1 河北工业大学先进激光技术研究中心,天津 300401
2 河北省先进激光技术与装备重点实验室,天津 300401
针对梯度掺杂晶体和均匀掺杂晶体,采用数值模拟的方式分析了泵浦光束腰半径、光束质量因子()与束腰位置对模式匹配效率的影响,并通过实验验证了不同束腰位置对激光器输出功率的影响。由计算结果得到,在不同的泵浦光参数下,与均匀掺杂晶体相比,梯度掺杂晶体均具有更稳定的模式匹配;当泵浦光为10和50,束腰半径为0.5 mm时,对于任意位置的束腰,梯度掺杂晶体的模式匹配效率都高于均匀掺杂晶体。在实验上对比分析了泵浦光不同束腰位置的输出功率,结果表明,梯度掺杂晶体的模式匹配效率受泵浦光束腰位置的影响较小。当晶体位于谐振腔中心时,在高于70 W的泵浦条件下,梯度掺杂晶体的输出功率高于均匀掺杂晶体,最高输出功率为44.8 W,与均匀掺杂晶体相比,提高了4.67%;当晶体紧贴输入镜时,梯度掺杂晶体的最高输出功率为34.0 W,与均匀掺杂晶体相比,提高了11.84%。因此,梯度掺杂晶体更适用于高功率泵浦。
激光器 梯度掺杂晶体 模式匹配 激光器理论 端面泵浦 高功率激光
1 中国科学院半导体研究所半导体超晶格国家重点实验室, 北京 100083
2 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电子技术学院, 北京 100049
3 北京量子信息科学研究院, 北京 100193
半导体带间级联量子阱是实现3~5 μm波段中红外激光器的重要前沿,其在半导体光电器件技术、气体检测、医学医疗以及自由空间光通信等诸多领域具有重要科学意义和应用价值。半导体带间级联量子阱发光机理是以二类量子阱中的电子与空穴的带间辐射复合发光为主导,再通过电子注入区与空穴注入区形成级联放大,实现多个量子阱周期内电子与空穴的重复利用。本文综述了半导体带间级联激光器从提出能带结构、外延材料到器件制备技术的发展历程,剖析了器件结构各功能区基本概念和工作原理,介绍了器件结构设计与制备工艺技术难点的里程碑突破,详细解释了载流子再平衡、分别限制层等设计,最后展望了半导体带间级联激光器的发展方向和趋势。
激光器 半导体 量子阱 激光理论
长春理工大学 高功率半导体激光国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130022
为了提高976 nm宽条形高功率半导体激光器的光束质量, 基于严格的二阶矩理论搭建了一套适用于高功率半导体激光器的光束质量检测装置。利用该装置测量了实验室研制的976 nm宽条形高功率半导体激光器在1~10 A工作电流下的束腰位置、束腰尺寸和远场发散角。实验结果表明, 随着电流从1 A增加到10 A, 快轴方向束宽及远场发散角由于反导引效应有微小增加, 但由于垂直方向较强的折射率导引机制使得光束参数变化很小, 光束质量因子M2仅从1.32增加到1.48, 光束质量基本不变。慢轴方向由于反导引效应及热透镜效应而导致高阶模式激射, 使得束宽及远场发散角随工作电流增加逐渐增大, 光束质量因子M2从5.44增加到11.76, 光束质量逐渐变差。傍轴光束定义及非傍轴光束定义下的光束质量因子测试结果表明, 在快轴方向, 两者差别较大, 不能使用傍轴光束定义近似计算; 在慢轴方向, 两者近似相等, 可以使用傍轴光束定义近似计算。
半导体激光器 一般激光理论 激光器 semiconductor laser general laser theory lasers

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Physics Gleb Wataghin, State University of Campinas, Campinas 13083-872, Brazil
2 Department of Applied Mathematics, State University of Campinas, Campinas 13083-250, Brazil
Ellipsometry is a powerful and well-established optical technique used in the characterization of materials. It works by combining the components of elliptically polarized light in order to draw information about the optical system. We propose an ellipsometric experimental set-up to study polarization interference in the total internal reflection regime for Gaussian laser beams. The relative phase between orthogonal states can be measured as a power oscillation of the optical beam transmitted through a dielectric block, and the orthogonal components are then mixed by a polarizer. We show under which conditions the plane wave analysis is valid, and when the power oscillation can be optimized to reproduce a full pattern of oscillation and to simulate quarter- and half-wave plates.
140.3430 Laser theory 260.3160 Interference Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(3): 031406

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Engineering and Natural Science, Sabanci University, Istanbul 34956, Turkey
2 e-mail: eesa@sabanciuniv.edu
The chimera state is the concurrent combination of synchronous and incoherent oscillations in a set of identical oscillators. In this study, we demonstrate the states for optical nanoresonators where the oscillators are designed based on a plasmonic dimer cavity. This resonator interchanges radiative energy with an active medium located at its hotspot, and therefore forms an amplitude-mediated oscillating system. Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD)-based numerical analysis of a circular array of the coupled oscillators reveals that regardless of identical nature, oscillator phase is not concordant over time for all members. The effect of coupling strength on the phase escape/synchronization of the oscillators is investigated for the plasmonic nanoresonator system. It is shown that for identical oscillators, which are placed symmetrically over the perimeter of a disc, the array can be divided to several subgroups of concurrent coherent and incoherent members. While the oscillator of each subgroup seems to be locked together, one member can escape from synchronization for a while and return to coherency, or it can sync with the other groups. The effect of coupling strength and number of oscillators on the phase-escape pace is studied for this system, and strong coupling is shown to force the array members to fully synchronize while weaker coupling causes chimera states in the array.
Chaos Optical resonators Nonlinear optical materials Surface plasmons Laser theory Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000427
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Applied Physics, School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, 3-4-1 Okubo, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 169-8555, Japan
2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Science and Engineering, Kanazawa University, Kakuma-machi, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920-1192, Japan
We numerically performed wave dynamical simulations based on the Maxwell–Bloch (MB) model for a quadrupole-deformed microcavity laser with spatially selective pumping. We demonstrate the appearance of an asymmetric lasing mode whose spatial pattern violates both the x- and y-axes mirror symmetries of the cavity. Dynamical simulations revealed that a lasing mode consisting of a clockwise or counterclockwise rotating-wave component is a stable stationary solution of the MB model. From the results of a passive-cavity mode analysis, we interpret these asymmetric rotating-wave lasing modes by the locking of four nearly degenerate passive-cavity modes. For comparison, we carried out simulations for a uniform pumping case and found a different locking rule for the nearly degenerate modes. Our results demonstrate a nonlinear dynamical mechanism for the formation of a lasing mode that adjusts its pattern to a pumped area.
(140.3945) Microcavities (140.3410) Laser resonators (270.3430) Laser theory (000.1600) Classical and quantum physics. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000B47
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Applied Physics, School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University, 3-4-1 Okubo, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 169-8555, Japan
2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Science and Engineering, Kanazawa University, Kakuma-machi, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920-1192, Japan
For a fully chaotic two-dimensional (2D) microcavity laser, we present a theory that guarantees both the existence of a stable single-mode lasing state and the nonexistence of a stable multimode lasing state, under the assumptions that the cavity size is much larger than the wavelength and the external pumping power is sufficiently large. It is theoretically shown that these universal spectral characteristics arise from the synergistic effect of two different kinds of nonlinearities: deformation of the cavity shape and mode interaction due to a lasing medium. Our theory is based on the linear stability analysis of stationary states for the Maxwell–Bloch equations and accounts for single-mode lasing phenomena observed in real and numerical experiments of fully chaotic 2D microcavity lasers.
(140.3945) Microcavities (140.3410) Laser resonators (270.3430) Laser theory (000.1600) Classical and quantum physics. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000B39
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Dipartimento di Fisica, Politecnico di Milano and Istituto di Fotonica e Nanotecnologie del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Piazza L. da Vinci 32, I-20133 Milano, Italy
2 Department of Electrical Engineering, The State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York 14260, USA
Recent experiments demonstrated that chiral symmetry breaking at an exceptional point (EP) is a viable route to achieve unidirectional laser emission in microring lasers. By a detailed semiconductor laser rate equation model, we show here that unidirectional laser emission at an EP is a robust regime. Slight deviations from the EP condition can break preferential unidirectional lasing near threshold via a Hopf instability. However, above a “second” laser threshold, unidirectional emission is restored.
(270.3430) Laser theory (140.3560) Lasers ring (140.3945) Microcavities. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 060000B1
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Tunable Laser Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
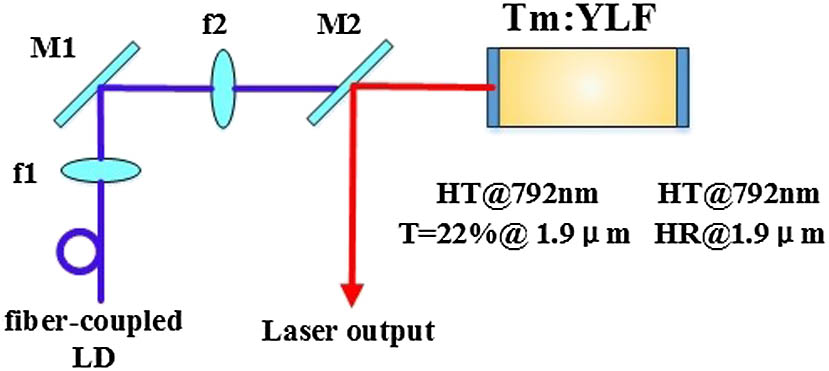
We report a monolithic Tm:YLF micro laser in this Letter. In order to improve the relaxation oscillation of the laser, both ends of the crystal are coated, making the Tm:YLF crystal itself a resonant cavity. The micro laser is pumped by a 792 nm laser diode operated in the continuous wave (CW) mode. We obtain maximum output powers of 7.78 and 10.4 W at the total incident power of 43.6 W with focus lenses of 37.5 and 40 mm, respectively, corresponding to the slope efficiencies of 25.6% and 40.0% and the optical–optical conversion efficiencies of 17.8% and 23.8%. It is clear that the amplitude of the relaxation oscillation is smaller and the beam quality is better with the focus length of 37.5 mm; however, the laser with the focus length of 40 mm produces a higher output power and a more stable wavelength centering at 1878.44 nm.
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3425 Laser stabilization 140.3430 Laser theory Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 061401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Science and Technology, School of Physics Science and Information Engineering, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, Shandong 252059, China
We investigate a novel Smith–Purcell terahertz source. This device is composed of an electron gun, a cylindrical resonator, a metallic grating, and a collector. The characteristics of the Smith–Purcell terahertz source are discussed with the help of three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulation. In this device, coherent and high-power Smith–Purcell radiation (SPR) at the terahertz frequency range can be produced for the reasonable parameters of charge energy and grating. Our results indicate that coherent SPR at 506.529 GHz with a power around 1000 W can be obtained for a grating of period l = 0.3 mm operating at the beam energy E = 50 keV and beamcurrent I = 10 A.
Spectroscopy Spectroscopy terahertz terahertz Spectroscopy Spectroscopy modulation modulation Laser theory. Laser theory. Photonics Research
2016, 4(5): 05000162





