1 国防科技大学气象海洋学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 中国气象局高影响天气重点开放实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
准确获取飞秒激光成丝横截面图像及其沉积能量空间分布信息,对于成丝动力机制研究和促进诸多基于光丝的实际大气应用发展具有重要意义。本文基于热传导方程和波动方程构成的光声信号前向仿真模型,理论模拟了利用环阵式光声层析系统接收飞秒激光在空气介质中成丝诱导产生超声脉冲信号的过程;然后,利用延迟叠加算法对飞秒激光大气传输成丝沉积能量横向分布图像进行了反向重建,并分析了测量系统中关键器件超声换能器的中心频率、带宽、表面尺寸和探测表面灵敏度等性能参数对光丝沉积能量分布图像重建结果的影响。结果表明,单丝诱导产生的声压脉冲信号频谱为单峰结构,而多丝声压脉冲信号频谱为多峰结构;相比于单丝图像重建,多丝图像重建受“孔径效应”影响更显著;换能器的性能参数对光丝图像的重建效果有显著的影响,换能器的带宽越大、表面直径越小,以及表面灵敏度系数越大,越有利于光丝沉积能量分布图像重建效果的提升。该研究结果可为真实大气条件下飞秒激光传输成丝沉积能量空间分布的实验测量提供一定的理论支撑。
飞秒激光 激光成丝 能量沉积 光声信号 超声换能器 反投影 光学学报
2024, 44(12): 1201011

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics and CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Laser Fusion Research Center and Science & Technology on Plasma Physics Laboratory, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621999, China
The characteristics of plasmas play an important role in femtosecond laser filament-based applications. Spectroscopic analysis is used to experimentally investigate the plasma density and its temperature of the air filament under different pulse repetition rates. In our experiments, the measured average plasma density of the filament is and the temperature of the plasma is about 5100 K under 100 Hz pulse repetition rate. The plasma density decreases to and the temperature increases to 6230 K as the pulse repetition rate increases to 1000 Hz. The experimental observation agrees with the numerical simulation by solving the nonlinear Schrödinger equations with repetition rate related “low density hole” correction.
femtosecond laser filamentation cumulative effects electron density Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(1): 013201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Nonlinear compression has become an obligatory technique along with the development of ultrafast lasers in generating ultrashort pulses with narrow pulse widths and high peak power. In particular, techniques of nonlinear compression have experienced a rapid progress as ytterbium (Yb)-doped lasers with pulse widths in the range from hundreds of femtoseconds to a few picoseconds have become mainstream laser tools for both scientific and industrial applications. Here, we report a simple and stable nonlinear pulse compression technique with high efficiency through cascaded filamentation in air followed by dispersion compensation. Pulses at a center wavelength of 1040 nm with millijoule pulse energy and 160 fs pulse width from a high-power Yb:CaAlGdO4 regenerative amplifier are compressed to 32 fs, with only 2.4% loss from the filamentation process. The compressed pulse has a stable output power with a root-mean-square variation of 0.2% over 1 hour.
femtosecond pulse filamentation nonlinear compression High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(6): 06000e84
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Modern Optics, Eye Institute, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
2 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
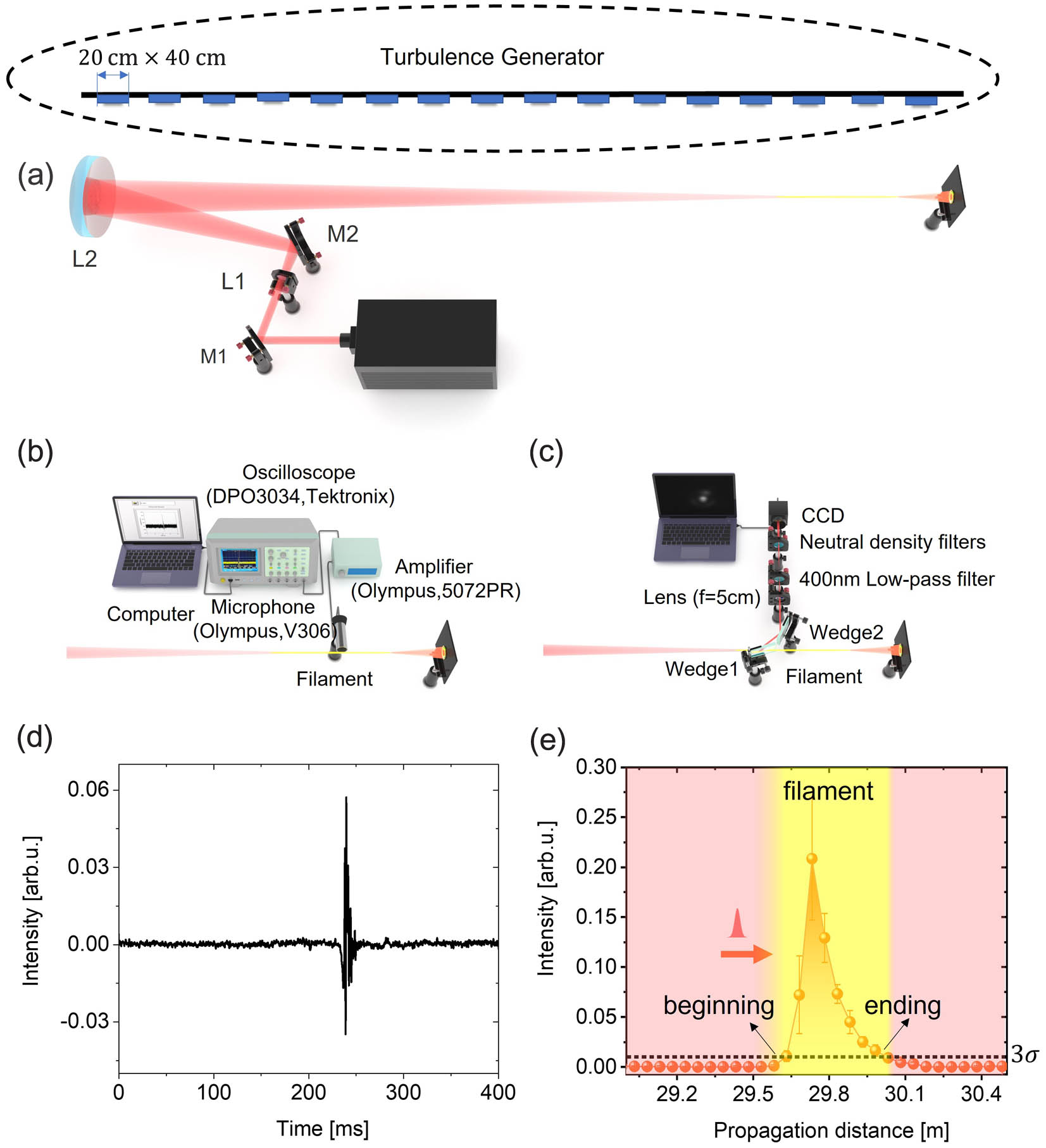
The effects of turbulence intensity and turbulence region on the distribution of femtosecond laser filaments are experimentally elaborated. Through the ultrasonic signals emitted by the filaments, it is observed that increasing turbulence intensity and an expanding turbulence active region cause an increase in the start position of the filament and a decrease in filament length, which can be well explained by theoretical calculation. It is also observed that the random perturbation of the air refractive index caused by atmospheric turbulence expands the spot size of the filament. Additionally, when the turbulence refractive index structure constant reaches , multiple filaments are formed. Furthermore, the standard deviation of the transverse displacement of filament is found to be proportional to the square root of the turbulent structure constant under the experimental turbulence parameters in this paper. These results contribute to the study of femtosecond laser propagation mechanisms in complex atmospheric turbulence conditions.
femtosecond laser filamentation turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110004
1 上海理工大学太赫兹技术创新研究院,上海 200093
2 南开大学现代光学研究所,天津 300350
3 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津 300072
飞秒激光成丝辐射太赫兹波兼具宽频带和高强度特性,其物理机制研究已成为近年来的前沿课题。在此领域,本课题组发现太赫兹波沿激光等离子体光丝被限制在亚波长空间尺度内进行传输,即“太赫兹波空间强束缚效应”,并据此提出了能够全面阐述太赫兹波辐射机理的三过程模型,为统一当前主流宏观与微观理论、化解相关文献中重要结论的矛盾奠定了基础。本文以太赫兹波空间强束缚效应为中心,综述了本课题组近年来的一系列研究工作,包括实验探测技术、物理机理解释及多项创新应用等,并对未来的工作进行了展望。
中国激光
2023, 50(17): 1714010
1 中国人民解放军国防科技大学理学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室及超强激光科学卓越中心,上海 201800
3 中国电子科技集团公司信息科学研究院,北京 100086
强飞秒激光在大气中的成丝过程伴随着自聚焦、群速度色散和等离子散焦等非线性光学现象,对于研究激光雷达、新型光源、人工降雨、大气污染物探测、激光远程探测和激光遥感等具有重要意义。飞秒激光在大气中传输时,通常会由于大气湍流导致的空气折射率扰动以及飞秒激光初始能量分布不均匀而产生随机多丝现象,从而影响了光丝的能量分布,缩短了光丝的传播距离并降低了光斑质量,限制了光丝的实际应用。本文介绍了近20年来国内外有关多丝调控研究的进展,分析了调节入射光束的椭圆率、改变激光场强梯度、调制激光相位、引入像散等多丝调控手段,旨在为研究飞秒激光多丝调控提供参考。这些调控手段都能在一定程度上消除多丝产生的随机性,但仍然存在多丝分布控制精度不高、激光能量损耗偏大、激光传输距离不够远等问题。因此,对多丝的调控还有待更加深入的研究。
非线性光学 飞秒激光成丝 自聚焦 多丝操控 多丝抑制 中国激光
2023, 50(14): 1400001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics and CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
3 Laser Fusion Research Center and Science & Technology on Plasma Physics Laboratory, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, China
As intense, ultrashort, kHz-repetition-rate laser systems become commercially available, pulse cumulative effects are critical for laser filament-based applications. In this work, the pulse repetition-rate effect on femtosecond laser filamentation in air was investigated both numerically and experimentally. The pulse repetition-rate effect has negligible influence at the leading edge of the filament. Clear intensity enhancement from a high-repetition pulse is observed at the peak and tailing edge of the laser filament. As the repetition rate of the laser pulses increases from 100 to 1000 Hz, the length of the filament extends and the intensity inside the filament increases. A physical picture based on the pulse repetition-rate dependent ‘low-density hole’ effect on filamentation is proposed to explain the obtained results well.
clamping intensity cumulative effects femtosecond laser filamentation High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(4): 04000e46
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Applied Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
It was shown experimentally that for a 65-fs 17-J pulse, the effect of filamentation instability, also known as small-scale self-focusing, is much weaker than that predicted by stationary and nonstationary theoretical models for high B-integral values. Although this discrepancy has been left unexplained at the moment, in practice no signs of filamentation may allow a breakthrough in nonlinear pulse post-compression at high laser energy.
B-integral cubic Kerr nonlinearity filamentation instability high-power femtosecond laser nonlinear post-compression High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(2): 02000e28
1 南开大学电子信息与光学工程学院现代光学研究所,天津 300350
2 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室,天津 300350
3 北京空间机电研究所,北京 100094
为满足激光雷达收集系统对远距离荧光信号探测要求,提出了一种基于多软件协同循环优化各环带面形的非球面环带菲涅耳透镜设计方法,并进行了透镜面形误差分析及透镜样件性能测试。利用该方法设计了一个直径为300 mm、焦距为670 mm的高收集效率菲涅耳透镜,使用LightTools软件对设计的菲涅耳透镜进行了光学仿真,收集效率可达52.2%。仿真和实验结果均表明:在400~950 nm光谱范围内,设计的菲涅耳透镜减小了透镜球差和色差对收集系统的影响,具有较高的能量收集效率,提高了系统光能利用率,满足系统性能指标要求。
非线性光学 光学设计 菲涅耳透镜 光丝激光雷达 收集系统 非球面透镜
1 北京大学物理学院人工微结构和介观物理国家重点实验室,北京 100871
2 南开大学现代光学研究所,天津 300350
3 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室,天津 300350
4 天津市光电传感器与传感网络重点实验室,天津 300350
飞秒激光成丝表征是光丝调控及应用的基础,成丝过程中光、声和热信号之间丰富的能量转换效应为利用声学和光学等方法探索和诊断光丝打开了大门。由于成丝过程中声波和荧光辐射微观物理机制的区别,两种信号与光丝物理参数之间的定量关系存在差异,然而目前仍缺乏两种方法的准确性对比研究。基于此,实验上通过研究脉冲能量对光丝空间分布的影响,系统对比了声学及荧光法两种光丝表征方法的异同。结果表明:两种方法都可以实现对光丝空间特征的表征,相比于荧光法,声学法对光丝起始和结束位置表现出更高的灵敏度,光丝内自由电子动能对光场强度的依赖性是造成差异的主要原因。
非线性光学 飞秒激光成丝 声学 荧光 空间特征 电子动能





