2022, 20(4) Column
Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Imaging Systems and Image Processing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Nonlinear Optics Optical Design and Fabrication Optoelectronics Ultrafast Optics and Attosecond/High-field Physics Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics Light-matter Interaction
Chinese Optics Letters 第20卷 第4期
This study proposes a novel interferometric fiber optic gyroscope (IFOG) based on an integrated optical chip, application-specific integrated circuit, and small-diameter sensing coil. The overall size and weight of the prototype are
gyroscopes fiber optics fiber optics sensors integrated optics Highly efficient and stable coupling of kilowatt-level continuous wave laser into hollow-core fibers
Fiber gas lasers based on gas-filled hollow-core fibers (HCFs) perfectly combine the advantages of fiber lasers and gas lasers and have obtained fast development in the past years. However, stable and efficient coupling of high-power pump lasers into the HCFs is one of the key problems to be solved. In this paper, we study the coupling of high-power continuous wave fiber lasers into anti-resonant HCFs through an end-cap. By optimizing the splicing parameters, a maximum laser power of 1167 W was injected into the 1-m-long HCFs, and 1021 W was obtained at the output end, giving a total transmission efficiency of
hollow-core fibers end-caps high power coupling methods A Michelson interferometer (MI) composite cavity fiber laser sensing system based on radio frequency (RF) interrogation is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The system down-converts the traditional MI light frequency detection to RF detection, which improves the stability of the system. The optic fiber MI is placed in the laser resonator to form a composite cavity structure, which greatly improves the sensitivity of beat frequency signal demodulation.
Michelson interferometer compound cavity multi-longitudinal mode beat frequency radio-frequency detection Light field imaging has shown significance in research fields for its high-temporal-resolution 3D imaging ability. However, in scenes of light field imaging through scattering, such as biological imaging in vivo and imaging in fog, the quality of 3D reconstruction will be severely reduced due to the scattering of the light field information. In this paper, we propose a deep learning-based method of scattering removal of light field imaging. In this method, a neural network, trained by simulation samples that are generated by light field imaging forward models with and without scattering, is utilized to remove the effect of scattering on light fields captured experimentally. With the deblurred light field and the scattering-free forward model, 3D reconstruction with high resolution and high contrast can be realized. We demonstrate the proposed method by using it to realize high-quality 3D reconstruction through a single scattering layer experimentally.
computational imaging light field imaging scattering imaging deep learning We designed and demonstrated experimentally a silicon photonics integrated dynamic polarization controller. The overall size of the dynamic polarization controller on chip is
dynamic polarization controller simulated annealing approach dynamic polarization extinction ratio Monolithic integration of III-V lasers with small footprint, good coherence, and low power consumption based on a CMOS-compatible Si substrate have been known as an efficient route towards high-density optical interconnects in the photonic integrated circuits. However, the material dissimilarities between Si and III-V materials limit the performance of monolithic microlasers. Here, under the pumping condition of a continuous-wave 632.8 nm He–Ne gas laser at room temperature, we achieved an InAs/GaAs quantum dot photonic crystal bandedge laser, which is directly grown on an on-axis Si (001) substrate, which provides a feasible route towards a low-cost and large-scale integration method for light sources on the Si platform.
lasers bandedge photonic crystal monolithic integration quantum dots silicon substrate A single-frequency 1645 nm pulsed laser with frequency stability close to 100 kHz was demonstrated. The laser oscillator is injection-seeded by a single-frequency narrow linewidth
single-frequency pulse high-frequency stability injection-seeding We demonstrate a novel approach to achieve wavelength-tunable ultrashort pulses from an all-fiber mode-locked laser with a saturable absorber based on the nonlinear Kerr beam clean-up effect. This saturable absorber was formed by a single-mode fiber spliced to a graded-index multimode fiber, and its tunable band-pass filter effect is described by a numerical model. By adjusting the bending condition of the graded-index multimode fiber, the laser could produce dissipative soliton pulses with their central wavelength tunable from 1040 nm to 1063 nm. The pulse duration of the output laser could be compressed externally to 791 fs, and the signal to noise ratio of its radio frequency spectrum was measured to be 75.5 dB.
nonlinear Kerr beam clean-up effect tunable wavelength mode-locking numerical simulation Copper welding with an infrared (IR) Gaussian laser beam usually shows obvious instability, spatters, and worse surface morphology due to the Gaussian distribution, temperature-dependent IR absorption, and high thermal conductivity in copper. In this paper, the IR quasi-continuous-wave Gaussian beam was converted into a vortex ring beam with a phase-plate and then applied to the micro-spot-welding of copper sheets. The welding with the vortex beam demonstrated a significantly improved welding performance, smoother surface morphology, and higher welding stability. Besides, no spatters appeared in the welding process.
Gaussian beam vortex beam micro-spot-welding copper sheets IR fiber laser Direct generation of a stable multi-beam pulsed 355 nm UV laser based on a micro-lens array Download:733次
Download:733次
 Download:733次
Download:733次Multi-beam laser processing is a very popular method to improve processing efficiency. For this purpose, a compact and stable multi-beam pulsed 355 nm ultraviolet (UV) laser based on a micro-lens array (MLA) is presented in this Letter. It is worth noting that the MLA is employed to act as the spatial splitter as well as the coupling lens. With assistance of the MLA, the 1064 nm laser and 532 nm laser are divided into four sub-beams and focused at different areas of the third-harmonic generation (THG) crystal. As a result, the multi-beam pulsed 355 nm UV laser is successfully generated inside the THG crystal. The measured pulse widths of four sub-beams are shorter than 9 ns. Especially, the generated four sub-beams have good long-term power stability benefitting from the employed MLA. We believe that the generated stable multi-beam 355 nm UV laser can meet the requirement of high-efficiency laser processing, and the presented method can also pave the way to generate stable and long-lived multi-beam UV lasers.
micro-lens array third-harmonic generation direct generation pulsed UV laser The linewidth of the
optical parametric oscillation narrow linewidth BaGa4Se7 Light bullets (LBs) are localized nonlinear waves propagating in high spatial dimensions. Finding stable LBs and realizing their control are desirable due to the interesting physics and potential applications. Here, we show that nonlocal LBs generated in a cold Rydberg atomic gas via the balance among the dispersion, diffraction, and giant nonlocal Kerr nonlinearity contributed by long-range Rydberg-Rydberg interaction can be actively manipulated by using a weak gradient magnetic field. Nonlocal LBs are generated by a balance among dispersion, diffraction, and large nonlocal Kerr nonlinearities contributed by long-range Rydberg-Rydberg interactions. Here, we find that active manipulation can be achieved by weak gradient magnetic fields in cold Rydberg atomic gases. Especially, the LBs may undergo significant Stern–Gerlach deflections, and their motion trajectories can be controlled by adjusting the magnetic-field gradient. The results reported here are helpful not only for understanding unique properties of LBs in nonlocal optical media but also for finding ways for precision measurements of magnetic fields.
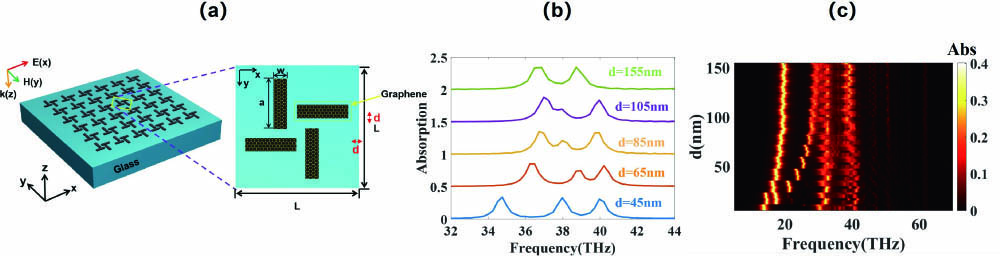
nonlinear optics optical soliton Rydberg atom Plasmonics could provide compact and powerful solutions for manipulating light in deep-subwavelength dimensions, which is promising for a great range of nanophotonic technologies such as plasmonic rulers and sensors. However, the effective area of enhanced localized field induced by surface plasmon polaritons is typically restricted to the structural boundaries. In this work, we propose a method to generate high quality-factor extended electromagnetic fields via hybridizing the super-radiant state and the quasi bound state in the continuum of graphene metasurfaces. The coupling interaction involved operates as a three-level system with multiple sharp resonances immune to the polarization, which holds great promise for developing nanodevices with high sensing capacity in two dimensions.
plasmon hybridization quasi bound state in the continuum high-Q sensing Nonlinear coded nonuniform superposition QAM by trellis-coding for MISO system in visible light communication Download:511次
Download:511次
 Download:511次
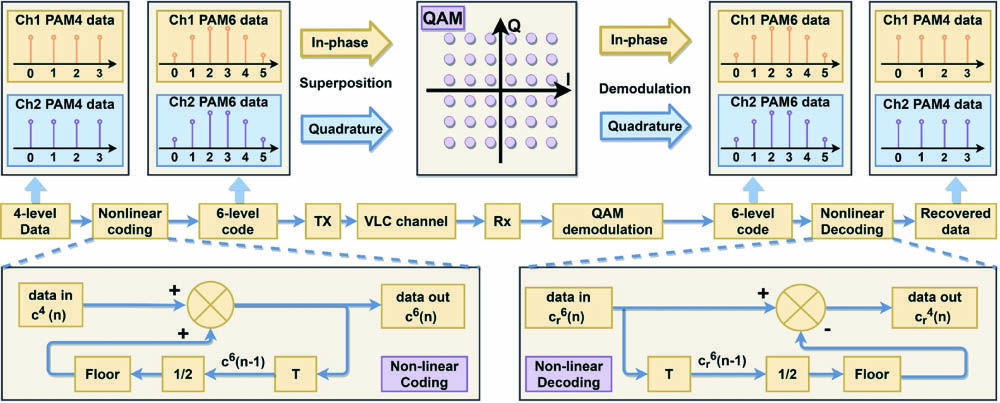
Download:511次In this paper, we propose a 36-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) superposition modulation technique that is featured with uneven symbol probability by nonlinear precoding, named nonlinear coded nonuniform superposition (NCNS) QAM. Its aim is to alleviate the nonlinearity effect caused by high instantaneous power in multi-input single-output (MISO) visible light communication (VLC) system, with an uneven probabilistic-shaped constellation. The transmitter includes two LEDs to send signals independently, and the receiver uses a photo detector to receive the superposed QAM signal. The experiment results show that NCNS has a better robustness against nonlinearity than pulse amplitude modulation 4, approximately gaining a 16% increase in maximum usable peak-to-peak voltage and a 33% enlargement in dynamic range area. It is a simple but effective approach to solve the bandwidth limits related to signal power and hopefully be applied in large power VLC systems such as underwater VLC, or to improve the robustness against power fluctuation.
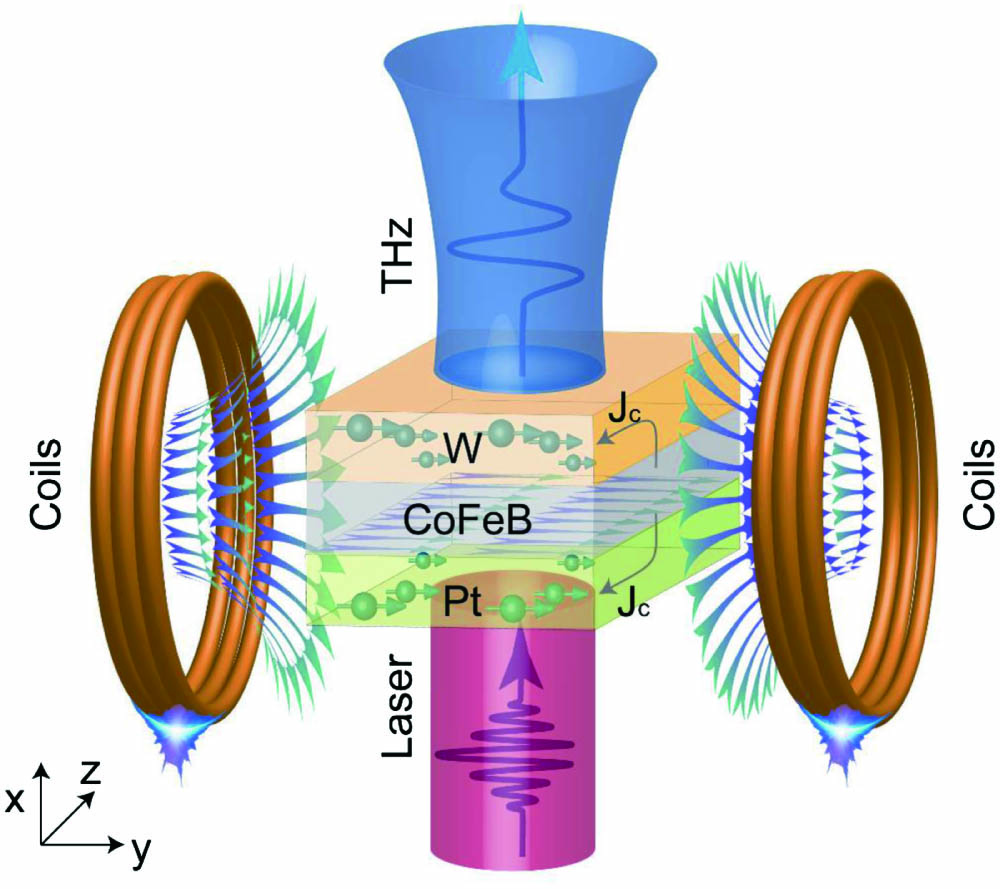
visible light communication light-emitting diode multi-input single-output quadrature amplitude modulation nonlinear coding spectral shaping Spintronic thin films are considered as one of the promising terahertz (THz) source candidates, owing to their high performance and low cost. Much effort has been made to achieve spintronic THz sources with broadband and high conversion efficiency. However, the development of spintronic THz emitters with good compatibility, low cost, and miniaturized technology still faces many challenges. Therefore, it is urgent to extend commercial and portable spintronic THz emitters to satisfy many practical applications. Herein, we design a new generation of spintronic THz emitters composed of an alternating electromagnet and a miniaturized electronic controller. Not only can this new type of spintronic THz emitter largely simplify the ancillary equipment for spintronic sources, it also has a twice larger THz signal compared to the traditional THz time-domain spectroscopy systems with a mechanical chopper. Experimental results and theoretical calculations for electromagnetic coils show that our design can stably generate THz signals that are independent of the frequency and magnetic field of alternating signals. As the spin thin film is optimized, a magnetic field as low as 75 G satisfies the requirement for high performance THz emission. Hence, not only is the efficiency of the pump power enhanced, but also the driving current in the electromagnet is decreased. We believe that it has a wide range of applications and profound implications in THz technology based on spintronic emitters in the future.
spintronic THz emitters trilayer heterostructure electromagnet electrically driven control Manipulation of polarization conversion and multiplexing via all-silicon phase-modulated metasurfaces Download:671次
Download:671次
 Download:671次
Download:671次Phase-modulated metasurfaces that can implement the independent manipulation of co- and cross-polarized output waves under circularly polarized (CP) incidence have been proposed. With this, we introduce one particular metasurface composed of meta-atoms with a phase difference of
phase-modulated metasurfaces polarization conversion multiplexing “Lotus effect” glass surfaces with fluorinated ethylene propylene were successfully fabricated by using a femtosecond laser-induced backward transfer (LIBT) method. By space-selectively modifying both the surface morphology and surface chemistry in a single step, LIBT provides a convenient and flexible route to fabricate superhydrophobic surfaces with ultralow adhesion. A systematic mechanism responsible for the anisotropic wetting behaviors and adhesion modulation was proposed with a combination of the Cassie and Wenzel models. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that oxidation and defluorination were induced by laser radiation. LIBT is proved to be a promising method for programmable manipulations of functional surfaces with diverse wettability.
superhydrophobic surface laser-induced backward transfer fluorinated ethylene propylene glass 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦