Wei Yin 1,2,3†Yuxuan Che 1,2,3†Xinsheng Li 1,2,3Mingyu Li 1,2,3[ ... ]Chao Zuo 1,2,3,****
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210019, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging & Intelligent Sense, Nanjing 210094, China
4 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China
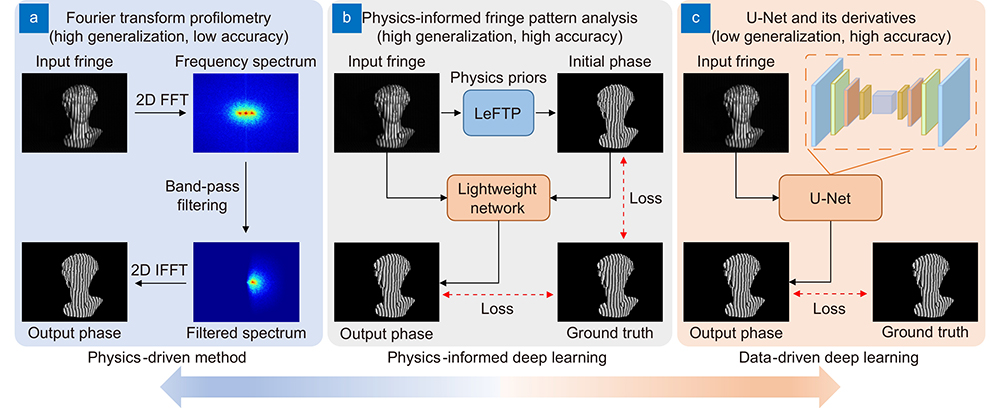
Recently, deep learning has yielded transformative success across optics and photonics, especially in optical metrology. Deep neural networks (DNNs) with a fully convolutional architecture (e.g., U-Net and its derivatives) have been widely implemented in an end-to-end manner to accomplish various optical metrology tasks, such as fringe denoising, phase unwrapping, and fringe analysis. However, the task of training a DNN to accurately identify an image-to-image transform from massive input and output data pairs seems at best na?ve, as the physical laws governing the image formation or other domain expertise pertaining to the measurement have not yet been fully exploited in current deep learning practice. To this end, we introduce a physics-informed deep learning method for fringe pattern analysis (PI-FPA) to overcome this limit by integrating a lightweight DNN with a learning-enhanced Fourier transform profilometry (LeFTP) module. By parameterizing conventional phase retrieval methods, the LeFTP module embeds the prior knowledge in the network structure and the loss function to directly provide reliable phase results for new types of samples, while circumventing the requirement of collecting a large amount of high-quality data in supervised learning methods. Guided by the initial phase from LeFTP, the phase recovery ability of the lightweight DNN is enhanced to further improve the phase accuracy at a low computational cost compared with existing end-to-end networks. Experimental results demonstrate that PI-FPA enables more accurate and computationally efficient single-shot phase retrieval, exhibiting its excellent generalization to various unseen objects during training. The proposed PI-FPA presents that challenging issues in optical metrology can be potentially overcome through the synergy of physics-priors-based traditional tools and data-driven learning approaches, opening new avenues to achieve fast and accurate single-shot 3D imaging.
optical metrology deep learning physics-informed neural networks fringe analysis phase retrieval Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230034
1 重庆邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,重庆 400065
2 重庆邮电大学智能通信与网络安全研究院,重庆 400065
提出了一种渐进式训练方案来重新配置马赫-曾德尔干涉仪(MZI)前馈光学神经网络(ONN)的相移,从而对抗MZI的相位误差和分束器误差,提高识别准确率。为了验证所提方案,利用Neuroptica Python仿真平台搭建了3层MZI-ONN结构,并在考虑到MZI相位误差和分束器误差的情况下,利用Iris和MNIST数据集验证了所提方案的有效性。仿真结果表明:在Iris数据集下,对于3层4×4 MZI-ONN结构,所提方案的识别准确率能够提升64.15百分点;在MNIST数据集下,对于4×4、6×6、8×8和16×16规模的MZI-ONN,所提方案的识别准确率能够提升2.00~37.00百分点。所提方案极大地提高了MZI-ONN的抗误差性能,有助于未来大规模、高准确率MZI-ONN的实现。
光计算 马赫-曾德尔干涉仪 光学神经网络 相位误差 分束器误差 渐进式训练 抗误差
1 西安工业大学 光电工程学院, 陕西西安70032
2 西安交通大学 机械制造系统工程国家重点实验室, 陕西西安710049
为满足点衍射干涉测量对解包算法高精度、高效以及抗干扰的检测需求。提出一种基于空洞空间卷积的相移点衍射干涉图像的相位解包方法,通过将自编码器结构和空洞空间卷积结合获得更高的相位解包精度,实现对包裹相位图像可控的多尺度特征提取。根据点衍射图像特点制作的大量多样化数据集对其进行训练和优化,从而实现准确识别包裹相位所在阶次,最终可以快速处理包裹图像得到高精度的解包结果。利用所提方法对实际点衍射干涉图像进行处理,并与ESDI专业干涉图像处理软件以及其他解包算法处理结果进行比对,结果表明:本文解包结果与软件枝切法解包处理结果均方根误差值为0.022 2 rad,面形拟合结果与软件面形拟合结果峰谷差值仅为0.012 1λ、均方根差值仅为0.004 2λ;时间效率上,完成一幅图像的处理平均仅需0.035 s,而传统方法均大于1 s。与其他方法相比,所提方法在处理包裹相位方面具有快速、高精度的特性,为点衍射干涉图像处理的高精度相位解包提供了新的可行方案。
干涉测量 面形检测 干涉成像 神经网络 相位解包 interferometry surface measurement interference fringe neural networks phase unwrapping 陆文强 1,2,3杨世植 1,2,3,*罗涛 1,2,3李学彬 1,2,3[ ... ]韩叶颜 1,2,3
1 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所中国科学院大气光学重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230031
2 中国科学技术大学研究生院科学岛分院,安徽 合肥 230026
3 先进激光技术安徽省实验室,安徽 合肥 230037
4 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所基础科学研究中心,安徽 合肥 230031
5 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所通用光学定标与表征技术重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230031
基于中分辨率成像光谱仪/云和气溶胶探测激光雷达(MODIS/CALIOP)的匹配数据集,提出一个分类神经网络进行透明卷云的识别,利用两个回归神经网络对透明卷云的光学厚度和云顶高度进行反演。结果表明,分类网络的精确度可达到84%,检测率达到79%。对成功识别的透明卷云参数进行了反演,得到透明卷云光学厚度的平均绝对误差为0.2,均方根误差为0.25,相关系数为0.79。对云顶高度进行了反演,得到云顶高度的平均绝对误差为0.61 km,均方根误差为0.74 km,相关系数达到0.87。本研究利用MODIS/CALIOP匹配数据集以及神经网络算法,可得到透明卷云的分布以及其参数特性,为其在南海海域上空的分布情况提供了数据支撑,有助于相关研究人员了解该地区透明卷云的分布情况,提高辐射计算的精度。
大气光学 透明卷云 中分辨率成像光谱仪 云和气溶胶探测激光雷达 神经网络 中国南海海域
1 宁波大学信息科学与工程学院,浙江 宁波 315211
2 宁波大学医学院,浙江 宁波 315211
3 宁波市海曙区第二医院,浙江 宁波 315099
4 宁波大学附属第一医院,浙江 宁波 315000
在检测侧面脊柱关键点时,由于受到器官遮挡的影响,以往的热图回归方法难以区分不同椎骨上的关键点,容易出现关键点与对应椎骨的匹配错误。为了解决这个问题,提出了一个新的单阶段侧面脊柱关键点检测方法,该方法同时预测关键点热图和关键点匹配线索(椎骨中心热图和关键点offset),利用匹配线索建立关键点与对应椎骨的匹配关系。为了提升匹配效果,提出几何感知特征增强模块,通过提取关键点特征增强椎骨中心的特征表达。此外,利用加权损失函数缓解关键点热图和椎骨中心热图中正负样本比例失衡问题。实验结果表明,所提方法的平均检测误差为8.84,相较于性能第二的方法精度提升36%。
医用光学 关键点检测 卷积网络 可变形卷积 脊柱侧弯 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(4): 0417001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Institute of Electrical and Micro Engineering, Ecublens, Switzerland
2 Koc University, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey
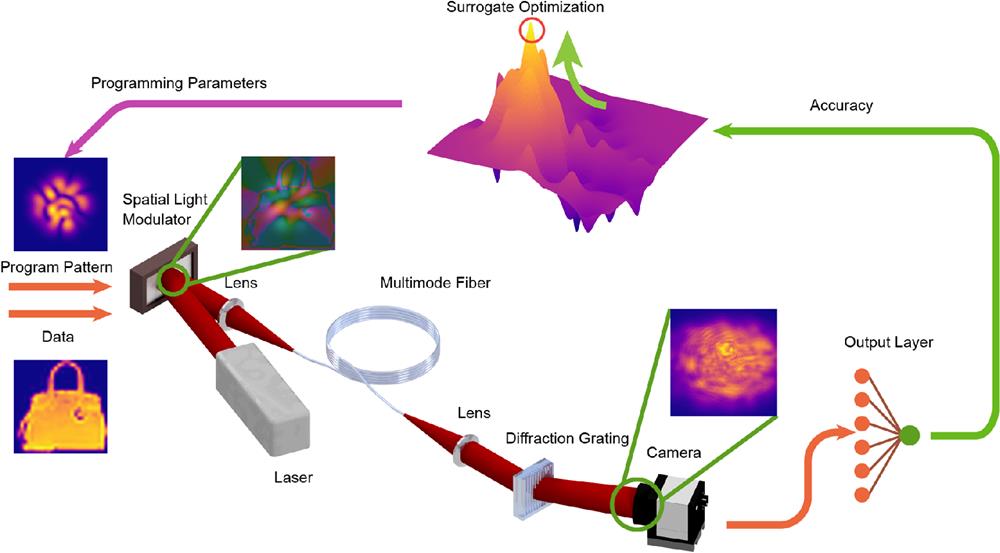
The ever-increasing demand for training and inferring with larger machine-learning models requires more efficient hardware solutions due to limitations such as power dissipation and scalability. Optics is a promising contender for providing lower power computation, since light propagation through a nonabsorbing medium is a lossless operation. However, to carry out useful and efficient computations with light, generating and controlling nonlinearity optically is a necessity that is still elusive. Multimode fibers (MMFs) have been shown that they can provide nonlinear effects with microwatts of average power while maintaining parallelism and low loss. We propose an optical neural network architecture that performs nonlinear optical computation by controlling the propagation of ultrashort pulses in MMF by wavefront shaping. With a surrogate model, optimal sets of parameters are found to program this optical computer for different tasks with minimal utilization of an electronic computer. We show a remarkable decrease of 97% in the number of model parameters, which leads to an overall 99% digital operation reduction compared to an equivalently performing digital neural network. We further demonstrate that a fully optical implementation can also be performed with competitive accuracies.
neural networks nonlinear optics fiber optics surrogate optimization neuromorphic computing wavefront shaping Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 016002

Xilin Yang 1,2,3†Md Sadman Sakib Rahman 1,2,3Bijie Bai 1,2,3Jingxi Li 1,2,3Aydogan Ozcan 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of California, Los Angeles, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Los Angeles, California, United States
2 University of California, Los Angeles, Bioengineering Department, Los Angeles, California, United States
3 University of California, Los Angeles, California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI), Los Angeles, California, United States
As an optical processor, a diffractive deep neural network (D2NN) utilizes engineered diffractive surfaces designed through machine learning to perform all-optical information processing, completing its tasks at the speed of light propagation through thin optical layers. With sufficient degrees of freedom, D2NNs can perform arbitrary complex-valued linear transformations using spatially coherent light. Similarly, D2NNs can also perform arbitrary linear intensity transformations with spatially incoherent illumination; however, under spatially incoherent light, these transformations are nonnegative, acting on diffraction-limited optical intensity patterns at the input field of view. Here, we expand the use of spatially incoherent D2NNs to complex-valued information processing for executing arbitrary complex-valued linear transformations using spatially incoherent light. Through simulations, we show that as the number of optimized diffractive features increases beyond a threshold dictated by the multiplication of the input and output space-bandwidth products, a spatially incoherent diffractive visual processor can approximate any complex-valued linear transformation and be used for all-optical image encryption using incoherent illumination. The findings are important for the all-optical processing of information under natural light using various forms of diffractive surface-based optical processors.
optical computing optical networks machine learning diffractive optical networks diffractive neural networks image encryption Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016010
1 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 清华大学电子工程系,北京 100084
3 北京信息科学与技术国家研究中心,北京 100084
4 国防科技大学新型纳米光电信息材料与器件湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
5 国防科技大学南湖之光实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
光学神经网络是区别于冯·诺依曼计算架构的一种高性能新型计算范式,具有低延时、低功耗、大带宽以及并行信号处理等优势。片上集成是光学神经网络微型化发展的一种典型方式,近年来片上集成光学神经网络获得了学术界及工业界的广泛关注。对基于不同计算单元结构的片上集成光学神经网络的相关研究工作进行了梳理,并分析了其设计原理、实现方法及系统架构特征。同时结合国内外最新研究进展,进一步分析了片上集成光学神经网络在计算单元大规模拓展、可重构、非线性运算和实用化等方面面临的挑战及其未来发展趋势。
集成光学 光计算 光学神经网络 芯片 人工智能
河北工业大学电子信息工程学院, 天津 300401
随着越来越多的大型光谱巡天计划的实施, 产生了海量的恒星光谱数据, 这对于恒星演化理论的研究具有重大意义, 但也给传统的光谱分类和处理带来极大挑战。 2021年发布的LAMOST DR7(v2.0版本)光谱数据集中, 恒星光谱总量为百万量级, 但其中O型星的数量仅为129条, 远远小于其他六类恒星光谱数量。 对于这种数据量大、 数据集严重不平衡的情况, 传统的机器学习分类方法达不到较好的效果, 因此多用于对相邻两类、 部分类或子类恒星光谱进行分类。 针对以上问题, 使用一维卷积神经网络(CNN)和一维生成对抗网络(GAN)相结合的半监督学习模式对七类恒星光谱进行全分类。 实验首先对每条光谱进行裁剪和去噪, 截取光谱波长范围为370.00~867.16 nm部分, 然后进行均匀采样和归一化, 生成大小为1×3 700的数据集样本, 送入CNN进行训练。 为了避免过拟合并提高模型对未知数据的预测能力, 在CNN的全连接层和池化层之间添加正则项Dropout。 使用该网络对除O型星以外的六类光谱进行分类, 平均分类准确率达到98.08%。 针对O型星数量严重偏少的问题, 采用GAN来扩充数据集。 GAN的输入是1×900大小的噪声信号, 经过生成器中全连接的三层跨步卷积运算, 输出大小为1×3 700的数据。 通过对生成器和判别器进行单独交替迭代训练使GAN收敛, 最终输出所需数量的O型星样本, 达到扩充数据集的目的。 和常见的通过过采样扩充数据集相比, 利用GAN扩充数据集, 结合一维CNN对恒星光谱进行全分类, 可以将O型星的分类准确率由72.92%提升至97.92%, 整个分类器的准确率达到96.28%。 实验结果表明, 使用这种半监督模式的恒星光谱自动分类方法可以实现对七类恒星光谱的快速、 准确分类, 也可以用于对标记为“Unknown”的未分类恒星光谱进行挖掘, 达到充分利用光谱的目的。
恒星光谱 自动分类 卷积神经网络 生成对抗网络 半监督模式 Star spectra Automatic classification Convolutional neural networks Generative adversarial networks Semi-supervised mode 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(6): 1875





