3D color images. To verify our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments.
030.5260 Photon counting 100.6890 Three-dimensional image processing 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 170.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 070301





