
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang Laboratory, Research Center for Frontier Fundamental Studies, Hangzhou, China
2 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Extreme Photonics and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
3 ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center, Hangzhou, China
4 Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Chip Hub for Integrated Photonics Xplore (CHIPX), Wuxi, China
With the rapid development of sensor networks, machine vision faces the problem of storing and computing massive data. The human visual system has a very efficient information sense and computation ability, which has enlightening significance for solving the above problems in machine vision. This review aims to comprehensively summarize the latest advances in bio-inspired image sensors that can be used to improve machine-vision processing efficiency. After briefly introducing the research background, the relevant mechanisms of visual information processing in human visual systems are briefly discussed, including layer-by-layer processing, sparse coding, and neural adaptation. Subsequently, the cases and performance of image sensors corresponding to various bio-inspired mechanisms are introduced. Finally, the challenges and perspectives of implementing bio-inspired image sensors for efficient machine vision are discussed.
bio-inspired image sensor machine vision layer-by-layer processing sparse coding neural adaptation Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 024001
重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室,重庆 400044
激光线宽作为表征激光相干性的重要参数,自激光技术诞生以来就备受人们关注。窄线宽激光器由于光谱纯度高、相干长度长、相位噪声低等优点,被广泛应用于引力波探测、冷原子物理、相干光通信、光学精密测量,以及微波光子信号处理等领域。随着现代信息技术的发展,窄线宽激光器作为这些应用的核心光源,在固有的线宽、噪声等参数得到进一步优化的同时也被期望拥有一些新的性能,如参数的极致调控、时频超稳、波长调谐,以及波长扫描等。激光本征线宽源于自发辐射噪声,激光器线宽压缩的发展历程是研究人员与自发辐射噪声对抗的历程。纵观窄线宽激光的发展历史,激光腔构型从简单的两个反射镜构成的单主腔、多布拉格反射面(DBR)构成的单主腔、分布反馈(DFB)结构构成的单主腔,到激光单主腔加固定单外腔,再到波长自适应分布弱反馈激光构型,其核心思想都是利用反馈信号对自发辐射噪声进行抑制。本文以激光主腔构型的演化发展为叙述脉络,总结窄线宽激光技术的研究进展,对比激光谐振腔构型在激光线宽压缩、噪声抑制思想上的异同,最后重点介绍新近发展的波长自适应分布弱反馈窄线宽激光器,对该类新型激光器的物理思想、核心器件和系统性能进行分析和讨论。
激光 窄线宽 波长自适应 分布弱反馈 瑞利散射 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(1): 0114003

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
2 Faculty of Chemistry, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
3 Institute for Advanced Brain Studies, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
4 P. K. Anokhin Research Institute of Normal Physiology, Moscow 125315, Russia
Artificial synapses utilizing spike signals are essential elements of new generation brain-inspired computers. In this paper, we realize light-stimulated adaptive artificial synapse based on nanocrystalline zinc oxide film. The artificial synapse photoconductivity shows spike-type signal response, long and short-term memory (LTM and STM), STM-to-LTM transition and paired-pulse facilitation. It is also retaining the memory of previous exposures and demonstrates spike-frequency adaptation properties. A way to implement neurons with synaptic depression, tonic excitation, and delayed accelerating types of response under the influence of repetitive light signals is discussed. The developed artificial synapse is able to become a key element of neuromorphic chips and neuromorphic sensorics systems.
neuromorphic photonics synaptic adaptation spiking neuron neuromorphic computing optoelectronic synaptic devises nanocrystalline metal-oxide film Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(10): 230016
哈尔滨工业大学仪器科学与工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
单分子定位技术通过随机激发荧光标记获得一组稀疏的图像序列,同时对荧光点进行亚像素级别定位,最终实现超分辨显微成像。基于拟合的单分子定位算法,如单发射(SE)及多发射(ME)定位算法,通过对估计器性能进行改进提高了单分子定位的精度和速度;然而,受失配误差和串扰误差的影响,SE算法和ME算法在不同密度情况下各有优劣,均无法达到全密度范围内最优的估计效果,并且分别存在荧光分子利用效率低和计算量大的缺点。本文提出了自适应混合发射单分子定位(SM)算法,该算法通过图像荧光发射密度及强度自适应地确定的拟合区域以及所采用的拟合模型及模型初值,有效避免了上述两种误差的影响,达到了全密度范围内一致、良好的定位效果。在仿真和实验数据上将所提SM算法与SE算法、ME算法进行比较,结果显示,SM算法重构图像的分辨率和对比度在不同发射密度下均具有优势。
生物医学 单分子定位显微技术 超分辨成像 单发射模型 多发射模型 自适应算法 中国激光
2023, 50(21): 2107106
1 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,吉林长春3002
2 中国科学院 苏州生物医学工程技术研究所,江苏苏州15163
针对高光谱遥感图像分类时有标注的源域训练数据与无标注目标域数据分布不一致的问题,提出基于部分最优传输的无监督领域自适应方法,实现对处于不同数据分布的高光谱遥感地物像素级分类。利用深度卷积神经网络将样本映射到潜在高维空间,根据部分最优传输理论建立样本传输方案,最小化域间分布差异,构建适配模型。采用类感知采样技术和质量分数因子自适应调整策略,促进域间类别对齐,建立全局最优传输。在两组公开高光谱遥感图像数据集上进行实验,从总体分类精度OA(%)、类别平均分类精度AA(%)、分类一致性检验Kappa(×100)等3个评价指标对像素分类结果量化比较。实验结果显示,在两组迁移任务上,相较于仅使用源域数据的基线模型,总体分类准确率分别提升2.21%和2.75%,相较于原始最优传输策略提升1.71%和2.01%,表明模型能够有效提升高光谱遥感影像中像素级地物的分类精度。
计算机视觉 神经网络 领域自适应 最优传输 高光谱图像 computer vision neural network domain adaptation optimal transport hyperspectral image 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(17): 2555
1 哈尔滨理工大学 测控技术与通信工程学院 黑龙江省激光光谱技术及应用重点实验室, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 50080
2 国网黑龙江省电力有限公司 综合信息中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150010
3 中部大学 计算机科学学院,日本 爱知 487-8501
针对跨场景高光谱遥感图像分类中源域和目标域的频谱偏移问题,提出一种结合空谱域适应与极度梯度提升树(eXtreme Gradient Boosting, XGBoost)的跨场景高光谱图像分类模型。将深度超参数卷积模型(Depthwise Over-parameterized Convolution Model,DOCM)和大核注意力(Large Kernel Attention,LKA)结合,构成空谱注意力模型,提取源域空谱特征。利用相同的空谱注意力模型对目标域进行特征提取,并与鉴别器完成对抗域适应,减少源域与目标域之间的频谱偏移;通过目标域中少量有标签数据对目标域特征提取器进行有监督域适应,使目标域特征提取器进一步学习目标域的真实分布,并对源域和目标域的特征进行映射,形成相似的空间分布,完成聚类域适应。最后,使用集成分类器XGBoost进行高光谱图像分类,进一步提高模型的训练速度与置信度。在Pavia和Indiana高光谱数据集上的实验结果表明,本文算法的总体分类精度分别达到了91.62%和 65.98%。相比较于其他跨场景高光谱图像分类模型,本文所提模型具有更高的地物分类精度。
高光谱图像 域适应 大核注意力 XGBoost hyperspectral images domain adaptation large kernel attention XGBoost 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(13): 1950
1 中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学部物理与光电工程学院,山东 青岛 266100
2 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院,浙江 杭州 310027
由于光在水下传播时受到吸收、散射、衰减的影响,在水下场景中采集的图像退化明显,存在对比度低、蓝绿色偏严重等现象。基于此,提出一种基于图像分割和色适应变换白平衡的水下图像增强算法。将色适应变换引入水下颜色校正,将基于图像三通道反转去雾的低照度增强方法应用于水下图像增强,并提出基于图像分割的白平衡策略,同时将所提算法与经典算法进行比较。实验结果表明,所提算法处理后图像的underwater color image quality evaluation metric(UCIQE)指标平均值为0.5839,underwater image quality measures(UIQM)指标平均值为1.3689,中性色角度误差平均值为5.0972,均优于两种经典算法。所提算法在颜色校正效果和清晰度提升上具有一定的优越性。
图像处理 图像增强 白平衡 暗通道先验 色适应 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(14): 1410003
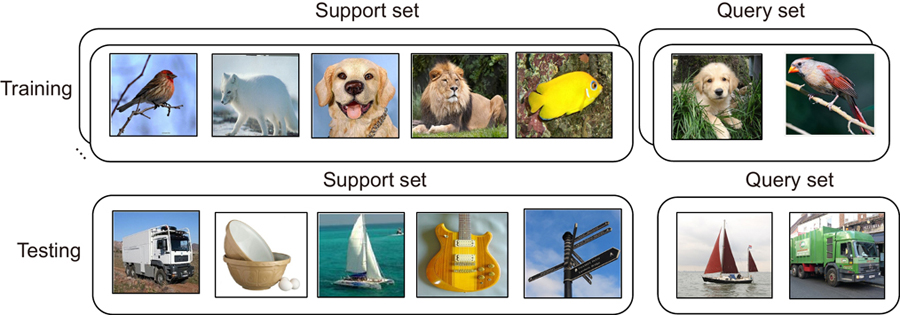
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学电子电气与通信工程学院,北京 100049
To improve the performance of few-shot classification, we present a general and flexible method named Multi-Scale Attention and Domain Adaptation Network (MADA). Firstly, to tackle the problem of limited samples, a masked autoencoder is used to image augmentation. Moreover, it can be inserted as a plug-and-play module into a few-shot classification. Secondly, the multi-scale attention module can adapt feature vectors extracted by embedding function to the current classification task. Multi-scale attention machine strengthens the discriminative image region by focusing on relating samples in both base class and novel class, which makes prototypes more accurate. In addition, the embedding function pays attention to the task-specific feature. Thirdly, the domain adaptation module is used to address the domain shift caused by the difference in data distributions of the two domains. The domain adaptation module consists of the metric module and the margin loss function. The margin loss pushes different prototypes away from each other in the feature space. Sufficient margin space in feature space improves the generalization performance of the method. The experimental results show the classification accuracy of the proposed method is 67.45% for 5-way 1-shot and 82.77% for 5-way 5-shot on the miniImageNet dataset. The classification accuracy is 70.57% for 5-way 1-shot and 85.10% for 5-way 5-shot on the tieredImageNet dataset. The classification accuracy of our method is better than most previous methods. After dimension reduction and visualization of features by using t-SNE, it can be concluded that domain drift is alleviated, and prototypes are more accurate. The multi-scale attention module enhanced feature representations are more discriminative for the target classification task. In addition, the domain adaptation module improves the generalization ability of the model.
小样本图像识别 注意力机制 领域自适应 相似性度量 few-shot image classification attention mechanism domain adaptation similarity metric 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
Multiphoton microscopy is the enabling tool for biomedical research, but the aberrations of biological tissues have limited its imaging performance. Adaptive optics (AO) has been developed to partially overcome aberration to restore imaging performance. For indirect AO, algorithm is the key to its successful implementation. Here, based on the fact that indirect AO has an analogy to the black-box optimization problem, we successfully apply the covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy (CMA-ES) used in the latter, to indirect AO in multiphoton microscopy (MPM). Compared with the traditional genetic algorithm (GA), our algorithm has a greater improvement in convergence speed and convergence accuracy, which provides the possibility of realizing real-time dynamic aberration correction for deep in vivo biological tissues.
multiphoton microscopy 1700-nm window adaptive optics covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(5): 051701





