2021, 19(5) Column
Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Optical Materials Biophotonics Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第19卷 第5期
The bidirectional error diffusion (BERD) algorithm is free from random phase modulation that introduces speckle noise on the reconstructed images, compared with other computer-generated phase-only hologram (POH) approaches. During the POH generation process, the amplitudes of all pixels are traditionally set to one for diffusing the errors to their neighborhood of unprocessed pixels. In this paper, we reveal that the reconstruction quality depends on the uniform amplitude value for different object pattern. The pattern-adaptive BERD (PA-BERD) algorithm is proposed for high-quality holographic reconstruction. The optimized amplitude value can be acquired for each object pattern and each propagation distance. The PA-BERD-based POHs have shown higher reconstruction quality than traditional BERD-based POHs in simulations as well as optical experiments.
holography computer holography holographic display A multi-focus optical fiber lens is numerically demonstrated based on an all-dielectric metasurface structure. The metasurface consists of an array of rectangular silicon resonators with varying widths in order to obtain the required phase distribution. The core diameter of the multimode fiber is large enough to contain sufficient resonance units. The spatial distribution of the dielectric resonators is dictated by spatial multiplexing, including interleaving meta-atoms and lens aperture division, to achieve multi-focus properties. The proposed optical fiber metalens can produce two or three focal points along the longitudinal direction with high focusing efficiency. The size of every focal point is close to the diffraction limit, and the relative intensity on each focus can be controlled by adjusting the number of the respective resonators. The proposed optical fiber lens will have a great potential in the fields of integrated optics and multifunctional micro/nano devices.
multi-focus lens optical fiber metasurface Improved optical coupling based on a concave cavity lens fabricated by optical fiber facet etching Download:730次
Download:730次
 Download:730次
Download:730次We report a low-fabrication-complexity and wideband fiber lens, which is formed by fiber facet etching and filling high refractive index UV adhesive. The optical field can be significantly shrunk by the facet lens so as to obtain improved optical coupling. Numerical simulations were carried out for different coupling conditions, on both fundamental mode and high-order mode, for a nine-mode fiber. The fundamental mode area can be reduced from 152.17 to
fiber lens optical coupling Secure orthogonal time-frequency multiplexing with two-dimensional encryption for optical-wireless communications Download:602次
Download:602次
 Download:602次
Download:602次This paper firstly, to the best of our knowledge, proposed two-dimensional (2D) encryption based on the Arnold transformation for implementing a secure DC-biased optical orthogonal time-frequency multiplexing (DCO-OTFM) in optical-wireless communications (OWCs). The encrypted data is transformed to the particular 2D matrix and decrypted by the only key to get the correct information. Meanwhile, the number of keys in 2D encryption is enormous, which prevents eavesdroppers from exhaustively searching secret keys rapidly to find the right decryption. Numerical results demonstrate that the secure DCO-OTFM based on 2D encryption can effectively prevent signal decryption from the eavesdropper, which has good secure performance for applying in OWC.
orthogonal time-frequency multiplexing two-dimensional encryption physical layer security optical-wireless communications Machine-vision-based acquisition, pointing, and tracking system for underwater wireless optical communications Download:764次
Download:764次
 Download:764次
Download:764次Due to the proliferation of underwater vehicles and sensors, underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) is a key enabler for ocean exploration with a strong reliance on short-range bandwidth-intensive communications. A stable optical link is of primary importance for UWOC. A compact, low-power, and low-cost acquisition, pointing, and tracking (APT) system is proposed and experimentally demonstrated to realign the optical link within 0.04 s, even when the UWOC transmitter and receiver are in relative motion. The system successfully achieves rapid auto-alignment through a 4 m tap water channel with a relatively large number of bubbles. Furthermore, the required minimum illumination value is measured to be as low as 7.1 lx, implying that the proposed APT scheme is robust to dim underwater environments. Meanwhile, mobility experiments are performed to verify the performance of the APT system. The proposed system can rapidly and automatically align moving targets in complex and unstable underwater environments, which can potentially boost the practical applications of UWOC.
acquisition pointing and tracking underwater wireless optical communication Design of low frequency fiber optic Fabry–Perot seismometer based on transfer function analysis Download:508次
Download:508次
 Download:508次
Download:508次We develop a low frequency fiber Fabry–Perot (F-P) seismometer based on transfer function analysis. The seismometer structure and demodulation system accuracy are limitations of low frequency seismic monitoring. The transfer function of the F-P seismometer is analyzed, and the mass displacement spectrum (MDS) is introduced. MDS provides guidance for mechanical structure design and optical interferometer analysis to achieve low noise. The F-P seismometer prototype is built. The experiment shows that the prototype has an average noise of
fiber optics seismometers frequency Efficiently tuning the output intensity of an optical device is of vital importance for the establishment of optical interconnects and networks. Thermo-optical modulation is an easily implemented and convenient approach and has been widely employed in photonic devices. In this paper, we proposed a novel thermo-optical modulator based on a microfiber knot resonator (MKR) and graphene heater. Upon applying voltage to graphene, the resonant property of the MKR could be thermally tuned with a maximum phase shift of
microfiber knot resonator graphene heater thermo-optical modulation Effective strategy to achieve a metal surface with ultralow reflectivity by femtosecond laser fabrication Download:608次
Download:608次
 Download:608次
Download:608次An effective and simple method is proposed for fabricating the micro/nano hybrid structures on metal surfaces by adjusting femtosecond laser fluence, scanning interval, and polarization. The evolution of surface morphology with the micro/nano structures is discussed in detail. Also, the mechanism of light absorption by the micro/nano hybrid structures is revealed. Compared with the typical periodic light-absorbing structures, this type of micro/nano hybrid structures has an ultralow average reflectivity of 2% in the 250–2300 nm spectral band and the minimum 1.5% reflectivity in UV band. By employing this method, large areas of the micro/nano hybrid structures with high consistency could be achieved.
femtosecond laser titanium alloy micro/nano structures ultralow reflectivity In this Letter, Ti–Si bilayer was deposited on white silk to achieve coloration of the silk. By controlling the thickness of the Ti layer and Si layer, the saturation and the hue of the color on the silk could be preciously modulated, respectively. The structural colors on the silk could cover the major colors in the International Commission on Illumination 1931 chromaticity diagram, and it exhibits good durability, which is demonstrated by rubbing and stretching treatments. The developed textile coloration method may provide an eco-friendly technology in the silk dyeing industry.
structural color silk coloration Ti-Si bilayer Deep-learning-based prediction of living cells mitosis via quantitative phase microscopy Download:560次
Download:560次
 Download:560次
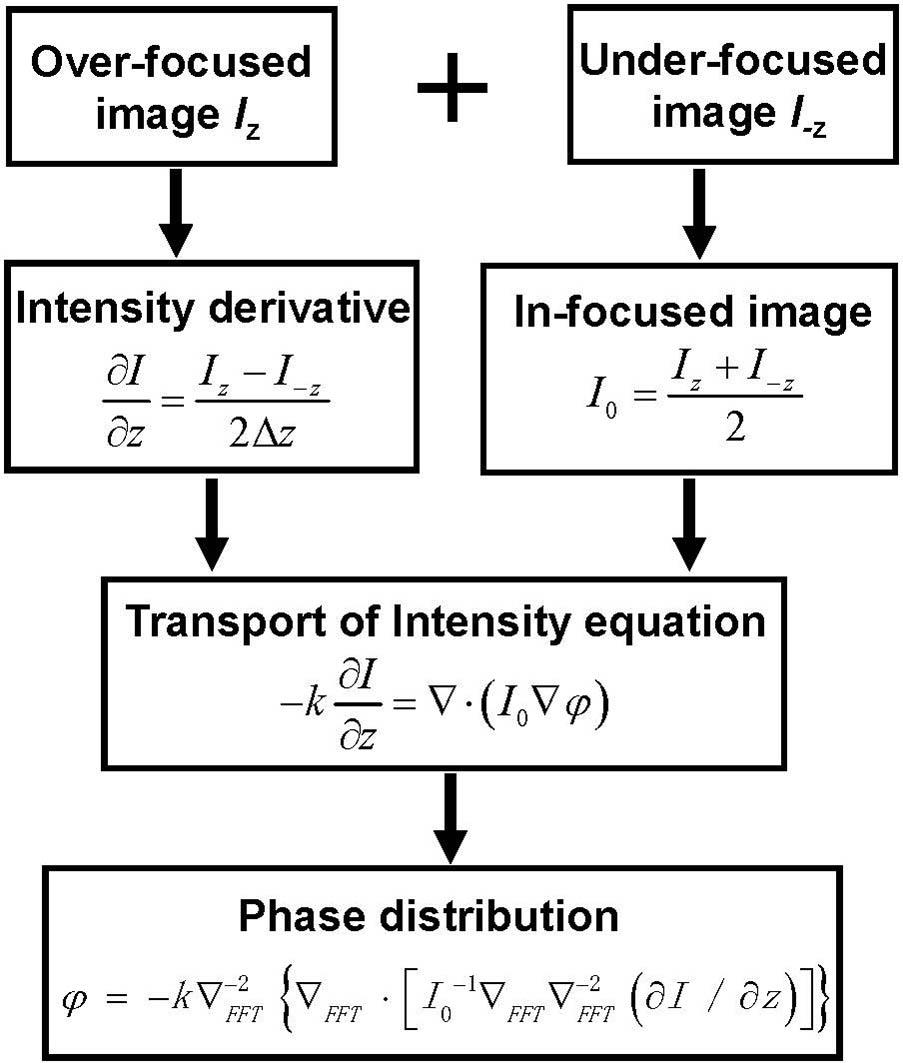
Download:560次We present a deep learning approach for living cells mitosis classification based on label-free quantitative phase imaging with transport of intensity equation methods. In the approach, we applied a pretrained deep convolutional neural network using transfer learning for binary classification of mitosis and non-mitosis. As a validation, we demonstrated the performances of the network trained by phase images and intensity images, respectively. The convolutional neural network trained by phase images achieved an average accuracy of 98.9% on the validation data, which outperforms the average accuracy 89.6% obtained by the network trained by intensity images. We believe that the quantitative phase microscopy in combination with deep learning enables researchers to predict the mitotic status of living cells noninvasively and efficiently.
cell classification quantitative phase imaging deep learning We propose a spatial diffraction diagnostic method via inserting a millimeter-gap double slit into the collimated terahertz beam to monitor the minute variation of the terahertz beam in strong-field terahertz sources, which is difficult to be resolved in conventional terahertz imaging systems. To verify the method, we intentionally fabricate tiny variations of the terahertz beam through tuning the iris for the infrared pumping beam before the tilted-pulse-front pumping setups. The phenomena can be well explained by the theory based on the tilted-pulse-front technique and terahertz diffraction.
spatial diffraction diagnostic method strong-field terahertz sources tilted-pulse-front pumping terahertz diffraction We suggest tailoring of the illumination’s complex degree of coherence for imaging specific two- and three-point objects with resolution far exceeding the Rayleigh limit. We first derive a formula for the image intensity via the pseudo-mode decomposition and the fast Fourier transform valid for any partially coherent illumination (Schell-like, non-uniformly correlated, twisted) and then show how it can be used for numerical image manipulations. Further, for Schell-model sources, we show the improvement of the two- and three-point resolution to 20% and 40% of the classic Rayleigh distance, respectively.
optical coherence imaging light manipulation Topological photonics provides a new opportunity for the examination of novel topological properties of matter, in which the energy band theory and ideas in topology are utilized to manipulate the propagation of photons. Since the discovery of topological insulators in condensed matter, researchers have studied similar topological effects in photonics. Topological photonics can lead to materials that support the robust unidirectional propagation of light without back reflections. This ideal transport property is unprecedented in traditional optics and may lead to radical changes in integrated optical devices. In this review, we present the exciting developments of topological photonics and focus on several prominent milestones of topological phases in photonics, such as topological insulators, topological semimetals, and higher-order topological phases. We conclude with the prospect of novel topological effects and their applications in topological photonics.
topological photonics states artificial microstructures The first photon bias of photon detection results in distortion of the photon waveform, which seriously affects the accurate acquisition of target information. A rapid universal recursive correction method is proposed, which is suitable for multi-trigger and single-trigger modes of photon detection. The calculation time is 2 to 3 orders of magnitude faster than that of Xu et al.’s method. In the experiment, we have obtained good correction results for area targets and targets with varying depths. When the average number of echo photons is 0.89, the correlation distance of the correction waveform is reduced by 85%.
photon counting Lidar waveform correction waveform distortion single pixel Engineering the spectral profile of photon pairs by using multi-stage nonlinear interferometers Download:525次
Download:525次
 Download:525次
Download:525次Using the quantum interference of photon pairs in N -stage nonlinear interferometers (NLIs), the contour of the joint spectral function can be modified into an islands pattern. We perform two series of experiments. One is that all of the nonlinear fibers in pulse pumped NLIs are identical; the other is that the lengths of N pieces of nonlinear fibers are different. We not only demonstrate how the pattern of spectral function changes with the stage number N , but also characterize how the relative intensity of island peaks varies with N . The results well agree with theoretical predictions, revealing that the NLI with lengths of N pieces of nonlinear fibers following binomial distribution can provide a better active filtering function. Our investigation shows that the active filtering effect of multi-stage NLI is a useful tool for efficiently engineering the factorable two-photon state—a desirable resource for quantum information processing.
quantum state engineering optical parametric amplifier nonlinear quantum interference Noise transfer of pump field noise with analysis frequency in a broadband parametric downconversion process Download:655次
Download:655次
 Download:655次
Download:655次Our previous work had proved pump field noise coupling in the seed field injected optical parametric amplifier (OPA) at a certain analysis frequency. Inspired by this noise coupling mechanism, the frequency dependent squeezing factor due to excess pump noise was experimentally demonstrated. Apart from a reduced squeezing level with an increased noise, the results also prove that a broadband squeezing noise spectrum is not frequency dependent on the amplitude modulated pump field, but limited by the bandwidth of the amplitude modulator and OPA resonator, and the effective measurement is carried out in the frequency range of 2–10 MHz. It provides a guidance to design a broader-bandwidth, higher-level bright squeezed light.
quantum optics nonlinear optics parametric processes squeezed states Independent phase manipulation of co- and cross-polarizations with all-dielectric metasurface Download:789次
Download:789次
 Download:789次
Download:789次Phase carried by two orthogonal polarizations can be manipulated independently by controlling both the geometric size and orientation of the dielectric nanopost. With this characteristic, we demonstrate a novel multifunctional metasurface, which converts part of the incident linearly polarized light into its cross-polarization and encodes the phase of the two orthogonal polarizations independently. A beam splitter and a bifocal metalens were realized in a single-layer dielectric metasurface by this approach. We fabricated the bifocal metalens and demonstrated that two focal spots in orthogonal polarizations can be separated transversely or longitudinally at will. The proposed approach shows a new route to design multifunctional metasurfaces with various applications in holography and three-dimensional display.
multifunctional metasurface polarization conversion beam splitting bifocal metalens Laser printing based on curvature-driven shape transition of aluminum nanodiscs [Invited] Download:524次
Download:524次
 Download:524次
Download:524次Plasmonic structural colors have plenty of advantages over traditional colors based on colorants. The pulsed laser provides an important method generating plasmonic structural colors with high efficiency and low cost. Here, we present plasmonic color printing Al nanodisc structures through curvature-driven shape transition. We systematically study the mechanism of morphologic evolution of the Al nanodisc below the thermal melting threshold. A multi-pulse-induced accumulated photothermal effect and subsequent curvature-driven surface atom diffusion model are adopted to explain the controllable shape transition. The shape transition and corresponding plasmonic resonances of the nanodisc can be independently and precisely modulated by controlled irradiations. This method opens new ways towards high-fidelity color prints in a highly efficient and facile laser writing fashion.
photothermal effects color subwavelength structures surface plasmons 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦