Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 iXblue Photonics, Rue Paul Sabatier, 22300 Lannion, France
2 iXblue, 34 Rue de la Croix de Fer, 78100 Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
3 Laboratoire Hubert Curien, UJM-CNRS-IOGS, 18 Rue Professeur Benoît Lauras, 42000 Saint-Etienne, France
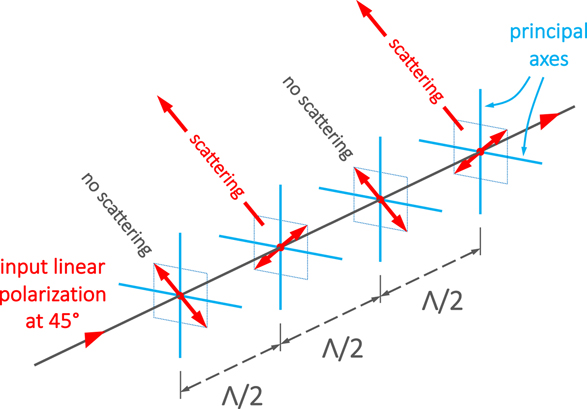
A recent JEOS-RP publication proposed Comments about Dispersion of Light Waves, and we present here complementary comments for birefringence dispersion in polarization-maintaining (PM) fibers, and for its measurement techniques based on channeled spectrum analysis. We start by a study of early seminal papers, and we propose additional explanations to get a simpler understanding of the subject. A geometrical construction is described to relate phase birefringence to group birefringence, and it is applied to the measurement of several kinds of PM fibers using stress-induced photo-elasticity, or shape birefringence. These measurements confirm clearly that the difference between group birefringence and phase birefringence is limited to 15–20% in stress-induced PM fibers (bow-tie, panda, or tiger-eye), but that it can get up to a 3-fold factor with an elliptical-core (E-core) fiber. There are also surprising results with solid-core micro-structured PM fibers, that are based on shape birefringence, as E-core fibers.
Birefringence Birefringence dispersion Channeled-spectrum analysis Group birefringence Phase birefringence Polarization-maintaining fiber Polarization-mode dispersion Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2022014

Author Affiliations
Abstract
iXblue, 34 rue de la Croix de Fer, 78100 Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
Dispersion of light waves is well known, but the subject deserves some comments. Certain classical equations do not fully respect causality; as an example, group velocity vg is usually given as the first derivative of the angular frequency ω with respect to the angular spatial frequency km (or wavenumber) in the medium, whereas it is km that depends on ω. This paper also emphasizes the use of phase index n and group index ng, as inverse of their respective velocities, normalized to 1/c, the inverse of free-space light velocity. This clarifies the understanding of dispersion equations: group dispersion parameter D is related to the first derivative of ng with respect to wavelength λ, whilst group velocity dispersion GVD is also related to the first derivative of ng, but now with respect to angular frequency ω. One notices that the term second order dispersion does not have the same meaning with λ, or with ω. In addition, two original and amusing geometrical constructions are proposed; they simply derive group index ng from phase index n with a tangent, which helps to visualize their relationship. This applies to bulk materials, as well as to optical fibers and waveguides, and this can be extended to birefringence and polarization mode dispersion in polarization-maintaining fibers or birefringent waveguides.Dispersion of light waves is well known, but the subject deserves some comments. Certain classical equations do not fully respect causality; as an example, group velocity vg is usually given as the first derivative of the angular frequency ω with respect to the angular spatial frequency km (or wavenumber) in the medium, whereas it is km that depends on ω. This paper also emphasizes the use of phase index n and group index ng, as inverse of their respective velocities, normalized to 1/c, the inverse of free-space light velocity. This clarifies the understanding of dispersion equations: group dispersion parameter D is related to the first derivative of ng with respect to wavelength λ, whilst group velocity dispersion GVD is also related to the first derivative of ng, but now with respect to angular frequency ω. One notices that the term second order dispersion does not have the same meaning with λ, or with ω. In addition, two original and amusing geometrical constructions are proposed; they simply derive group index ng from phase index n with a tangent, which helps to visualize their relationship. This applies to bulk materials, as well as to optical fibers and waveguides, and this can be extended to birefringence and polarization mode dispersion in polarization-maintaining fibers or birefringent waveguides.
Birefringence Chromatic dispersion Dispersion Effective index First-order dispersion Group birefringence Group index Group velocity dispersion Index of refraction Polarization mode dispersion Refractive index Second-order dispersion Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2022, 18(1): 2022001
1 中国电子科技集团公司 第三十四研究所, 广西 桂林 541004
2 火箭军装备部驻北京地区第八军事代表室, 北京 100085
光纤是远距离传输时钟信号的重要途径之一, 光纤振动会对光纤的偏振模色散产生变化, 从而影响时钟信号的传输性能。为了降低光纤振动对时钟传输的影响, 详细分析了光纤振动对时钟信号传输劣化的原因, 提出了一种新的抗光纤振动传输技术方案, 并通过实验方法验证了该技术方案可以改善相位噪声10~15 dB。
高精度时钟 光传输 相位噪声 抗光纤振动 偏振模色散 high pricision clock optical transmission phase noise anti fiber vibration polarization mode dispersion

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Luminescence and Optical Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
We propose and demonstrate a novel scheme of semi-open-loop polarization control (SOL-PC), which controls the state of polarization (SOP) with high accuracy and uniform high speed. For any desired SOP, we first adjust the initial SOP using open-loop control (OLC) based on the matrix model of a three-unit piezoelectric polarization controller, and quickly move it close to the objective one. Then closed-loop control (CLC) is performed to reduce the error and reach precisely the desired SOP. The response time is three orders faster than that of the present closed-loop polarization control, while the average deviation is on par with it. Finally, the SOL-PC system is successfully applied to realize the suppression of the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) effect and reduce the first-order PMD to near zero. Due to its perfect performance, the SOL-PC energizes the present polarization control to pursue an ideal product that can meet the future requirements in ultrafast optical transmission and quantum communication.
polarization control polarization mode dispersion fiber optics components coherent communications Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 050601
科锐安通讯技术(上海)有限公司, 上海 201203
线路侧光模块CFP2-DCO在4G/5G网络建设中具有重要而广泛的应用, 而光信噪比(OSNR)指标是评估其性能的重要参数。光纤通信系统中的偏振模色散(PMD)及色度色散(CD)的干扰, 对OSNR性能有重要的影响, PMD及CD的干扰对系统OSNR造成的劣化即为PMD、CD的OSNR代价。探讨了OSNR的不同测试方法, 并针对通信设备制造商在实验室对OSNR进行测试的需求, 搭建了一种OSNR及PMD、CD干扰代价的自动化测试平台。利用该平台对CFP2-DCO的OSNR及PMD、CD的OSNR代价进行了测试, 并进一步测试得到叠加PMD、CD干扰后的OSNR代价及PMD、CD与OSNR的关系曲线。测试结果表明: PMD、CD的干扰越大, 通信系统对OSNR的要求越高, 因此应尽量降低系统的PMD、CD干扰, 从而可以优化系统性能, 提高通信质量。
数字相干光模块 密集波分复用 可重构光分插复用器 光信噪比 光传送网 偏振模式色散 色度色散 digtal coherent opic module dense wavelength division multiplexing reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer optical signal-to-noise ratio optical transmission network polarization mode dispersion chromatic dispersion
1 北京邮电大学信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
2 北京邮电大学理学院, 北京 100876
针对固定分析仪法在测量光纤偏振模色散时会引入误差、降低测量精度这一问题,提出了一种基于小波阈值的去噪方案,以提升固定分析仪法的测量精度。给出了算法的具体流程,并详细讨论了小波阈值、阈值函数、基函数以及分解层数的选取原则及方案。搭建了实验平台并进行测定,将测定结果与常用的傅里叶变换法及商用的偏振模色散测量仪的测量结果进行对比。实验结果表明,所提出的小波阈值去噪方案能够有效地降低噪声对测量结果的影响,且对于不同类型、不同长度的测试光纤样本均适用。以商用仪器的测量结果为参考,本方案测量结果的最大误差为2.27%,该数据表明本方案显著提升了固定分析仪法测量偏振模色散的精度。
光纤光学 信号处理 偏振模色散 小波阈值去噪 固定分析仪法 噪声 中国激光
2018, 45(11): 1106006
1 黄河交通学院 机电工程学院, 焦作 454950
2 郑州轻工业学院 计算机与通信工程学院, 郑州 450002
为了降低光传送网传输过程中产生的偏振模色散对传输信号质量的影响, 采用将光环形器置于光传送网光放大器前端的方法, 对光传送网通信传输中的偏振模色散效果进行了仿真。经过偏振模色散抑制后, 传输眼图具有更加明显的张开状态, 系统的传输性能有一定的提高, 在一定程度上抑制了光传送网中存在的偏振模色散, 有效改善了信号的质量。结果表明, 从添加光环形器前后补偿偏振模色散的误比特率计算结果发现, 误比特率的效率提高了约1倍, 光环形器对光传送网通信的偏振模色散现象具有显著的抑制效果。该方案对不同传输速度的偏振态光信号延迟进行等效补偿, 最终实现补偿偏振模色散的效果。
光通信 偏振模色散 光环形器 误比特率 optical communication polarization mode dispersion optical circulator bit error rate
1 聊城大学物理科学与信息工程学院, 山东 聊城 252059
2 山东省光通信科学与技术重点实验室, 山东 聊城 252059
基于环状光纤的OAM-PMD动态方程和固定双折射级联模型,推导了OAM模式的一阶OAM-PMD系数方程,并仿真了环状光纤具有一定椭圆度时,几何双折射对OAM模式对应的本征奇-偶模的有效折射率差的影响,以及一阶OAM-PMD系数随角频率的变化。结果表明,OAM模式的一阶OAM-PMD系数不仅与OAM模式对应的奇-偶模的有效折射率差有关,还会随角频率变化而变化,并且环状光纤椭圆度的增大会导致OAM模式的一阶OAM-PMD系数增大,且对相对低阶的OAM模式的一阶OAM-PMD系数影响更明显,从而严重影响OAM模式复用系统的性能和传输距离。
光通信 椭圆双折射 轨道角动量 偏振模色散 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(7): 070601
华中科技大学 光学与电子信息学院, 武汉 430074
为了实现对脉冲位置调制传输系统光纤信道中偏振模色散的动态监测, 提出了一种新型偏振膜色散监测方案, 并基于监测原理构建了数学模型。该方案基于单边带内不同偏振信号相位差实现, 具有结构简单、易于实现、成本低等优点。结果表明, 本方案可以实现对光信号的差分群延时与偏振态的动态监测, 即当差分群延时在0ps~100ps范围内时, 可准确监测; 同时证实了其与信号速率关系较小, 能够适应不同速率的系统, 且可对脉冲位置调制传输系统的偏振模色散进行实时动态监测。该方案是一个高效可行的偏振模色散监测方案。
光通信 偏振膜色散监测 光纤信道 单边带 相位差 optical communication polarization mode dispersion monitoring fiber communication channel single sideband phase difference





