Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, P. R. China
2 School of Mechatronic Engineering and Automation, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, P. R. China
3 China-Australia Institute for Advanced Materials and Manufacturing, Jiaxing University, Jiaxing 314001, P. R. China
4 School of Materials Science and Hydrogen Energy, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, P. R. China
5 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, P. R. China
Ferroelectric ceramics have the potential to be widely applied in the modern industry and military power systems due to their ultrafast charging/discharging speed and high energy density. Considering the structural design and electrical properties of ferroelectric capacitor, it is still a challenge to find out the optimal energy storage of ferroelectric ceramics during the phase-transition process of amorphous/nanocrystalline and polycrystalline. In this work, a finite element model suitable for the multiphase ceramic system is constructed based on the phase field breakdown theory. The nonlinear coupling relationship of multiple physical fields between multiphase ceramics was taken into account in this model. The basic structures of multiphase ceramics are generated by using the Voronoi diagram construction method. The specified structure of multiphase ceramics in the phase-transition process of amorphous/nanocrystalline and polycrystalline was further obtained through the grain boundary diffusion equation. The simulation results show that the multiphase ceramics have an optimal energy storage in the process of amorphous polycrystalline transformation, and the energy storage density reaches the maximum when the crystallinity is 13.96% and the volume fraction of grain is 2.08%. It provides a research plan and idea for revealing the correlation between microstructure and breakdown characteristics of multiphase ceramics. This simulation model realizes the nonlinear coupling of the multiphase ceramic mesoscopic structure and the phase field breakdown. It provides a reference scheme for the structural design and performance optimization of ferroelectric ceramics.
Ferroelectric ceramics phase transition phase-field model dielectric breakdown energy storage Journal of Advanced Dielectrics
2024, 14(1): 2245001
1 理论物理研究所 量子光学与光量子器件国家重点实验室,极端光学协同创新中心 山西大学 山西 太原 030006
2 理论物理研究所 量子光学与光量子器件国家重点实验室,山西省沁县中学 山西 沁县 046400
Rabi模型一直是近年来研究的热点, 本文研究该模型在多光子跃迁下的量子相变及多稳态。通过自旋相干态变分法等效的赝自旋哈密顿量被对角化并解得了系统的能量泛函表达式, 同时根据变分结果求得光子数解的情形和临界值, 最后给出基于光子数解和系统稳定性相图。本文主要给出了单光子、两光子和多光子跃迁对Rabi模型量子态、多稳性和量子相变的影响。该结果有助于实验上通过调控腔频来诱导有趣的量子相变。
Rabi模型 多光子跃迁 量子相变 自旋相干态变分法 能量泛函 Rabi model multiple-photon transition quantum phase transition spin-coherent-state variational method the energy functional 量子光学学报
2023, 29(4): 040101
1 苏州大学 工程训练中心,苏州 215006
2 上海海事大学 海洋科学与工程学院,上海 201306
为了探讨1维微尺度热传导模型不同激光能量对石墨转化纳米金刚石相变机理的影响,采用基于密度泛函理论的分子动力学方法模拟优化后的石墨结构,用有限差分法计算了激光辐照石墨表面的温度分布; 基于sp3杂化键可以明显地区分金刚石和石墨结构,根据能量耦合得到不同激光能量条件下辐照石墨的态密度带隙,研究了碳原子键合条件。结果表明,只有当激光能量达到5 J时,才能形成少量sp3杂化碳原子; 随着激光能量的增加,液相下受辐照的石墨表面的温度随之增加,碳原子中的自由电子更容易移动到成键分子轨道,电子的电负性增强,从而增强sp3键的极性,并有助于将sp2键转变为sp3键。该研究结果对在液相激光辐照下提升纳米金刚石制备效率、探究纳米金刚石制备机理有重要的现实意义。
激光技术 相变机制 分子动力学模拟 激光能量 温度分布 sp3杂化 laser technique phase transition mechanism molecular dynamics simulation laser energy temperature distribution sp3 hybridization
传统三氟乙酸金属有机化学溶液沉积法(TFA-MOD)制备YBa2Cu3O7-δ (YBCO)超导层, Ba倾向于与F结合, 从而避免BaCO3的形成。本工作开展了新型基于BaCl2/BaF2途径的化学溶液法生长YBCO超导薄膜的研究。重点研究了添加Cl对YBCO薄膜晶粒取向、微观结构和超导性能的影响, 并通过生长反应的热化学计算, 分析了BaCl2途径YBCO薄膜的物相转变机制。结果表明: 添加Cl有利于抑制a轴晶粒取向, 促进c轴晶粒成核。添加Cl的YBCO双层膜起始转变温度(Tc-onset)没有明显变化, 约为89.6 K, 其临界电流密度(Jc)显著提升, Jc达到2.07 MA/cm2 (77 K, 自场)。此外, 生长反应过程的物相转变分析表明Cl优先与Ba结合形成BaCl2, 有效避免BaCO3的形成。本研究结果表明: 添加Cl对制备YBCO超导厚膜有促进作用, 这为MOD法制备YBCO提供了一种新思路。
YBCO薄膜 MOD法 Cl添加 物相转变 YBCO thin film MOD method Cl addition phase transition
1 中国电子科技集团公司第二十七研究所,河南 郑州 450047
2 光电对抗测试评估技术重点实验室,河南 洛阳 471026
3 长春理工大学 物理学院,吉林 长春 130022
从理论仿真计算方面开展了脉冲激光诱导CCD探测器铝层金属温升变化的液-固相变时间特性研究。通过傅里叶热传导方程计算仿真了纳秒激光诱导CCD探测器铝层金属材料的温升曲线,获得了铝层金属材料液-固相变起始时刻和液-固相变时间长度随激光脉冲峰值功率和激光入射角度的变化规律。理论计算结果表明,随着入射激光脉冲峰值功率增加,激光诱导CCD探测器铝层表面的最高温度逐渐升高,铝层材料的液-固相变起始时刻往后延迟,且液-固相变时间长度增加;随激光入射角度的增大,铝层表面的最高温度逐渐降低,液-固相变起始时刻不断前移,而液-固相变时间长度逐渐变短。研究结果表明,激光脉冲峰值功率密度和激光入射角对激光诱导CCD探测器的液-固相变时间特性有重要影响,对揭示纳秒激光诱导CCD探测器的热损伤机制有重要的理论意义。
激光辐照 液-固相变 CCD探测器 激光入射角度 laser irradiation liquid-solid phase transition CCD detector laser incident angle
1 同济大学物理科学与工程学院先进微结构材料教育部重点实验室,上海 200092
2 山西大同大学物理与电子科学学院微结构电磁功能材料山西省重点实验室,山西 大同 037009
近年来受拓扑绝缘体启发而兴起的拓扑光子学有力地促进了电磁波调控和新型波功能器件的研究。光子人工带隙材料因其丰富的物态调控机制和高度定制化的设计自由度成为了研究拓扑光子学和研制鲁棒性光子器件的重要平台。本文主要综述了周期性二聚化以及准周期性Harper光子拓扑链中光子与人工带隙材料的相互作用,揭示了非厄密物理、宇称-时间对称转变和拓扑相变对能带和带隙的作用规律,以及光场本征态的调控和传输机制。围绕实际的共振耦合技术,介绍了非厄密拓扑物理启发下的具有拓扑保护特性的高性能近场无线传能和传感方案,并对非厄密拓扑物理对于无线传能和传感的发展将起到的作用进行了展望。
光学器件 非厄密物理 光拓扑结构 拓扑相变 无线传能 无线传感 光学学报
2023, 43(16): 1623011
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Ioffe Institute, Polytekhnicheskaya 26, 194021, St.-Petersburg, Russia
One of the key points in the physics of the relaxors is their response to the applied DC field. Many studies of this topic were made, in particular on the influence of the field on the dielectric properties. However, practically, in all the cases, the measurements were performed at a fixed frequency and usually with the change in the temperature at the fixed field strength. In this paper, we report the evolution of the dielectric spectra at low frequencies (0.1 Hz 1 kHz) at fixed temperature 246 K on changing the DC electric field applied in (111) from 1 kV to 7 kV. Cole-Cole function was used to describe the spectra and the field dependences of the mean relaxation time , the oscillation strength and the width parameter were determined. The obtained () and () provide evidence of the field-induced transition from the nonpolar glass-like phase to the nonpolar paraelectric phase at around 1.5 kV/cm. In the paraelectric phase, very fast hardening of the spectra was observed with changing from 10 s to about s. The performed analysis demonstrated that the earlier reported positive C-V effect is completely determined by the spectra hardening, while does not show any change in the glass-like phase and monotonously decreases with a field increase in the paraelectric state. For complete understanding of the microscopic origin of the observed phenomena, a detailed study on the short-and long-range structures at the same condition is necessary.
Relaxor ferroelectrics dielectric spectroscopy phase transition lead magnoniobate Journal of Advanced Dielectrics
2023, 13(2): 2250021
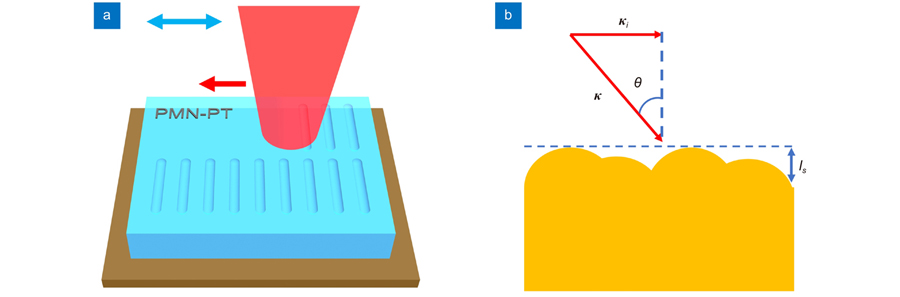
1 南开大学电子信息与光学工程学院微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室,天津 300350
2 山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室,山东 济南 250100
Overview: With the development of modern manufacturing, the size of optical devices is gradually developing towards miniaturization, and integrated optics is also developing to become a topical area of research for many scholars. One of the methods used for producing micro/nano optical devices is femtosecond laser direct writing, a fine three-dimensional processing technique that has been extensively studied by many scholars for its applicability to most materials and can be applied to the fabrication of a wide range of optical devices. Micro/nano-optical devices prepared by femtosecond laser direct writing in crystals have been applied in a broad range of applications in different wavelengths. PMN-PT crystal with relaxed ferroelectric has attracted much attention in recent years for its superior piezoelectric property and large electromechanical coupling coefficient, and its application in the infrared band is more prominent, so the fabrication of the optical devices based on PMN-PT crystal has gradually become a relevant research hotspot. The LIPSS is one of the micro/nano-structures that can be processed by femtosecond laser direct writing. The LIPSS is prevalent in many materials and has been found in metals, semiconductors, dielectrics, etc. Similarly, LIPSS can be induced by femtosecond lasers in PMN-PT crystal. The LIPSS has a wide range of applications in the fields of anti-reflectivity, permanent coloration, and wettability. Nevertheless, the physical processes and the mechanisms involved in the formation of LIPSS have different interpretations in different materials. In this paper, we describe the LIPSS induced by femtosecond laser on the surface of the PMN-PT crystal and characterize it theoretically. We have achieved a change in the period of the LIPSS from 750 nm to 3000 nm after experimenting with different laser parameters. Afterward, we simultaneously obtained the phase transition of the LIPSS in PMN-PT crystal through temperature modulation, and this phase transition can be analyzed by the variation of the Raman spectra. At the same time, we have obtained the Curie temperature for the LIPSS structure that is approximately 10 ℃ lower than that of the PMN-PT crystal and have analyzed the phase transition process through the structural properties of the PMN-PT crystal. The results of our experiments and analyzes on the LIPSS in PMN-PT crystal reported in this paper can provide some experience for the subsequent development of the optical devices related to the LIPSS in PMN-PT crystal.
飞秒激光直写 表面周期结构 PMN-PT晶体 相变 femtosecond laser direct writing LIPSS PMN-PT crystal phase transition





