2022, 20(11) Column
Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Nonlinear Optics Optoelectronics Physical Optics Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics Infrared and Terahertz Photonics Light-matter Interaction Microwave Photonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第20卷 第11期
Measuring the topological charge (TC) of optical vortex beams by the edge-diffraction pattern of a single plate is proposed and demonstrated. The diffraction fringes can keep well discernible in a wide three-dimensional range in this method. The redundant fringes of the diffracted fork-shaped pattern in the near-field can determine the TC value, and the orientation of the fork tells the handedness of the vortex. The plate can be opaque or translucent, and the requirement of the translucent plate for TC measurement is analyzed. Measurement of TCs up to
optical vortex orbital angular momentum topological charge measurement Security is one of the key issues in communications, but it has not attracted much attention in the field of underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC). This Letter proposes a UWOC encryption scheme with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation, based on the three-layer chaotic encryption and chaotic discrete Fourier transform (DFT) precoding. The three-layer chaotic encryption processes are bit stream diffusion, in-phase/quadrature encryption, and time-frequency scrambling. With multi-fold data encryption, the scheme can create a keyspace of
security underwater wireless optical communication chaotic encryption chosen-plaintext attacks Visible light communication (VLC) based on the micro light emitting diode (micro-LED) has attracted increasing attention owing to its high bandwidth, low power consumption, and high security. Compared with semi-polar or non-polar micro-LEDs, the commercial polar micro-LED has the advantages of low cost and more mature epitaxy technique. In this study, green micro-LEDs with different indium tin oxide (ITO) sizes are fabricated based on the commercial c-plane LED epitaxial wafer. The transmission performance of 80, 100, and 150 µm devices has been studied in detail. A partial pre-equalization scheme is utilized to increase data rates. Finally, the VLC system with a 100 µm green micro-LED as the transmitter could achieve a maximum data rate of 3.59 Gbit/s. Such a result will be beneficial to promote the further development of low-cost, high-speed VLC devices in the future.
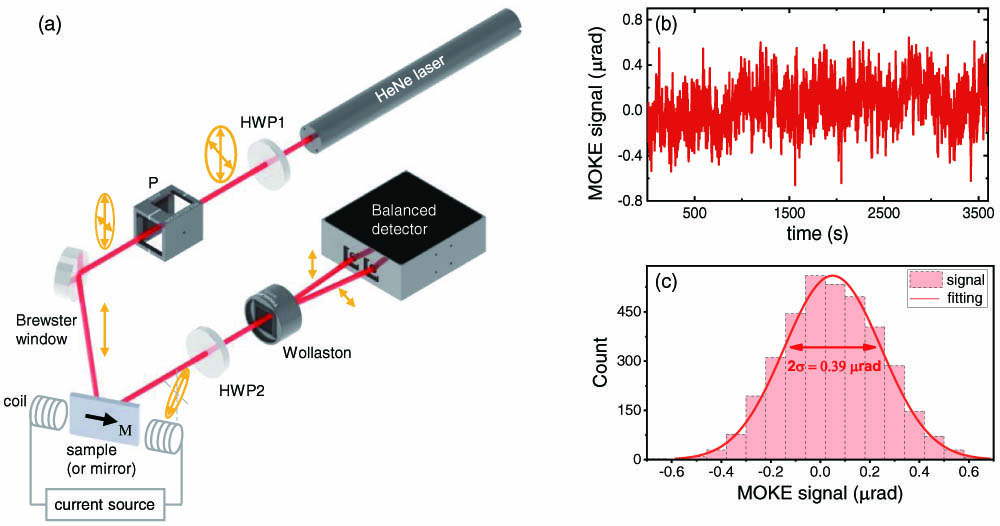
micro-LED visible light communication c-plane discrete multi-tone A high-sensitivity DC magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) apparatus is described in this Letter. Via detailed analysis on several dominating noise sources, we have proposed solutions that significantly lower the MOKE noise, and a sensitivity of
high sensitivity direct current magneto-optical Kerr effect Fabrication and characterization of on-chip silicon spherical-like microcavities with high Q-factors
An effective way to fabricate high-quality (Q) silicon microcavities on-chip is proposed and studied. Our fabrication technique consists of two significant steps: (1) patterning a special silicon micro-pillar by Bosch processes and (2) subsequent reflow of the pillar into a spherical-like microcavity using a laser pulse at 532 nm. Its shape and surface roughness are characterized using a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope. The root-mean-square roughness of the surface is about 0.6 nm. A representative value for the loaded Q-factors of our silicon spherical-like microcavities is on the order of
optical microcavity whispering gallery mode high Q-factor We demonstrate a simple method to obtain accurate optical waveforms with a gigahertz-level programmable modulation bandwidth and a watt-level output power for wideband optical control of free atoms and molecules. Arbitrary amplitude and phase modulations are transferred from microwave to light with a low-power fiber electro-optical modulator. The sub-milliwatt optical sideband is co-amplified with the optical carrier in a power-balanced fashion through a tapered semiconductor amplifier (TSA). By automatically keeping TSA near saturation in a quasi-continuous manner, typical noise channels associated with pulsed high-gain amplifications are efficiently suppressed. As an example application, we demonstrate interleaved cooling and trapping of two rubidium isotopes with coherent nanosecond pulses.
pulse shaping laser cooling and trapping high gain optical pulse amplification self-phase modulation amplified spontaneous emission sideband modulation A highly efficient milli-joule-level Q-switched
2 µm thulium laser acousto-optical Q-switching Tm,La:CaF2 crystal dual-wavelength high energy high efficiency We demonstrate manipulating the interactions of a second-order soliton with a weak probe pulse under the condition of group velocity match and group velocity mismatch (GVMM). During these interactions, the second-order soliton acting as an effective periodic refractive-index barrier leads to the polychromatic scattering of the probe pulse, which is represented as unequally spaced narrow-band sources with adjustable spectral width. In the case of GVMM, almost all the spectral components of the narrow-band sources meet the nonlinear frequency conversion relationship by using the wavenumber-matching relationship due to the robustness of the second-order soliton under moderate high-order-dispersion perturbations, so this case is more conducive to the study of the soliton wells. In addition, different transmission states of a soliton well are demonstrated under different probe pulse properties in the fiber-optical analog of the event horizon. When the power of the probe pulse is strong enough, a dispersive wave can be generated from the collision of two fundamental solitons split from the two second-order solitons. These interesting phenomena investigated in this work as a combination of white- and black-hole horizons can be considered as promising candidates for frequency conversion and broadband supercontinuum generation.
second-order soliton well probe wave optical event horizon Lithium-niobate microcavities have not only the ability to resonantly enhance light–matter interaction but also excellent nonlinear optical properties, thereby providing an important platform for nonlinear optical investigations. In this paper, we report the observation of multi-peak spectra in the near infrared range in lithium-niobate microcavities on a chip under the pump of a 1550 nm continuous laser. Such a multi-peak spectrum was attributed to the sum-frequency of the pump laser and its background. The conversion efficiencies of the sum-frequency processes are of the order of
lithium niobate microcavities nonlinear optics Solar-blind ultraviolet photodetectors (SBPDs) have attracted tremendous attention in the environmental, industrial, military, and biological fields. Aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN), a kind of representative III-nitride semiconductor, has promising prospects in solar-blind photodetection owing to its tunable wide bandgap and industrial feasibility. Considering the high defect density in the AlGaN epilayer directly grown on a sapphire substrate, employing an AlN/sapphire template turns out to be an effective method to achieve a high-quality AlGaN epilayer, thereby enhancing the SBPD performances. In recent years, a variety of remarkable breakthroughs have been achieved in the SBPDs. In this paper, the progress on photovoltaic AlGaN-based SBPDs is reviewed. First, the basic physical properties of AlGaN are introduced. Then, fabrication methods and defect annihilation of the AlN/sapphire template are discussed. Various photovoltaic SBPDs are further summarized, including Schottky barrier, metal-semiconductor-metal, p-n/p-i-n and avalanche photodiodes. Furthermore, surface modification and photoelectrochemical cell techniques are introduced. Benefitting from the development of fabrication techniques and optoelectronic devices, photovoltaic AlGaN photodiodes exhibit a promising prospect in solar-blind ultraviolet photodetection.
photovoltaic AlGaN photodiodes solar-blind ultraviolet photodetection AlN/sapphire template High-speed three-dimensional shape measurement with inner shifting-phase fringe projection profilometry Download:525次
Download:525次
 Download:525次
Download:525次Fringe projection profilometry (FPP) has been extensively studied in the field of three-dimensional (3D) measurement. Although FPP always uses high-frequency fringes to ensure high measurement accuracy, too many patterns are projected to unwrap the phase, which affects the speed of 3D reconstruction. We propose a high-speed 3D shape measurement method using only three high-frequency inner shifting-phase patterns (70 periods), which satisfies both high precision and high measuring speed requirements. Besides, our proposed method obtains the wrapped phase and the fringe order simultaneously without any other information and constraints. The proposed method has successfully reconstructed moving objects with high speed at the camera’s full frame rate (1700 frames per second).
fringe projection profilometry high-speed 3D measurement inner shifting-phase dynamic object measurement Ghost imaging (GI) is a technique to retrieve images by correlating intensity fluctuations. In this Letter, we present a novel scheme for GI referred to as second-order cumulants GI (SCGI). The image is retrieved from fluctuation information, and resolution may be enhanced compared to traditional GI. We experimentally performed SCGI image reconstruction, and the results are in agreement with theoretical predictions.
ghost imaging cumulants resolution A stimulated emission depletion is capable of breaking the diffraction limit by exciting fluorescent molecules with a solid Gaussian beam and quenching the excited molecules with another donut beam through stimulated emission. The coincidence degree of these two beams in three dimensions will significantly influence the spatial resolution of the microscope. However, the conventional alignment approach based on raster scanning of gold nanoparticles by the two laser beams separately suffers from a mismatch between fluorescence and scattering modes. To circumvent the above problems, we demonstrate a fast alignment design by scanning the second beam over the fabricated sample, which is made of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) dye resin. The relative positions of solid and donut laser beams can be represented by the fluorescent AIE from the labeled spots in the dye resin. This design achieves ultra-high resolutions of 22 nm in the x/y relative displacement and 27 nm in the z relative displacement for fast spatial matching of the two laser beams. This study has potential applications in scenarios that require the spatial matching of multiple laser beams, and the field of views of different objectives, for example, in a microscope with high precision.
nanophotonics stimulated emission depletion microscope aggregation-induced emission dual-beam alignment Lithium niobate (LN) metasurfaces have emerged as a new platform for manipulating electromagnetic waves. Here, we report a fabrication technique for LN nano-grating metasurfaces by combining focused ion beam (FIB) milling with inductively coupled plasma reactive ion etching (ICP-RIE). Steep sidewalls with angles larger than 80° are achieved. Sharp quasi-bound states in the continuum are observed from our metasurfaces. The measured transmission spectra show good agreement with the numerical simulations, confirming the high quality of the fabricated metasurfaces. Our technique can be applied to fabricate the LN metasurfaces with sharp resonances for various applications in optical communications, on-chip photonics, laser physics, sensing, and so on.
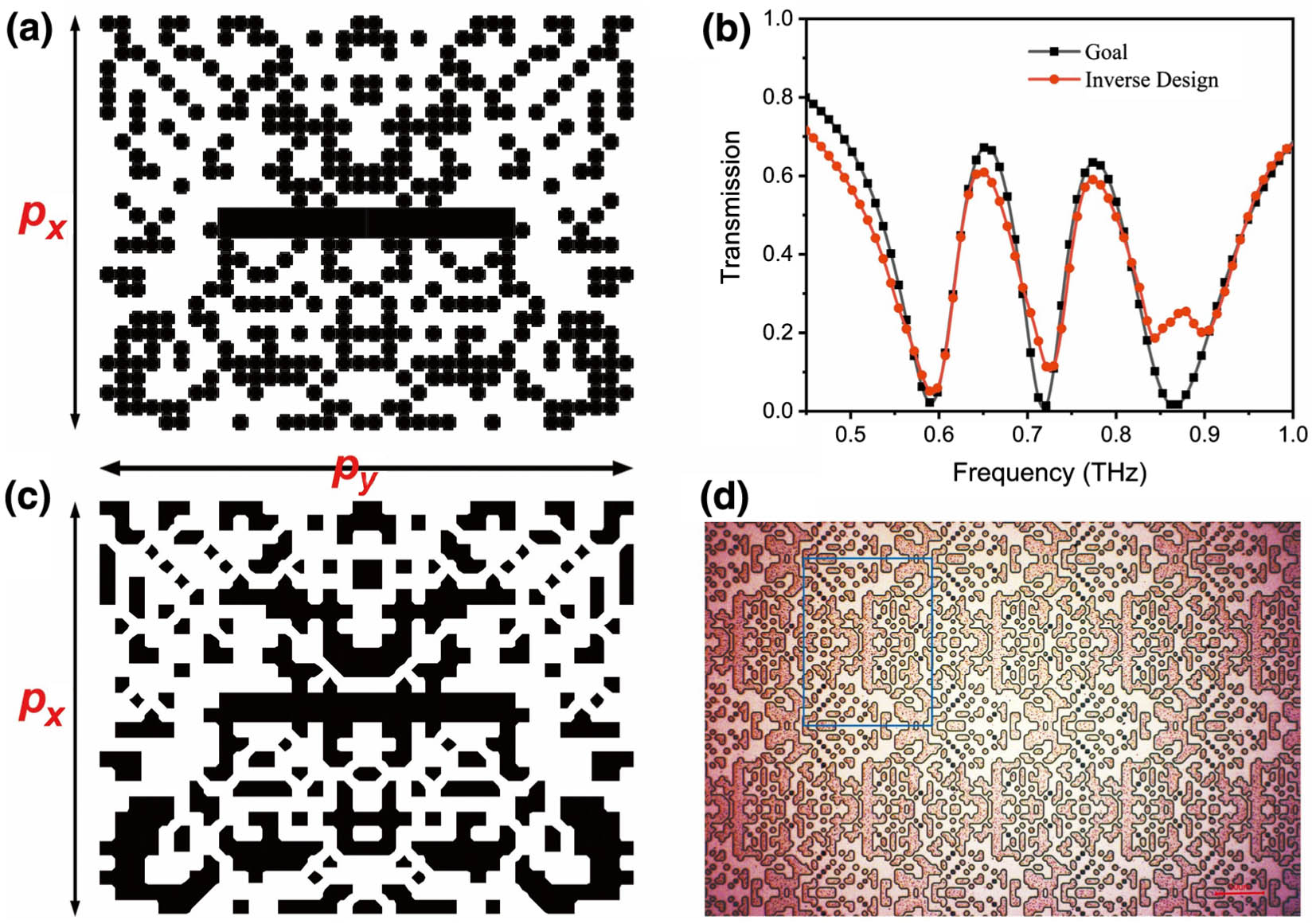
lithium niobate metasurfaces fabrication FIB ICP-RIE Terahertz metasurfaces have great applications for efficient terahertz modulation, but there are still problems in designing terahertz metadevices in terms of complexity and inefficiency. Herein, we demonstrate an inversely-designed terahertz metasurface with double electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like windows by incorporating a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. We prepared and tested the metadevices, and the experimental terahertz signals are close to the designed results. By hybridizing amorphous germanium film with the inversely-designed metasurface, two EIT-like windows, including transmission and slow-light effect, exhibit ultrafast modulation behavior in 25 ps excited by a femtosecond laser. The modulation depths of transmission in two transparency windows are 74% and 65%, respectively. The numerical simulations also illustrate the ultrafast dynamic process and modulation mechanism, which match well with the experiment results. Our work thus offers opportunities for designing other objective functions of the terahertz metadevice.
terahertz metasurfaces inverse design double electromagnetically induced transparency Ince–Gaussian (IG) beams, as eigenfunctions of the paraxial wave equation in elliptical coordinates, are attracting increasing interest owing to their propagation-invariant and full-field properties. Optical amplification via parametric interactions can further expand their application areas, yet it is rarely studied. In this work, we report on a high-fidelity parametric amplifier for IG beams. The nonlinear transformation of the spatial spectra of the signal and associated influences on the beam profiles of the amplified signal, under different pump structures, were theoretically and experimentally investigated. By using a perfect flattop beam as the pump, we show that the transverse structure of IG signals is well maintained, and the distortion induced by radial-mode degeneration is overcome during amplification. This proof-of-principle demonstration paves the way for a mode-independent and distortion-free amplifier of arbitrary structured light and has great significance in relevant areas, such as quantum optics, tunable infrared-laser generation, and image amplification.
optical parametric amplification Ince–Gaussian beam high fidelity perfect flattop beam Weak RF signal detection with high resolution and no blind zone based on directly modulated multi-mode optoelectronic oscillation has been proposed. The high-sensitivity optical modulators and optical filters are avoided because multi-mode oscillation is obtained based on directly modulating the semiconductor laser at the relaxation oscillation frequency. For the directly modulated optoelectronic oscillator, the detection characteristics such as gain for the RF signal, resolution, noise floor, and sensitivity are firstly analyzed. The experimental results are consistent with the simulated results. For the RF signal of unknown frequency, it can be detected out and amplified by tuning the bias current and delay time of the loop. There is no blind zone within 1–4.5 GHz. The system provides a maximum gain of 17.88 dB for the low-power RF signal. The sensitivity of the system can reach as high as
radio frequency detection optoelectronic oscillator distributed feedback semiconductor laser 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦