光子学报
2022, 51(11): 1111002
西安建筑科技大学信息与控制工程学院, 陕西 西安 710055
针对传统点云配准方法在处理大型点云模型时存在计算量大、效率低和移动扫描配准实时性较差等问题,提出基于卷积神经网络结合改进Harris-SIFT(Scale Invariant Feature Transform)的点云配准方法。首先改进Harris-SIFT算法,使其可以提取三维空间中点云模型的稳定关键点。进而将关键点的加权邻接矩阵作为卷积神经网络的输入特征图,实现源点云和目标点云关键点的预测匹配。然后基于匹配的关键点,采用迭代最近点(ICP)算法实现点云数据的精配准。相较于传统的点对点配准,所提方法不需要生成对应关系的点描述符,解决全局搜索开销大的问题。实验结果表明,相较于ICP算法,所提方法能够较好地完成即时点云配准,且计算量小,耗时短,效率高。
成像系统 三维图像采集 点云配准 Harris-SIFT算法 卷积神经网络 深度学习 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(20): 201102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Micromechanics and Photonics, Warsaw University of Technology, 02-525 Warsaw, Poland
2 Institute of Microelectronics and Optoelectronics, Warsaw University of Technology, 00-665 Warsaw, Poland
3 Geola Digital uab., Vilnius 03227, Lietuva
In this Letter, a method for shape visualization of small objects (microscopic) in the form of a hologram is presented. It consists of a standard optical set-up for small object registration (i.e., stereoscopic or biological microscope). The focus stacking technique is used to obtain a series of images with increased depth of field and on them a shape reconstruction procedure (structure from motion, SfM) is made. With use of a dense cloud of points, a sequence of parallax-related images suitable for Geola’s digital holographic printing is generated. The holographic printer produces single-parallax holographic (full three-dimensional) images of real or virtual objects.
digital holography three-dimensional image acquisition photography Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(6): 060901
1 浙江大学现代光学仪器国家重点实验室国家光学仪器工程技术研究中心, 浙江 杭州 310027
2 浙江大学台州研究院, 浙江 台州 318000
离焦抖动优化技术不仅能消除投影仪的非线性误差,而且不受投影仪刷新率的限制。然而抖动算法本质上只是一个简单的矩阵变换,导致离焦后的二值抖动条纹并不完全接近正弦条纹,产生了一定的测量误差。基于此,提出了一种基于离散粒子群算法的优化方法,对二值离焦抖动技术进行优化。为了加快优化过程,用二值块的优化来代替整个二值图案的优化,然后再利用正弦条纹图案的周期性和对称性,将二值块拼成一个完整的图案。仿真和实验结果表明:所提方法在不同的离焦程度下,都能获得高质量的测量结果。
测量 三维图像获取 二值图像 粒子群优化 抖动 中国激光
2019, 46(10): 1004003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
2 Beijing Engineering Research Center of Mixed Reality and Advanced Display, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 AICFVE of Beijing Film Academy, Beijing 100088, China
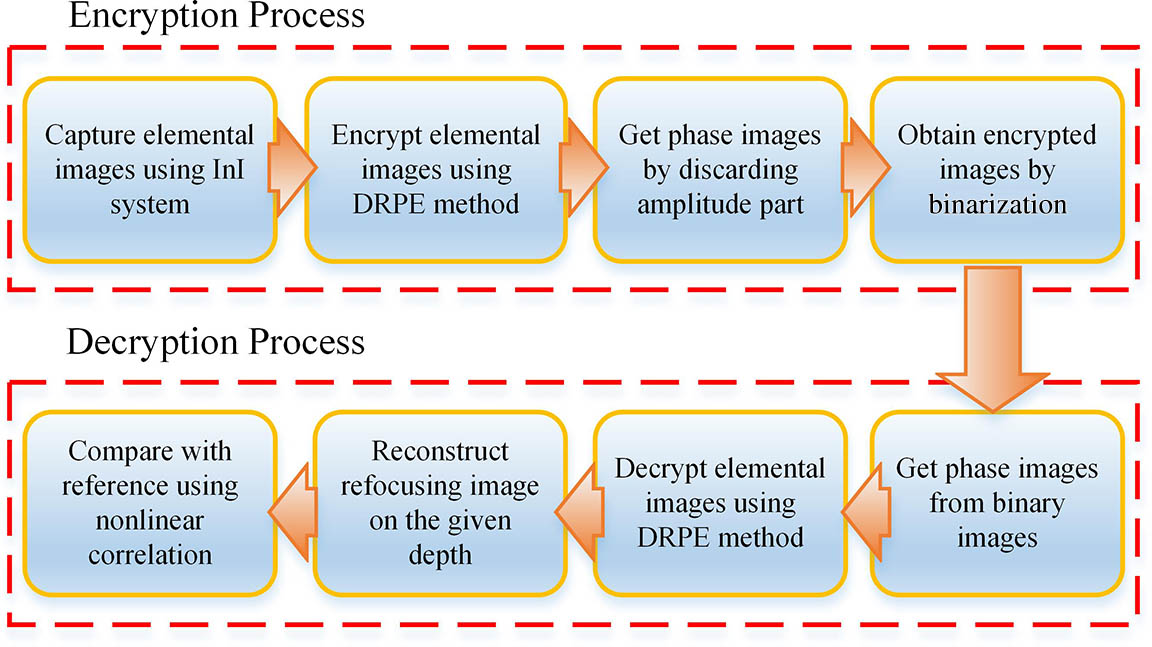
We proposed a three-dimensional (3D) image authentication method using binarized phase images in double random phase integral imaging (InI). Two-dimensional (2D) element images obtained from InI are encoded using a double random phase encryption (DRPE) algorithm. Only part of the phase information is used in the proposed method rather than using all of the amplitude and phase information, which can make the final data sparse and beneficial to data compression, storage, and transmission. Experimental results verified the method and successfully proved the developed 3D authentication process using a nonlinear cross correlation method.
100.4998 Pattern recognition, optical security and encryption 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
2 Heilongjiang Institute of Technology, Harbin 150050, China
The work proposes a three-laser-beam streak tube imaging lidar system. Besides the main measuring laser beam, the second beam is used to decrease the error of time synchronization. The third beam has n+0.5 pixels’ difference compared to the main measuring beam on a CCD, and it is used to correct the error caused by CCD discrete sampling. A three-dimensional (3D) imaging experiment using this scheme is carried out with time bin size of 0.066 ns (i.e., corresponding to a distance of 9.9 mm). An image of a 3D model is obtained with the depth resolution of <2 mm, which corresponds to ~0.2 pixel.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 280.3640 Lidar Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 041101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
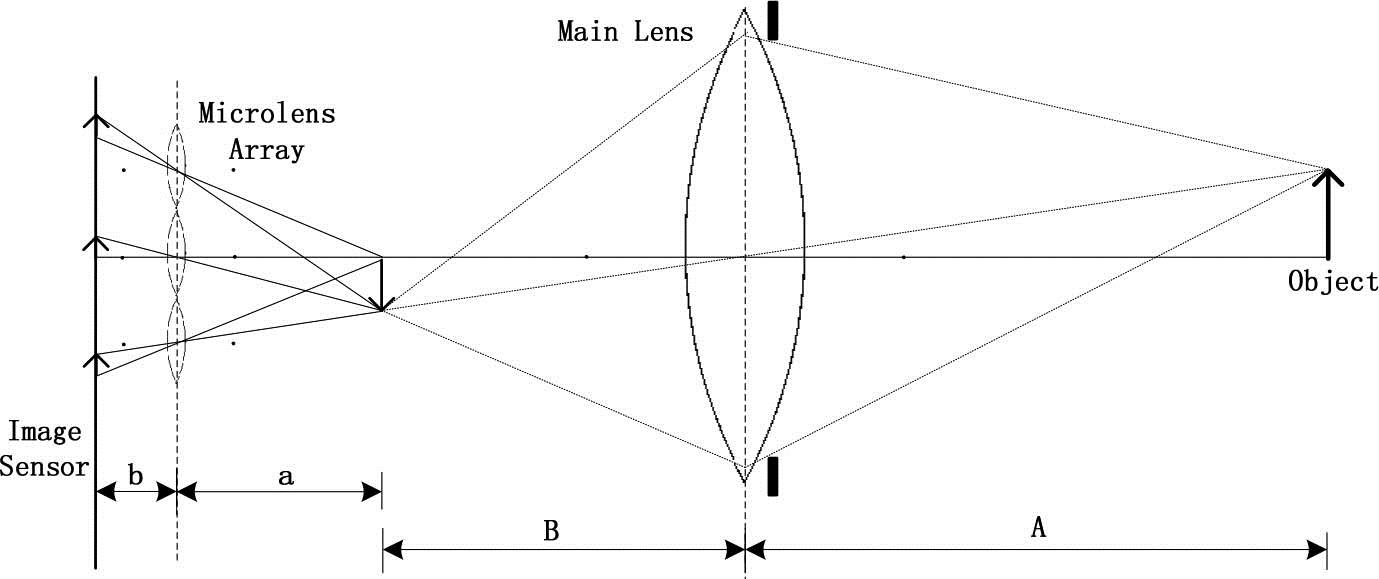
In this Letter, we propose an on-line inspection method based on a plenoptic camera to detect and locate flaws of optics. Specifically, due to the extended depth of field of the plenoptic camera, a series of optics can be inspected efficiently and simultaneously. Moreover, the depth estimation capability of the plenoptic camera allows for locating flaws while detecting them. Besides, the detection and location can be implemented with a single snapshot of the plenoptic camera. Consequently, this method provides us with the opportunity to reduce the cost of time and labor of inspection and remove the flaw optics, which may lead to performance degradation of optical systems.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 140.3330 Laser damage 330.3350 Vision - laser damage Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(4): 041102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
2 Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation, Children’s National Health System, Washington, DC 20010, USA
An endoscopic imaging system using a plenoptic technique to reconstruct 3-D information is demonstrated and analyzed in this Letter. The proposed setup integrates a clinical surgical endoscope with a plenoptic camera to achieve a depth accuracy error of about 1 mm and a precision error of about 2 mm, within a 25 mm×25 mm field of view, operating at 11 frames per second.
170.2150 Endoscopic imaging 170.4580 Optical diagnostics for medicine 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 051701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
2 College of Foundation Science, Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin 150028, China
Streak tube imaging lidar (STIL) is an active imaging system that has a high range accuracy with the use of a pulsed laser transmitter and streak tube receiver to produce 3D range images. This work investigates the effect of the time bin size on the range accuracy of STIL systems based on the peak detection algorithm. The numerical simulation indicates that the time bin size has a significant effect on the range accuracy, resulting in a modified analytical estimate of the range error. An indoor experiment with a planar target is carried out to validate the theory that shows the linear relationship between the range error and the time bin size. Finer 3D depth images of a fist model are acquired by using a smaller time bin size and the best range error of 0.003 m is achieved with the optimal time bin size of 0.07 ns.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 280.3640 Lidar 150.5670 Range finding 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 021101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Photonic Information Technology, College of Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
Because the bottom of the cavity has the shadow and occlusion, the angle between the projection system and imaging system is limited. So the traditional fringe projection technique based on the principle of optical triangulation is inapplicable. This Letter presents a 3D shape measurement method of using the light tube for the cavity. The method can measure an object from two opposite views at the same time, which means it will obtain two different groups of 3D data for the same object in a single measurement. The experimental results show the feasibility and validity of the 3D shape measurement method.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 120.5050 Phase measurement 150.1488 Calibration Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(1): 010010





