长光卫星技术股份有限公司,吉林 长春 130033
为解决传统柔性支撑中小口径空间反射镜组件热稳定性与结构刚度间的矛盾,提出了一种新型刚性支撑结构,并为某高分辨率空间相机研制了通光口径?214 mm的高精度次镜组件。采用“镜体-锥套-支撑筒-刚性基板”组合,通过延长、优化热应力在组件内部的传递路径实现了消热目的。刚性支撑次镜组件重2.6 kg、4 ℃均匀温升工况下面形变化均方根(RMS)仿真值为2.573 nm,装调重力工况下镜体倾角和位移分别为2.028″、0.566 μm,与传统柔性支撑方案相比具有突出的优势。实测次镜的面形精度RMS为0.0181λ(λ=632.8 nm),在16 ℃及24 ℃时次镜面形变化量不超过0.0025λ;组件基频达到502.1 Hz,在快速高低温循环及大量级振动后次镜面形基本维持不变;装配容差测试中,次镜在0.02 mm不平度的作用下仅发生微弱变形。刚性支撑结构可以显著提升中小口径反射镜工作性能,在遥感器光机结构研制领域内具有广阔的应用前景。
空间光学 反射镜 刚性支撑 消热 面形精度稳定性 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(5): 0522005
红外与激光工程
2023, 52(10): 20230065
红外与激光工程
2023, 52(4): 20220635
1 长光卫星技术股份有限公司,吉林 长春 130033
2 东北大学机械工程与自动化学院,辽宁 沈阳 110819
Overview: How to further improve the lightweight ratio of high-performance meter-level space mirrors is one of the core issues in the field of large aperture optomechanical structure design. In this paper, a primary mirror blank with a clear aperture of Φ1200 mm was developed for a high-resolution space camera, which achieves the goal of designing area density below 40 kg/m2. The SiC mirror blank was manufactured by gel injection molding and reaction sintering process, with the classical back three-point support scheme together with the testing state of the optical axis being horizontally adopted to simplify the supporting structure. Novel lightweight measures such as an alternate arrangement of main and auxiliary stiffeners and the addition of lightweight holes to vertical walls were used inside the semi-closed blank, which further improves the lightweight ratio of space mirrors with the sandwich structure. Distributed datums were proposed to replace the traditional datum setting, which reduces the machining area of datums by more than 80% and improves machining efficiency significantly. A robot arm is used for polishing in optical processing, and the local surface deformation is 47 nm in PV value under the typical polishing pressure of 1.77 kPa, with the mirror surface of 4 mm thick and the spacing between stiffener ribs of 81 mm. A parametric model of the mirror blank was built with shell elements, which contains ten variables including stiffener thickness and blank height, and integrated optimization was carried out so as to determine the optimal combination of structural parameters, using the multi-island genetic algorithm. The final design weight of the mirror blank is 46.9 kg, with corresponding area density of 38.8 kg/m2. The RMS value of self-weight deformation of the mirror blank is only 2.87 nm with its optical axis being horizontal, and the free fundamental frequency is 602 Hz, indicating that the mirror blank has good dynamic and static characteristics, which satisfies the design requirements of space cameras. After machining, the measured weight of the mirror blank is 51.3 kg, about 9.4% overweight than the design, and the facesheet is about 1 mm thicker, mainly caused by the inhomogeneity of the molding process. During the centroid position test of the primary mirror blank, the deviation between the measured and theoretical centroid position is about 3.7 mm in the axial direction and 2.0 mm in the radial direction, which can be compensated through adjustment of the supporting structure and has limited influence on the optical performance of mirror assembly. At present, the primary mirror blank has already been polished to RMS λ/8 (λ=632.8 nm) of surface shape accuracy, with no obvious print-through effect observed. The lightweight structure scheme and optimization method of the mirror blank proposed in this paper can provide an important reference for the design of similar space mirrors with the characteristics of large aperture and low areal density.
空间光学 反射镜 轻量化 大口径 反应烧结碳化硅 space optics mirror lightweight large aperture reaction bonded silicon carbide
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
This paper utilizes uniquely decodable codes (UDCs) in an M-to-1 free-space optical (FSO) system. Benefiting from UDCs’ nonorthogonal nature, the sum throughput is improved. We first prove that the uniquely decodable property still holds, even in optical fading channels. It is further discovered that the receiver can extract each source’s data from superimposed symbols with only one processing unit. According to theoretical analysis and simulation results, the throughput gain is up to the normalized UDC’s sum rate in high signal-to-noise ratio cases. An equivalent desktop experiment is also implemented to show the feasibility of the UDC-FSO structure.
free-space optics throughput enhancement uniquely decodable code Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(3): 030603
长光卫星技术股份有限公司,吉林 长春 130033
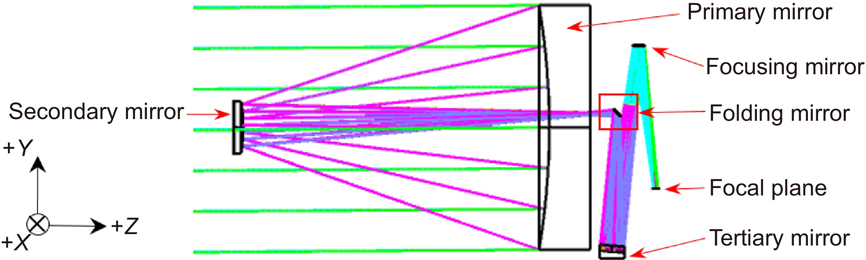
大口径长条形反射镜是大型离轴三反相机的核心部件之一,针对“吉林一号”宽幅01C星中通光口径为1250 mm×460 mm的主反射镜,系统论述了1.2 m量级大长宽比反射镜组件的结构设计方法,并对所研制的主镜开展了详细的验证。从材料属性和现有工艺出发,镜体材料选择反应烧结碳化硅,采用半封闭式轻量化形式,通过二目标全局优化确定了镜体结构参数的最佳组合,最终镜体设计质量为41.8 kg,面板厚5 mm、最薄加强筋仅厚3 mm。采用经典背部三点支撑方案,优化柔性支撑中的双轴柔性铰链结构参数以兼顾组件基频和热稳定性,并与镜体质心位置进行匹配。提出了主镜组件的装配流程和相应的消应力措施。测试结果表明:主镜在装调重力工况下全口径面形精度均方根值为0.016λ(λ=632.8 nm),翻转180°后主镜全口径面形精度均方根值为0.019λ;实测主镜组件一阶基频为127.8 Hz,经大量级随机振动和高低温循环后,主镜面形精度均方根值基本不变。主镜组件具有良好的动、静力学特性,且面形精度高、稳定性良好,能够满足高性能空间光学系统的使用要求。
空间光学 大口径反射镜 碳化硅 离轴三反 “吉林一号”卫星 space optics large aperture mirror silicon carbide off-axis TMA "Jilin-1" satellite 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(1): 20220363
1 国防科技大学自动目标识别重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410000
2 北京跟踪与通信技术研究所,北京 100000
为了提高海量空间碎片天基光学成像仿真的计算速度,提出了一种海量空间碎片天基光学观测图像快速仿真方法。首先,阐述了天基光学观测图像的成像原理,设计了成像仿真流程,给出了各流程的计算方法,分析出了多约束条件下关于空间碎片可见性的计算是限制成像仿真速度的主要原因。接着,以提升计算速度为出发点,建立了各约束条件对空间碎片可见性求解速度影响的评价指标。最后,根据建立的评价指标与实际观测任务的特点,提出了多约束条件下海量空间碎片的可见性快速求解策略。仿真实验结果表明,所提方法在保证仿真图像逼真度的同时,成像仿真速度明显优于传统成像仿真算法,对天基可见光观测平台的研制与效能评估具有重要意义。
空间光学 成像方法 仿真流程 空间碎片 可见性 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(16): 1611006





