
宋奇林 1,2,3,4李杨 1,3,4周子夜 1,3,4肖亚维 1,2,3,4[ ... ]饶长辉 1,2,3,4
1 自适应光学全国重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
4 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
Overview: Since the groundbreaking discovery of gravitational waves, the scientific community has fervently pursued the exploration of low-frequency gravitational waves to glean deeper insights into the cosmos. The inherent limitations of ground-based conditions, however, pose formidable challenges for detectors in capturing gravitational waves below the 1 Hz threshold. Consequently, the imperative has shifted toward the deployment of space-based gravitational wave detectors as the paramount solution for effective low-frequency gravitational wave detection. At the crux of space-based gravitational wave detection lies the pivotal role of spaceborne telescopes. Given the expansive transmission distances spanning magnitudes of 109 m between celestial constellations, the demand for nanoradian-level precision in telescope pointing accuracy becomes non-negotiable. The concomitant necessity for high-precision measurements and calibration emerges as a prerequisite for achieving the exacting standards of pointing accuracy in spaceborne telescopes dedicated to gravitational wave detection. To ameliorate the deleterious effects of pointing deviations on gravitational wave detection, this study strategically optimizes key parameters, including microlens structures, detector selection, and algorithmic frameworks, thereby achieving a breakthrough in high-precision pointing deviation measurements. Leveraging a low-density microlens array with extended sub-aperture focal lengths enhances the spatial scale of the light spot within each sub-aperture. This, coupled with detectors boasting a high signal-to-noise ratio, synergistically elevates the pointing detection accuracy of each discrete lens. Moreover, the paper introduces an innovative, Hartmann principle-based methodology for high-precision pointing deviation measurements, deploying a spatially reused paradigm across multiple sub-apertures. By aggregating measurement results from diverse sub-apertures, the approach effectively mitigates the influence of assorted random errors on measurement accuracy, thereby markedly enhancing the precision of pointing deviation measurements. Illustrating the efficacy of these methodologies, the paper exemplifies their application within the ambit of the "Tianqin Plan" for space-based gravitational wave detection. Employing numerical simulations and factoring in the design parameters of the Hartmann sensor, the study performs a meticulous analysis of pointing deviation measurement accuracy. Comparative analysis between single sub-aperture and sub-aperture correlation reuse technologies reveals a compelling enhancement in measurement accuracy, approximating a sevenfold improvement with the latter. The pointing deviation measurement accuracy achieved through sub-aperture correlation reuse technology is quantified at approximately 18.81 nanoradians. Considering the optical magnification inherent in spaceborne telescopes, estimated at around 30 times, the resultant pointing deviation measurement accuracy reaches an impressive 0.62 nanoradians. This design precision significantly surpasses the stipulated 1 nanoradian accuracy requirement for ground-based gravitational wave pointing deviation measurements. As a prudential measure, the proposed design incorporates a substantial margin to accommodate potential accuracy diminution attributable to external perturbations during empirical testing.
星载望远镜 指向偏差测量 哈特曼 多子孔径空间复用 spaceborne telescope pointing deviation measurement Hartmann multi-subaperture spatial multiplexing 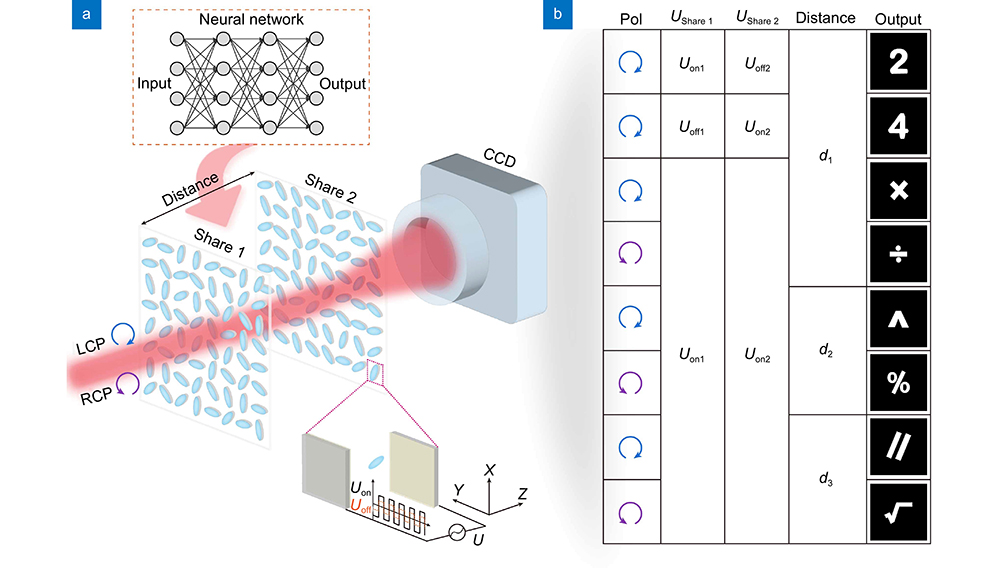
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Photonic Chips, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Centre for Artificial-Intelligence Nanophotonics, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
3 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Secret sharing is a promising technology for information encryption by splitting the secret information into different shares. However, the traditional scheme suffers from information leakage in decryption process since the amount of available information channels is limited. Herein, we propose and demonstrate an optical secret sharing framework based on the multi-dimensional multiplexing liquid crystal (LC) holograms. The LC holograms are used as spatially separated shares to carry secret images. The polarization of the incident light and the distance between different shares are served as secret keys, which can significantly improve the information security and capacity. Besides, the decryption condition is also restricted by the applied external voltage due to the variant diffraction efficiency, which further increases the information security. In implementation, an artificial neural network (ANN) model is developed to carefully design the phase distribution of each LC hologram. With the advantage of high security, high capacity and simple configuration, our optical secret sharing framework has great potentials in optical encryption and dynamic holographic display.
holographic encryption optical secret sharing cascaded liquid crystal hologram multi-dimensional multiplexing Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230121

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Inspur Artificial Intelligence Research Institute Company Limited, Jinan 250013, China
2 MIIT Key Laboratory of Photonics Information Technology, School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
Active metasurfaces have recently attracted more attention since they can make the light manipulation be versatile and real-time. Metasurfaces-based holography possesses the advantages of high spatial resolution and enormous information capacity for applications in optical displays and encryption. In this work, a tunable polarization multiplexing holographic metasurface controlled by an external magnetic field is proposed. The elaborately designed nanoantennas are arranged on the magneto-optical intermediate layer, which is placed on the metallic reflecting layer. Since the non-diagonal elements of the dielectric tensor of the magneto-optical material become non-zero values once the external magnetic field is applied, the differential absorption for the left and right circularly polarized light can be generated. Meanwhile, the amplitude and phase can be flexibly modulated by changing the sizes of the nanoantennas. Based on this, the dynamic multichannel holographic display of metasurface in the linear and circular polarization channels is realized via magnetic control, and it can provide enhanced security for optical information storage. This work paves the way for the realization of magnetically controllable phase modulation, which is promising in dynamic wavefront control and optical information encryption.
active metasurface magneto-optical effect polarization multiplexing holography dynamic holographic display Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043601
1 复旦大学信息学院电磁波信息科学教育部重点实验室,上海 200433
2 鹏城实验室,广东 深圳 518055
3 上海低轨卫星通信与应用工程技术研究中心,上海 200433
4 上海市低轨卫星通信技术协同创新中心,上海 200433
可见光通信因其显著优势逐渐成为星间通信的研究热点。可见光通信能够提供丰富且无需授权的频谱资源,传输速率高,保密性强以及抗电磁干扰等。可见光激光通信器件发射功率较高、抗辐照能力强、激光束散角小,有望应用于星间大容量长距离通信链路传输。实现了集成的40路波分复用可见光激光通信系统,复用29个可见光波长,采用离散多音比特加载调制和Levin-Campello算法,达到了418.3 Gbit/s的总传输数据。针对可见光激光通信系统中的带宽受限和高频衰落的问题,该系统采用了数字预均衡技术,根据该系统的信号特点,设计了相应的佐贝尔网络,通过增强高频信号能量和减小低频信号能量实现整体通信性能的提升。实验表明,数字预均衡可显著提升可见光激光通信性能。该系统证明了可见光激光通信在星间大容量通信中的巨大潜力。
波分复用 激光通信 可见光通信 卫星通信 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(7): 0706002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Ministry of Education, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
All-fiber few-mode erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (FM-EDFAs) with isolation and wavelength division multiplexers (IWDMs) have been developed to enable flexible pumping in different directions. The FM-EDFA can achieve >30 dB modal gain with <0.3 dB differential modal gain (DMG). We experimentally simulate the DMG performance of a cascade FM-EDFA system using the equivalent spectrum method. The overall DMG reaches 1.84 dB after 10-stage amplification. We also build a recirculating loop to simulate the system, and the developed FM-EDFA can support transmission up to 3270 km within a 2 dB overall DMG by optimizing the few-mode fiber length in the loop.
mode division multiplexing few-mode erbium-doped fiber amplifier gain equalization Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041401
香港中文大学(深圳)人工智能与机器人研究院,广东 深圳 518172
波分复用技术已被证明可以有效提高近红外波段光通信的容量,并减小通道间串扰。 然而,迄今为止,蓝绿光波段的波分复用系统仅支持有限数量的波长通道,通道间隔较大。这是因为没有适用于可见光的具有精细波长间隔的波分复用器和解复用器。为了阐述清楚这一问题,本文综述可见光波段波分复用技术的发展,特别关注基于集成光学相控阵解复用器的密集蓝绿波分复用技术的进展。最后,对目前蓝绿波分复用技术的发展趋势进行了总结和展望。
波分复用 可见光通信 蓝绿光通信 光学相控阵 解复用器 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(7): 0706006
复旦大学信息科学与工程学院电磁波信息科学教育部重点实验室,上海 200433
为了在保持帧结构完整性的同时,低代价地传输管理和控制信号,提出面向高速频分复用相干无源光网络(FDM-CPON)的两种传输管理和控制信号传输机制,即数字端辅助管理和控制通道(AMCC)和数据通道的相加和相乘。通过将AMCC传输的通断键控(OOK)信号映射为数据通道信号幅值的变化,完成数据通道信号幅值再调制,成功将AMCC与数据通道相结合,实现了管理和控制信号与数据通道信号的同步传输。实验结果表明,在基于16QAM传输20 km光纤的200 Gbit/s FDM-CPON系统中,当AMCC的带宽和调制因子(MI)相同时,乘性AMCC对于信号性能的影响更小,自身传输信号的质量也更高。在AMCC的MI为26.1%、带宽为24.4 MHz时,乘性AMCC对信号灵敏度的惩罚比加性AMCC小3 dB。以上研究为未来高速相干频分复用无源光网络AMCC传输与系统设计提供重要参考。
光通信 相干无源光网络 相干光通信 光纤通信 频分复用 辅助管理和控制通道
1 重庆邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,重庆 400065
2 东北大学计算机科学与工程学院,辽宁 沈阳 110819
为了解决强度调制-直接检测正交频分复用(IM-DD OFDM)光通信系统中由光纤色散和非线性效应导致的传输性能下降的问题,提出利用正交偏振泵浦非简并四波混频(NFWM)产生的无波长偏移光学相位共轭(OPC)波对系统中的信号损伤进行光域补偿。首先在理论上推导了利用正交偏振泵浦NFWM生成OPC波的原理,基于上述原理,设计了无波长偏移OPC实现方式,在正交偏振态上得到与原信号波长完全一致的OPC波。然后对影响生成OPC波功率的因素进行了具体分析。最后依据优化参数设置,进行仿真验证,结果表明所提系统能够以114.375 Gbit/s的传输速率在长度为240 km的标准单模光纤链路中传输。
光通信 强度调制-直接检测 正交频分复用 色散补偿 非线性抑制 光学相位共轭
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonics Research Centre, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Technology & Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
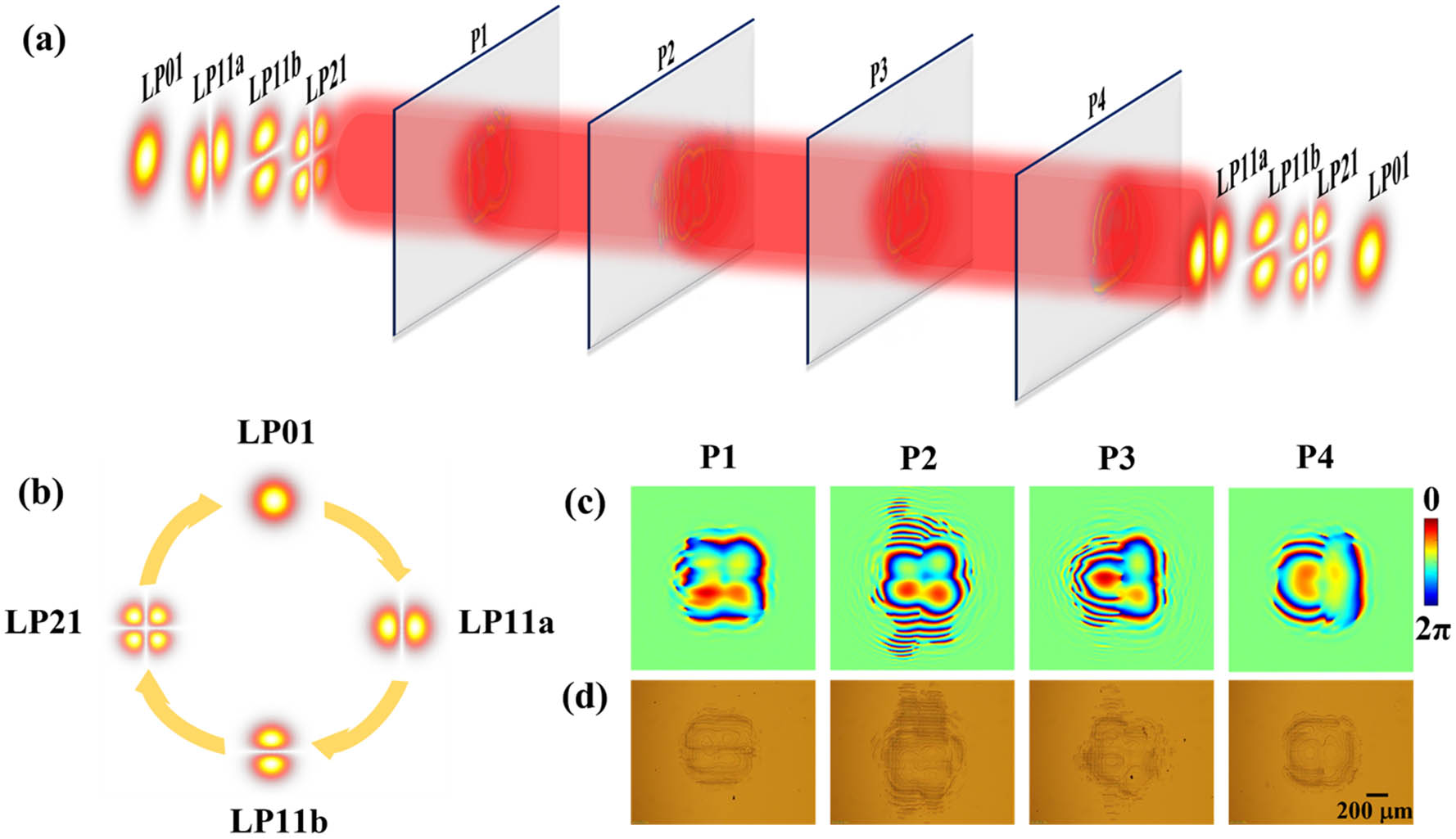
Data exchange between different mode channels is essential in the optical communication network with mode-division multiplexing (MDM). However, there are challenges in realizing mode exchange with low insert loss, low mode crosstalk, and high integration. Here, we designed and fabricated a mode exchange device based on multiplane light conversion (MPLC), which supports the transmission of LP01, LP11a, LP11b, and LP21 modes in the C-band and L-band. The simulated exchanged mode purities are greater than 85%. The phase masks were fabricated on a silicon substrate to facilitate the integration with optical systems, with an insert loss of less than 2.2 dB and mode crosstalk below -21 dB due primarily to machining inaccuracies and alignment errors. We carried out an optical communication experiment with 10 Gbit/s OOK and QPSK data transmission at the wavelength of 1550 nm and obtained excellent performance with the device. It paves the way for flexible data exchange as a building block in MDM optical communication networks.
mode exchange mode-division multiplexing multiplane light conversion Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 030602





