Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Future Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 National Biomedical Imaging Center, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
We present a novel noncontact ultrasound (US) and photoacoustic imaging (PAI) system, overcoming the limitations of traditional coupling media. Using a long coherent length laser, we employ a homodyne free-space Mach–Zehnder setup with zero-crossing triggering, achieving a noise equivalent pressure of 703 Pa at 5 MHz and a -6 dB bandwidth of 1 to 8.54 MHz. We address the phase uncertainty inherent in the homodyne method. Scanning the noncontact US probe enables photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT). Phantom studies demonstrate imaging performance and system stability, underscoring the potential of our system for noncontact US sensing and PAI.
noncontact ultrasound sensing photoacoustic imaging Mach–Zehnder interferometer Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031702
中国民航大学交通科学与工程学院, 天津 300300
工程水泥基复合材料(ECC)具有较好的延性和抗拉性能, 但成型收缩率较大, 容易导致试件成型开裂, 严重影响结构的耐久性。在ECC中掺入高性能硫铝酸钙(HCSA)膨胀剂以减小ECC成型收缩率, 研究了不同掺量的膨胀剂对ECC收缩率和力学性能的影响。结果表明: 膨胀剂掺量为6%~8%(质量分数, 下同)时可明显改善ECC的收缩率, 膨胀剂掺量过高会使ECC出现膨胀现象; 膨胀剂掺量为4%~6%时可明显提高ECC的抗压强度, 但对抗拉强度影响较小; 膨胀剂掺量为2%~4%时可明显提高ECC的剪切韧性, 但对抗剪强度影响较小; 膨胀剂掺量为6%~8%时可明显提高ECC的极限弯曲强度。
工程水泥基复合材料 膨胀剂 收缩率 力学性能 峰值应变 韧性 engineering cementitious composite expansion agent shrinkage rate mechanical property peak strain toughness
北京大学未来技术学院生物医学工程系,北京 100871
在生物医学成像方法中,光声成像(PAI)由于激发和探测的物理信号不同,是一个非常独特的存在。这种“混合”成像模式打破了一直困扰组织光学高分辨成像的深度壁垒,为探索生命奥秘和疾病的诊治提供了有巨大潜力的平台技术。但PAI迄今并没有被普遍使用,一方面受限于其自身机制,另一方面在实际应用中也存在一些挑战。基于作者在PAI领域长时间的科研体验和思考,对该技术做了一些探讨,与一般的研究综述不同,并没有详细介绍一些较为重要的相关技术和应用成果,而是重点关注PAI的历史发展、内涵及其主要面临的挑战,以促进对该技术的理解从而加快其推广。
激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(6): 0617005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 College of Future Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Ultrasonography, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) with a handheld linear ultrasound (US) probe is widely used owing to its convenient and inherent dual modality capability. However, the limited length of the linear probe makes PAI suffer from the limited view. In this study, we present a simple method to substantially increase the view angle aided by two US reflectors. Both phantom and animal study results have demonstrated that the imaging quality can be greatly improved with the reflector without sacrificing the imaging speed.
photoacoustic imaging limited view multimodal imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(12): 121702
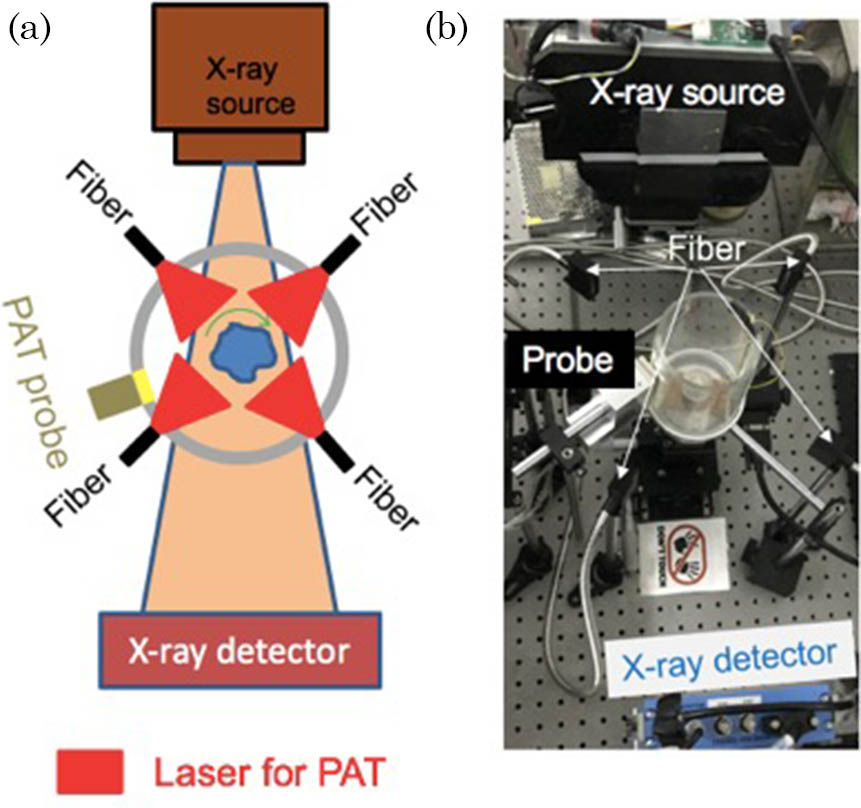
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Photoacoustic (PA) tomography (PAT) breaks the barrier for high-resolution optical imaging in a strong light-scattering medium, having a great potential for both clinical implementation and small animal studies. However, many organs and tissues lack enough PA contrast or even hinder the propagation of PA waves. Therefore, it is challenging to interpret pure PAT images, especially three-dimensional (3D) PA images for deep tissues, without enough structural information. To overcome this limitation, in this study, we integrated PAT with X-ray computed tomography (CT) in a standalone system. PAT provides optical contrast and CT gives anatomical information. We performed agar, tissue phantom, and animal studies, and the results demonstrated that PAT/CT imaging systems can provide accurate spatial registration of important complementary contrasts.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(12): 121701
1 陕西理工大学 物理与电信工程学院, 陕西 汉中 723001
2 北京大学 工学院生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
为了更形象直观的反映病变组织的位置、大小和形状, 利用高灵敏、大角度接收的多元线性阵列探测器接收光声信号, 并将多元线性阵列探测器进行平面扫描, 得到光声信号的三维数据, 再采用滤波反投影算法将探测到的三维数据直接在整个3D空间进行反投影重建, 得到了模拟血管、铅笔芯和鸡肝的3D重建图像。由实验结果表明, 通过该方法和系统构建的3D图像分辨率较高, 对比度较好, 其x、y、z方向的分辨率分别为0.67、0.34和1 mm。该装置和成像方法将为以后临床病变组织的3D光声成像检测提供一定的技术支持。
医用光学与生物技术 3D光声成像 多元线性阵列探测器 medical optics and biotechnology 3D photoacoustic imaging multi-linear array detector

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Department of Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
3 Laboratory Animal Center, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
4 School of Public Health, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
Since significant ocular differences in both anatomical structure and optical properties exist between rodents and humans, clinical imaging devices for human use are not suitable for use on rodents. In this study, we develop a contact probe with a flexible surface that can closely fit the rodent cornea for fundus imaging with a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Both Zemax simulation and in vivo fundus imaging demonstrate that this contact probe can significantly improve both the imaging quality and the operational convenience.
170.0170 Medical optics and biotechnology 170.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices 170.5755 Retina scanning 170.2520 Fluorescence microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(3): 031701
1 陕西理工大学 物理与电信工程学院,陕西 汉中 723001
2 北京大学 工学院 生物医学工程系,北京 100871
为了研究不同成像深度对光声层析成像质量的影响,利用多元线性阵列探测器在有限方位进行探测成像。由仿真和实验结果表明,吸收体离探测器越近,其成像效果较好,当多元线性阵列探测器的尺寸与成像深度比小于1时,重建图像畸变明显。在这种情况下,采用旋转扫描探测,其成像效果明显提高。该研究结果对光声层析成像扫描轨迹的设计、成像效果评估具有较好的参考价值。
光声层析成像 成像深度 医用光学与生物技术 photoacousitc tomography imaging depth medical optics and biotechnology
1 陕西理工大学 物理与电信工程学院, 陕西 汉中 723001
2 北京大学 工学院生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
为了实现单元探测器高质量的快速光声图像重建, 提出了不同旋转扫描次数对光声层析成像的影响方案。实验采用的光源为YAG激光器, 波长为1 064 nm, 重复频率为20 Hz, 脉宽为7 ns, 探测器为针状的PVDF膜水听器, 接收直径为1 mm, 得到了26个字母、12根头发丝、树叶骨架和模拟血管的光声重建图像。由仿真和实验结果表明, 在不牺牲光声重建图像质量的前提下, 单元探测器环形扫描一圈, 均匀采集100个位置的信号, 图像重建时间为5.903 s。该研究结果对于单元探测器的快速旋转扫描成像和环形阵列探测器阵元数的设计具有一定的指导意义。
医用光学与生物技术 光声层析成像 不同旋转扫描次数 medical optics and biotechnology photoacoustic tomography different rotating scanning times
1 北京大学工学院生物医学工程系, 北京 100871
2 上海交通大学生物医学工程系, 上海 200240
光声分子影像是近期发展起来的新型无创在体影像技术。该技术结合了光声层析成像和分子影像,具有成像深度深、分辨率高和特异性强的优点。光声分子影像已经被广泛用于活体动物实验中,在对一些恶性肿瘤和炎症的检测中获得了令人振奋的结果。重点介绍了光声分子影像的机制和研究现状,并对其应用前景进行展望。
生物医学成像 分子影像 光学成像 光声层析成像 无创成像 激光与光电子学进展
2011, 48(5): 051701





