Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Institute of Electrical and Micro Engineering, Ecublens, Switzerland
2 Koc University, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey
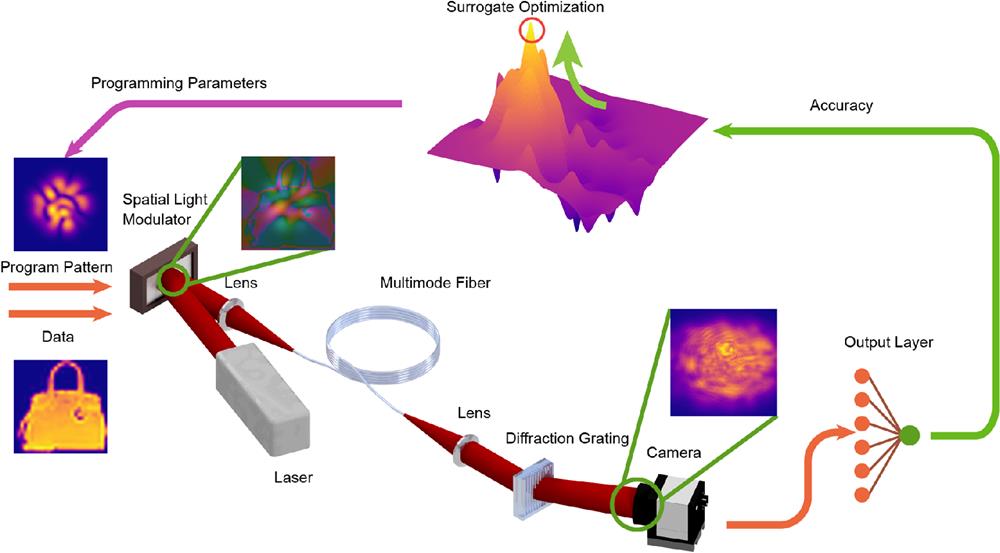
The ever-increasing demand for training and inferring with larger machine-learning models requires more efficient hardware solutions due to limitations such as power dissipation and scalability. Optics is a promising contender for providing lower power computation, since light propagation through a nonabsorbing medium is a lossless operation. However, to carry out useful and efficient computations with light, generating and controlling nonlinearity optically is a necessity that is still elusive. Multimode fibers (MMFs) have been shown that they can provide nonlinear effects with microwatts of average power while maintaining parallelism and low loss. We propose an optical neural network architecture that performs nonlinear optical computation by controlling the propagation of ultrashort pulses in MMF by wavefront shaping. With a surrogate model, optimal sets of parameters are found to program this optical computer for different tasks with minimal utilization of an electronic computer. We show a remarkable decrease of 97% in the number of model parameters, which leads to an overall 99% digital operation reduction compared to an equivalently performing digital neural network. We further demonstrate that a fully optical implementation can also be performed with competitive accuracies.
neural networks nonlinear optics fiber optics surrogate optimization neuromorphic computing wavefront shaping Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 016002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Physics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
2 Faculty of Chemistry, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
3 Institute for Advanced Brain Studies, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
4 P. K. Anokhin Research Institute of Normal Physiology, Moscow 125315, Russia
Artificial synapses utilizing spike signals are essential elements of new generation brain-inspired computers. In this paper, we realize light-stimulated adaptive artificial synapse based on nanocrystalline zinc oxide film. The artificial synapse photoconductivity shows spike-type signal response, long and short-term memory (LTM and STM), STM-to-LTM transition and paired-pulse facilitation. It is also retaining the memory of previous exposures and demonstrates spike-frequency adaptation properties. A way to implement neurons with synaptic depression, tonic excitation, and delayed accelerating types of response under the influence of repetitive light signals is discussed. The developed artificial synapse is able to become a key element of neuromorphic chips and neuromorphic sensorics systems.
neuromorphic photonics synaptic adaptation spiking neuron neuromorphic computing optoelectronic synaptic devises nanocrystalline metal-oxide film Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(10): 230016
1 1.宁波工程学院 电子与信息工程学院, 宁波 315211
2 2.中国科学院 宁波材料技术与工程研究所, 宁波 315201
3 3.中国科学院 脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心, 上海 200031
4 4.中国科学院大学 材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100029
5 5.浙江大学 温州研究院, 温州 325006
类脑神经形态计算通过电子或光子器件集成来模拟人脑结构和功能。人工突触是类脑系统中数量最多的计算单元。忆阻器可模拟突触功能, 并具有优异的尺寸缩放性和低能耗, 是实现人工突触的理想元器件。利用欧姆定律和基尔霍夫定律, 忆阻器交叉阵列可执行并行的原位乘累加运算, 从而大幅提升类脑系统处理模拟信号的速度。氧化物制备容易, 和CMOS工艺兼容性强, 是使用最广泛的忆阻器材料。本文梳理了氧化物忆阻器的研究进展, 分别讨论了电控、光电混合调控和全光控忆阻器, 主要聚焦阻变机理、器件结构和性能。电控忆阻器工作一般会产生微结构变化和焦耳热, 将严重影响器件稳定性, 改进器件结构和材料成分可有效改善器件性能。利用光信号调控忆阻器电导, 不仅能降低能耗, 而且可避免产生微结构变化和焦耳热, 从而有望解决稳定性难题。此外, 光控忆阻器能直接感受光刺激, 单器件即可实现感/存/算功能, 可用于研发新型视觉传感器。因此, 全光控忆阻器的实现为忆阻器的研究和应用打开了一扇新窗口。
氧化物忆阻器 光电器件 人工突触 类脑神经形态计算 综述 oxide memristor optoelectronic device artificial synapse brain-inspired neuromorphic computing review
国防科技大学电子科学学院,湖南 长沙 410073
当前物联网、云计算等产生的海量非结构化数据,极大提高了对数据处理算力和能效的需求。神经形态计算借鉴生物大脑的信息处理方式,以神经元与神经突触为基本单元,从互联架构与信息处理模式等方面模拟生物神经系统,能够实现实时、超低功耗信息处理,成为大数据时代计算技术发展的前沿热点。其中,光子神经形态计算技术是在光域上进行神经形态计算数据处理的技术,既能够充分发挥光子高速传输、低功耗、高并行度的优势,又能够避免光电和电光转换带来的额外时间功耗开销,具有很大的研究和应用价值。近年来,相变材料作为一种具有高折射率对比度和非易失特性的光学材料,可在光、电、热等激励作用下进行折射率的连续调节,为非易失光子神经形态计算提供了一种可行的解决方案,成为当前的研究热点。本文首先介绍了光子神经形态计算的基本原理和实现方法,在此基础上讨论了相变材料用于光子神经形态计算的原理。其次,针对不同类型的实现途径,研究了不同相变材料的特点和选型办法,综合分析了当前应用较多的两类相变材料以及各类光突触器件和阵列集成应用。最后对基于相变材料的光子神经形态计算技术的发展进行了展望。
材料 相变材料 神经形态计算 光神经网络 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(21): 2100007
1 1.北京理工大学 物理学院, 先进光电量子结构设计与测量教育部重点实验室, 北京 100081
2 2.北京理工大学 长三角研究院, 嘉兴 314019
忆阻器可以在单一器件上实现存储和计算功能, 成为打破冯·诺依曼瓶颈的核心电子元器件之一。它凭借独特的易失性/非易失性电阻特性, 可以很好地模拟大脑活动中的突触/神经元的功能。此外, 基于金属氧化物的忆阻器与传统的互补金属氧化物半导体(CMOS)工艺兼容, 受到了广泛关注。近年来, 研究提出了多种基于单介质层结构的金属氧化物忆阻器, 但仍然存在高低阻态不稳定、开关电压波动大和循环耐久性差等问题。在此基础上, 研究人员通过在金属氧化物忆阻器中引入双介质层成功优化了忆阻器的性能。本文首先详细介绍了氧化物双介质层忆阻器的优势, 阐述了氧化物双介质层忆阻器的阻变机理和设计思路, 并进一步介绍了氧化物双介质层忆阻器在神经形态计算中的应用。本文将为设计更高性能的氧化物双介质层忆阻器起到一定的启示作用。
忆阻器 突触 神经元 神经形态计算 双介质层金属氧化物 综述 memristor synapse neuron neuromorphic computing double dielectric layer metal-oxide review 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hubei Key Laboratory for Advanced Memories, School of Integrated Circuits, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Hubei Yangtze Memory Laboratories, Wuhan 430205, China
3 School of Microelectronics and Faculty of Physics and Electronics Science, Hubei University, Wuhan 430062, China
4 Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
With rapid advancement and deep integration of artificial intelligence and the internet-of-things, artificial intelligence of things has emerged as a promising technology changing people’s daily life. Massive growth of data generated from the devices challenges the AIoT systems from information collection, storage, processing and communication. In the review, we introduce volatile threshold switching memristors, which can be roughly classified into three types: metallic conductive filament-based TS devices, amorphous chalcogenide-based ovonic threshold switching devices, and metal-insulator transition based TS devices. They play important roles in high-density storage, energy efficient computing and hardware security for AIoT systems. Firstly, a brief introduction is exhibited to describe the categories (materials and characteristics) of volatile TS devices. And then, switching mechanisms of the three types of TS devices are discussed and systematically summarized. After that, attention is focused on the applications in 3D cross-point memory technology with high storage-density, efficient neuromorphic computing, hardware security (true random number generators and physical unclonable functions), and others (steep subthreshold slope transistor, logic devices,etc.). Finally, the major challenges and future outlook of volatile threshold switching memristors are presented.
AIoT threshold switching memristor selector neuromorphic computing hardware security Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(5): 053102
1 1.中国电子科技南湖研究院, 嘉兴 314002
2 2.湖北江城实验室, 武汉 430205
3 3.华中科技大学 光学与电子信息学院, 武汉光电国家实验室, 武汉 430074
4 4.华中科技大学 材料科学与工程学院, 材料加工与模具技术国家重点实验室, 武汉 430074
二维过渡金属硫化合物是构建纳米电子器件的理想材料, 基于该材料体系开发用于信息存储和神经形态计算的忆阻器, 受到了学术界的广泛关注。受制于低成品率和低均一性问题, 二维过渡金属硫化合物忆阻器阵列鲜见报道。本研究采用化学气相沉积得到厘米级二维碲化钼薄膜, 并通过湿法转移和剥离工艺制备得到碲化钼忆阻器件。该碲化钼器件表现出优异的保持性(保持时间>500 s)、快速的阻变(SET时间~60 ns, RESET时间~280 ns)和较好的循环寿命(阻变2000圈后仍可正常工作)。该器件具有高成品率(96%)、低阻变循环间差异性(SET过程为6.6%, RESET过程为5.2%)和低器件间差异性(SET过程为19.9%, RESET过程为15.6%)。本工作成功制备出基于MoTe2的3×3忆阻器阵列。在此基础上, 将研制的MoTe2器件用于手写体识别, 实现了91.3%的识别率。最后, 通过对MoTe2器件高低阻态的电子输运机制进行拟合分析, 揭示了该器件阻变源于类金属导电细丝的通断过程。本项工作表明大尺寸二维过渡金属硫化合物在未来神经形态计算中具有巨大的应用潜力。
二维材料 碲化钼 忆阻器阵列 神经形态计算 two-dimensional material MoTe2 memristor array neuromorphic computing 光子学报
2021, 50(10): 1020001
光子学报
2021, 50(10): 1020002





