
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Xiamen University, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Fujian Key Laboratory of Ultrafast Laser Technology and Applications, Xiamen, China
2 Shenzhen Research Institution of Xiamen University, Shenzhen, China
Although visible femtosecond lasers based on nonlinear frequency conversion of Ti:sapphire femtosecond oscillators or near-infrared ultrafast lasers have been well developed, limitations in terms of footprint, cost, and efficiency have called for alternative laser solutions. The fiber femtosecond mode-locked oscillator as an ideal solution has achieved great success in the 0.9 to 3.5 μm infrared wavelengths, but remains an outstanding challenge in the visible spectrum (390 to 780 nm). Here, we tackle this challenge by introducing a visible-wavelength mode-locked femtosecond fiber oscillator along with an amplifier. This fiber femtosecond oscillator emits red light at 635 nm, employs a figure-nine cavity configuration, applies a double-clad Pr3 + -doped fluoride fiber as the visible gain medium, incorporates a visible-wavelength phase-biased nonlinear amplifying loop mirror (PB-NALM) for mode locking, and utilizes a pair of customized high-efficiency and high-groove-density diffraction gratings for dispersion management. Visible self-starting mode locking established by the PB-NALM directly yields red laser pulses with a minimum pulse duration of 196 fs and a repetition rate of 53.957 MHz from the oscillator. Precise control of the grating pair spacing can switch the pulse state from a dissipative soliton or a stretched-pulse soliton to a conventional soliton. In addition, a chirped-pulse amplification system built alongside the oscillator immensely boosts the laser performance, resulting in an average output power over 1 W, a pulse energy of 19.55 nJ, and a dechirped pulse duration of 230 fs. Our result represents a concrete step toward high-power femtosecond fiber lasers covering the visible spectral region and could have important applications in industrial processing, biomedicine, and scientific research.
fiber lasers visible lasers mode locking femtosecond laser Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(2): 026004
1 福建省超快激光技术及应用重点实验室(厦门大学),福建 厦门 361005
2 厦门大学深圳研究院,广东 深圳 518129
位于人眼可见波段(380~780 nm)的激光,在显示、生物医疗、精密加工、精密光谱、光通信等领域有着重要的应用价值。在众多可见光激光的产生方法中,可见光掺稀土光纤激光器因具有高效率、高光束质量、结构简单且免维护等优势,近年来受到国内外的广泛关注。对可见光掺稀土光纤激光器的研究进展进行了详细综述,介绍了可见光连续波光纤激光器、可见光调Q脉冲光纤激光器及可见光锁模脉冲光纤激光器的产生方式和特点。最新研究进展表明,其可覆盖蓝(~480 nm)、青(~491 nm)、绿(~520 nm)、黄(~573 nm)、橙(~605 nm)、红(~635 nm)及深红(~717 nm)等丰富的可见光波长,全光纤可见光输出功率已迈向10 W,而且可见光锁模超短脉冲宽度已窄至<200 fs。结合应用需求,简要展望了可见光波段光纤激光器的发展趋势。
激光器 可见光激光 掺稀土光纤激光器 连续波 调Q 锁模
1 西安电子科技大学 光电工程学院, 西安
2 西安电子科技大学 前沿交叉研究院, 西安
3 中国科学院物理研究所北京凝聚态物理国家实验室, 北京
可见光波段激光在科研、工业、医疗以及通信领域应用广泛, 可通过半导体激光器、稀土离子掺杂激光器和非线性频率变换技术产生, 其中可见光稀土离子掺杂激光器近年来受到广泛关注。首先介绍了可见光波段激光的几种典型应用, 然后分析了目前可以产生可见光激光的稀土离子(镨、钕、钐、铕、铽、镝、钬、铒、铥)的发射吸收光谱和激光特性, 最后综述了其中较有潜力的镨离子和铽离子在可见光固体激光器方面的最新研究进展。
可见光激光 稀土离子 固体激光器 镨离子 铽离子 visible lasers rare earth ions solid-state lasers praseodymium ion terbium ion
1 哈尔滨工业大学仪器科学与工程学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150006
2 哈尔滨工业大学(威海)光电科学系,山东 威海 264209
超材料吸波体凭借其可以在特定波长处实现接近100%的“完美”吸收而被广泛应用在各个领域中。具有可饱和吸收特性的超材料可以用来调控激光脉冲,但超材料光学性质的研究主要集中于红外或太赫兹波段,可见光波段研究较少。基于传统的超材料吸波体三层结构模型,借助二氧化钒的电磁参数随温度变化的相变特性,设计了一种实用的可见光波段超材料饱和吸收体。该超材料的吸收率会随着入射电磁波引起的温度升高而饱和,最终其会转变为高反射状态,具有类似半导体饱和吸收镜的特性。对该结构进行数值模拟,发现其在405~650 nm波长范围内,平均饱和深度为16%。
材料 超材料 可饱和吸收 二氧化钒 可见光激光器 激光锁模 光学学报
2022, 42(15): 1516001
1 山东大学信息科学与工程学院山东省激光技术与应用重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266237
2 青岛海泰光电技术有限公司, 山东 青岛 266000
翠绿宝石是性能优良的宽带可调谐激光晶体,具有荧光寿命长、饱和能量密度高、吸收带宽较宽以及热力学性能优良等诸多优点。翠绿宝石晶体独特的吸收带表明除了使用闪光灯泵浦,还可以使用蓝光激光二极管(LD)、绿光激光器、黄光激光器、红光LD等多种可见光光源作为泵浦源。其中,基于日渐成熟的高功率红光LD泵浦源的翠绿宝石激光器具有效率高、体积小等优势,逐渐成为固体激光领域的研究热点。利用两台光纤耦合输出的638 nm高功率LD作为泵浦源,使用双端偏振泵浦结构对翠绿宝石晶体进行抽运,实现了中心波长为760 nm、功率达10.5 W的可见光波段激光输出,光-光转换效率为20%。这是目前国内利用红光LD泵浦翠绿宝石晶体实现的最高输出功率。
激光器 二极管泵浦 可见光激光器 翠绿宝石晶体 中国激光
2020, 47(10): 1015001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronics Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Engineering Technology Research Center for 2D Material Information Function Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou 325035, China
A power-scaled laser operation of Pr:YLiF4 (YLF) crystal at 720.9 nm pumped by a 443.6 nm laser diode (LD) module was demonstrated. The 20 W module was used to pump the Pr:YLF crystal, and a maximum output power of 3.03 W with slope efficiency of 30.04% was obtained. In addition, a 5 W blue LD was also used to pump the Pr:YLF laser, and a maximum output power of 0.72 W was obtained at room temperature. The output power was limited by the wavelength mismatch between the single-emitter LD and the absorption peak of the crystal.
rare earth and transition metal solid-state lasers visible lasers diode-pumped lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(1): 011405
山东大学晶体材料研究所晶体材料国家重点实验室, 山东 济南 250100
超快脉冲激光因具有超短的响应时间及较高的峰值功率而在激光加工及强场物理学等领域有重要应用。随着蓝光激光二极管及掺杂镨离子激光增益介质的发展,可见波段超快脉冲激光迅速发展,主要综述了可见波段超快脉冲激光的研究进展及现状,详细描述了克尔透镜锁模、高重复频率吉赫兹自锁模及基于可饱和吸收体的锁模等技术在可见光波段的应用,并展望了可见波段超快激光的发展方向及前景。
非线性光学 超快光学 可见激光 锁模
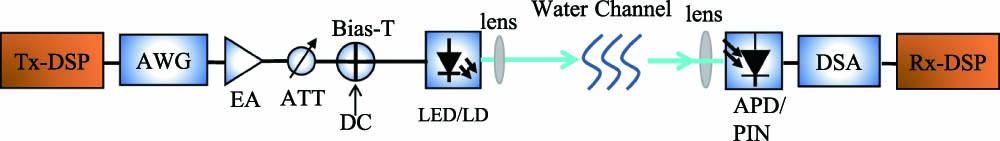
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, National Engineering Research Center for Optical Instruments, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
2 Ningbo Research Institute, Zhejiang University, Ningbo 315100, China
In this paper, recent advances in underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) are reviewed for both LED- and LD-based systems, mainly from a perspective of advanced modulation formats. Volterra series-based nonlinear equalizers, which can effectively counteract the nonlinear impairments induced by the UWOC system components, are discussed and experimentally demonstrated. Both the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed Volterra nonlinear equalizer in UWOC systems under different water turbidities are validated. To further approach the Shannon capacity limit of the UWOC system, the probabilistic constellation shaping technique is introduced, which can overcome the inherent gap between a conventional regular quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) format and the Shannon capacity of the channel. The experimental results have shown a significant system capacity improvement compared to the cases using a regular QAM.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 060.4080 Modulation 140.7300 Visible lasers 010.4450 Oceanic optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100012
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, TeCIP Institute, 56124 Pisa, Italy
The growing number of underwater activities is giving momentum to the development of new technologies, such as buoys, remotely operated vehicles, and autonomous underwater vehicles. The data collected by these vehicles need to be transmitted to a high-speed central unit. Clearly, wired solutions are not suitable, since they strongly impact the mobility. In this scenario, a promising solution is offered by underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC) technology, which can achieve both high-speed and wireless operation. Here, we provide a comprehensive survey on the challenges, the experimental realizations, and the state of the art in UOWC researches.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 140.7300 Visible lasers 010.7340 Water Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100009





