Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, School of Electronic Science & Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Department of Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
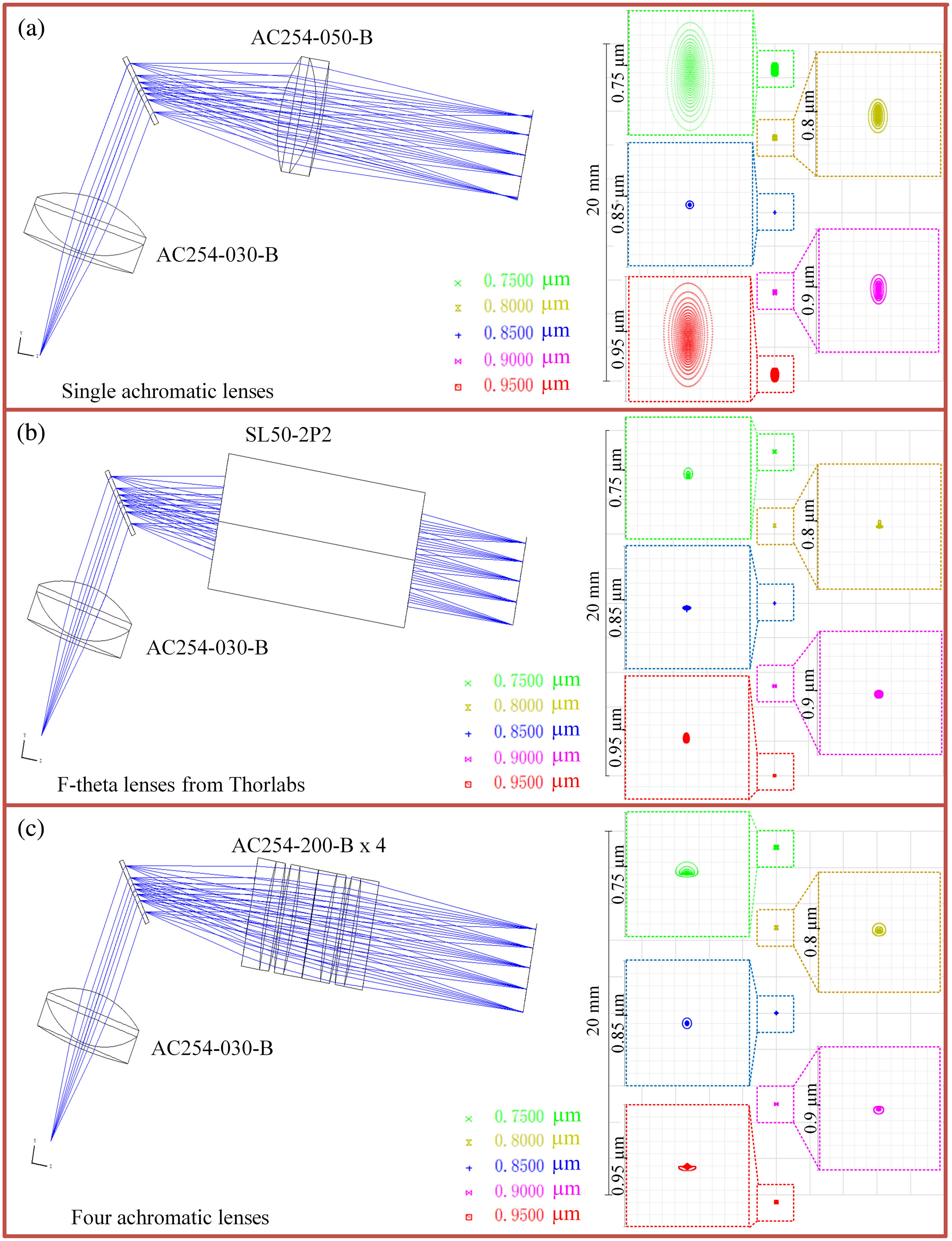
In this Letter, we present a low-cost, high-resolution spectrometer design for ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography (UHR-OCT), in which multiple standard achromatic lenses are combined to replace the expensive F-theta lens to achieve a comparable performance. For UHR-OCT, the spectrometer plays an important role in high-quality 3D image reconstruction. Typically, an F-theta lens is used in spectrometers as the Fourier lens to focus the dispersed light on the sensor array, and this F-theta lens is one of the most expensive components in spectrometers. The advantage of F-theta lens over the most widely used achromatic lens is that the aberrations (mainly spherical aberration, SA) are corrected, so the foci of the dispersed optical beams (at different wavelengths) with different incident angles could be placed on the sensor array simultaneously. For the achromatic lens, the foci of the center part of the spectrum are farther than those on the side in the longitudinal direction, causing degradations of the spectral resolution. Furthermore, in comparison with the achromatic lens with the same focal length, those with smaller diameters have stronger SA, but small lenses are what we need for making spectrometers compact and stable. In this work, we propose a simple method of using multiple long-focal-length achromatic lenses together to replace the F-theta lens, which is -fold cheaper based on the price of optical components from Thorlabs, US. Both simulations and in vivo experiments were implemented to demonstrate the performance of the proposed method.
low-cost spectrometer optical coherence tomography spherical aberration suppression ultrahigh-resolution non-invasive imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 101101
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所科技考古中心, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 河南省文物考古研究院, 河南 郑州 450000
为了验证将光学相干层析(OCT)成像技术应用于古代陶瓷无损检测,将OCT图像表现的釉面的断面特征用于古代陶瓷类别区分的可行性,利用宽波长频域OCT成像系统对选自5个窑口的8个不同釉系、色系的瓷片进行测试,得到了样品的断面结构图像,并分析了OCT图像中的气泡大小和分布、强散射颗粒分布、釉层均匀性、透射率、釉层的分层等特征。实验结果显示8个古代瓷釉样品OCT成像特征差异明显,说明OCT成像技术能基于断层图像特征对瓷釉的釉系、窑口进行区分。
测量 光学相干层析 无损成像 瓷釉
1 北京大学工学院生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
2 上海交通大学生物医学工程系, 上海 200240
光声分子影像是近期发展起来的新型无创在体影像技术。该技术结合了光声层析成像和分子影像,具有成像深度深、分辨率高和特异性强的优点。光声分子影像已经被广泛用于活体动物实验中,在对一些恶性肿瘤和炎症的检测中获得了令人振奋的结果。重点介绍了光声分子影像的机制和研究现状,并对其应用前景进行展望。
生物医学成像 分子影像 光学成像 光声层析成像 无创成像 激光与光电子学进展
2011, 48(5): 051701





