Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Micro-/Nano- Optoelectronic Devices of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Electronics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
2 SK Hynix Memory Solutions, 3103 North First Street, San Jose, CA 95134, USA
In this Letter, the effects of material/structure parameters of photonic crystal (PhC) parallel waveguides on the coupling length are investigated. The results show that, increasing the effective relative permittivity of the PhC leads to a downward shift of the photonic bandgap and a variation of the coupling length. A compact PhC 1.31/1.55 μm wavelength division multiplexer (WDM)/demultiplexer with simple structure is proposed, where the output power ratios are more than 24 dB. This WDM can multiplex/demultiplex other light waves efficiently.
130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 060.4510 Optical communications 060.4230 Multiplexing Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 011301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, UMR 9001 (CNRS/Université Paris-Sud), Université Paris-Saclay, 91405 Orsay, France
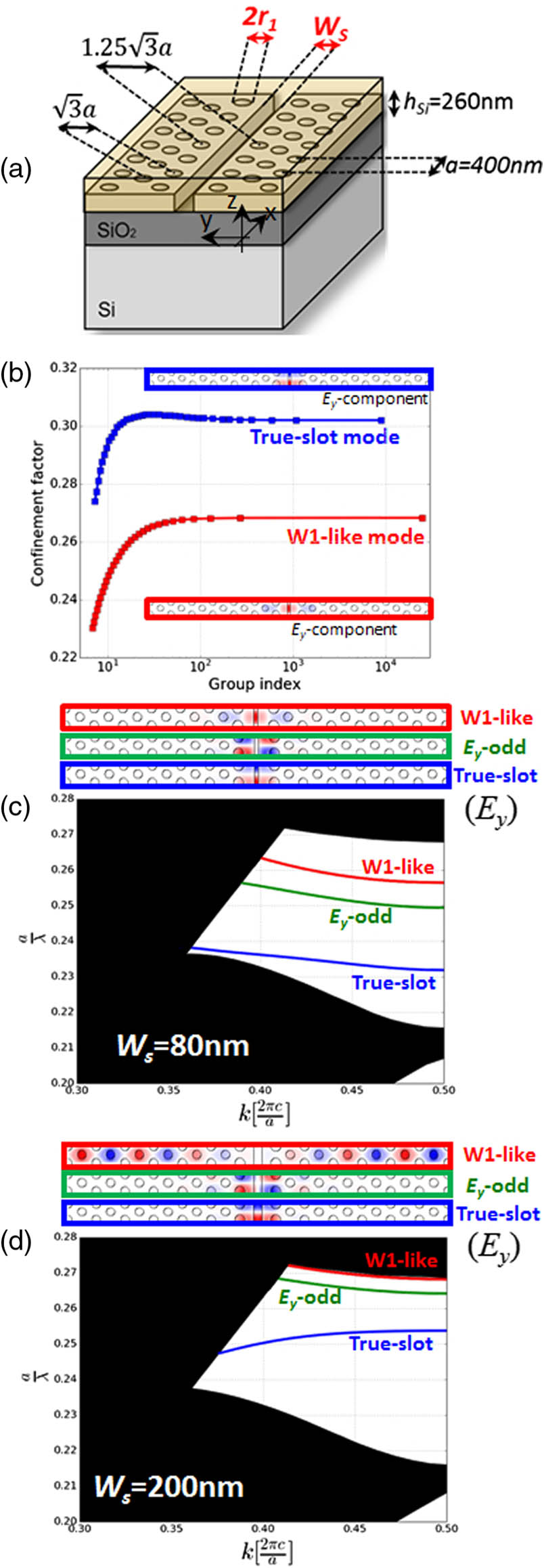
We introduce a family of slot photonic crystal waveguides (SPhCWs) for the hybrid integration of low-index active materials in silicon photonics with energy-confinement factors of ~30% in low-index regions. The proposed approach, which is based on a periodic indentation of the etched slot in the middle of the SPhCW, makes it possible to reconcile a simultaneously narrow and wide slot for exploiting the two modes of even symmetry of a SPhCW. The resulting mode-selection mechanism allows a flexible choice of the modes to be used. Furthermore, the proposed structure offers tremendous flexibility for adjusting the dispersive properties of the slot-confined modes, in particular of their slow-light effects. Flat band slow light in a bandwidth of about 60 nm with a group velocity dispersion factor |β2| below 1 ps2/mm is numerically demonstrated by this approach, corresponding to a normalized delay bandwidth product of around 0.4. These results, obtained from hollow-core periodic waveguides that are directly designed in view of hybrid integration of active materials in mechanically robust structures (not based on free-standing membranes) could pave the way for the realization of on-chip slow-light bio-sensing, active hybrid-silicon optoelectronic devices, or all-optical hybrid-silicon nonlinear functionalities.
Photonic crystal waveguides Photonic crystals Optical devices Photonics Research
2018, 6(1): 01000054

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of ECE, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104 USA
2 IETR, Université Bretagne Loire, University of Nantes, 44322 Nantes, France
3 Thales Research and Technology France, 91767 Palaiseau, France
This Letter introduces the design and simulation of a microstrip-line-based electro-optic (EO) polymer optical phase modulator (PM) that is further enhanced by the addition of photonic crystal (PhC) structures that are in close proximity to the optical core. The slow-wave PhC structure is designed for two different material configurations and placed in the modulator as a superstrate to the optical core; simulation results are depicted for both 1D and 2D PhC structures. The PM characteristics are modeled using a combination of the finite element method and the optical beam propagation method in both the RF and optical domains, respectively. The phase-shift simulation results show a factor of 1.7 increase in an effective EO coefficient (120 pm/V) while maintaining a broadband bandwidth of 40 GHz.
230.0230 Optical devices 250.0250 Optoelectronics 130.0130 Integrated optics 130.0250 Optoelectronics 130.4110 Modulators 130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 130.5460 Polymer waveguides 160.2100 Electro-optical materials 160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 College of Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
A novel H-plane cross-shaped circulator based on magneto-photonic crystals is experimentally investigated. The band gap of the TE mode for the photonic crystals is calculated by the plane wave expansion method. The transmission characteristics of the circulator are simulated by the finite element method. We perform the experiments in the microwave regime to validate the numerical results. At the central frequency of 10.15 GHz, the measured isolation and insertion loss of the circulator reaches 30.2 and 3.93 dB, respectively. The bandwidth of the circulator is about 550 MHz. The optimal experimental value of isolation is higher than the numerical value.
160.5293 Photonic bandgap materials 230.5298 Photonic crystals 130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, UMR 9001 (CNRS/Université Paris-Sud), Université Paris-Saclay, 91405 Orsay, France
2 Laboratoire Charles Fabry, Institut d’Optique, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud,2 Avenue Augustin Fresnel, 91127 Palaiseau Cedex, France
We investigate in this paper the influence of slow light on the balance between the Kerr and two-photon absorption (TPA) processes in silicon slotted hybrid nonlinear waveguides. Three typical silicon photonic waveguide geometries are studied to estimate the influence of the light slow-down factor on the mode field overlap with the silicon region, as well as on the complex effective nonlinear susceptibility. It is found that slotted photonic crystal modes tend to focalize in their hollow core with increasing group index (nG) values. Considering a hybrid integration of nonlinear polymers in such slotted waveguides, a relative decrease of the TPA process by more factor of 2 is predicted from nG � 10 to nG � 50. As a whole, this work shows that the relative influence of TPA decreases for slotted waveguides operating in the slow light regime, making them a suitable platform for third-order nonlinear optics.
Photonic crystals Photonic crystals Photonic crystal waveguides Photonic crystal waveguides Nonlinear optical devices Nonlinear optical devices Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics integrated optics integrated optics Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000257
宁波大学高等技术研究院红外材料与器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
通过改变最内层两排空气孔的半径,研究了Ge20Sb15Se65 硫基光子晶体平板波导的宽带慢光特性。利用三维平面波展开法,通过计算得到波导的能带结构、群折射率和色散,并分析了它们与内层空气孔半径大小的关系。同时优化第一层和第二层空气孔的半径大小,得到了群速度色散为零的对称型硫系光子晶体波导结构,并在20%的变化范围内获得大小分别为125、40和18的群折射率,对应通信波长处的带宽分别为1.7、5.6、9.7 nm,并讨论了折射率对光子晶体波导慢光性能的影响。并为高非线性、低色散的宽带慢光硫基光子晶体平板波导器件的设计及制备提供了理论基础。
集成光学 光子晶体波导 硫系玻璃 慢光 非线性光学 光学设计
1 宁波大学高等技术研究院红外材料与器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
2 浙江省光电探测材料及器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
通过平面波展开法(PWE)计算硫系光子晶体带隙并采用时域有限差分法(FDTD)模拟硫系60°弯曲光子晶体波导的传输特性,在波导弯曲部分线缺陷处添加小空气孔缺陷,提高了其带宽和透光性。在60°弯曲区域线缺陷外边缘处引入2个对称空气孔,通过改变其半径来改善波导传输效率。模拟结果表明,当引入半径为0.54R 的空气孔时,传输带宽由初始的60 nm 提高到161 nm,但此时透射率波动性较大。在此基础上在弯曲线缺陷中心处又引入若干个空气孔,当引入3个半径为0.48R 的空气孔时,此种结构不但提高了波导的传输效率,并且使传输带宽增加到340 nm。将单个60°弯曲波导优化结构应用于连续60°弯曲波导中,研究结果表明连续弯曲波导的传输效率得到显著提高。
集成光学 硫系玻璃 光子晶体波导 传输效率 带宽 中国激光
2015, 42(12): 1205001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
THz Technical Research Center, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Photonic Information Technology, College of Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
We propose a Y-type polarization beam splitter based on internal polarization-selective defects within crystal waveguides in a two-dimensional square-lattice photonic crystal with solid rods. When the nonpolarized light launches from the input port, different polarizations will be separated and can only transmit through their own channel. It is demonstrated by finite element method that the proposed structure can achieve good performance for both the transverse electric and transverse magnetic polarizations in a wide range of wavelength, with the polarization extinction ratio more than 25 dB, the degree of polarization nearly 1, and the insert loss less than 0.5 dB, respectively.
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 230.5440 Polarization-selective devices 230.1360 Beam splitters Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(s1): S11301
宁波大学高等技术研究院红外材料与器件实验室, 浙江 宁波 315211
利用平面波展开法计算GeSbSe 基质光子晶体带隙,研究光子晶体波导中带隙与空气孔(或介质柱)半径的变化关系,并结合光子晶体波导的工作波长,设计出周期为500 nm,半径为150 nm 的三角晶格空气孔型GeSbSe 光子晶体波导。采用时域有限差分法模拟所设计的直线型光子晶体波导和60°弯曲光子晶体波导的传输特性,模拟结果显示在传统结构光子晶体波导中,直线型光子晶体波导具有很高的光学传输效率,但在60°弯曲型波导中的传输效率较低,分析原因为光子晶体波导直线区域与弯曲区域光的传播模式不同。因此对60°弯曲型GeSbSe光子晶体波导进行了结构优化,优化后的光子晶体波导可以在较宽的波长范围内具有很高的传输效率。
光学设计 光子晶体波导 硫系玻璃 光子禁带 平面波展开法
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Combination of full-vector finite element method with anisotropic perfectly matched layers results in a novel structure of low-dispersion photonic crystal fiber with high birefringence. The negative dispersion can be obtained at a wavelength of 1.55 μm by adjusting the lattice constant Λ and the round air hole diameter d. Numerical results show that the dispersion variation is negative in the C band, the dispersion slope values are between 0.112 and 0.142 ps·km-1·nm-2 over the C band, and the birefringence is 5.7×10-3.
130.5296 Photonic crystal waveguides 060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S11302





