2023, 21(3) Column
Atmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental Optics Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Imaging Systems and Image Processing Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Nonlinear Optics Optoelectronics Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Spectroscopy Nanophotonics, Metamaterials, and Plasmonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第21卷 第3期
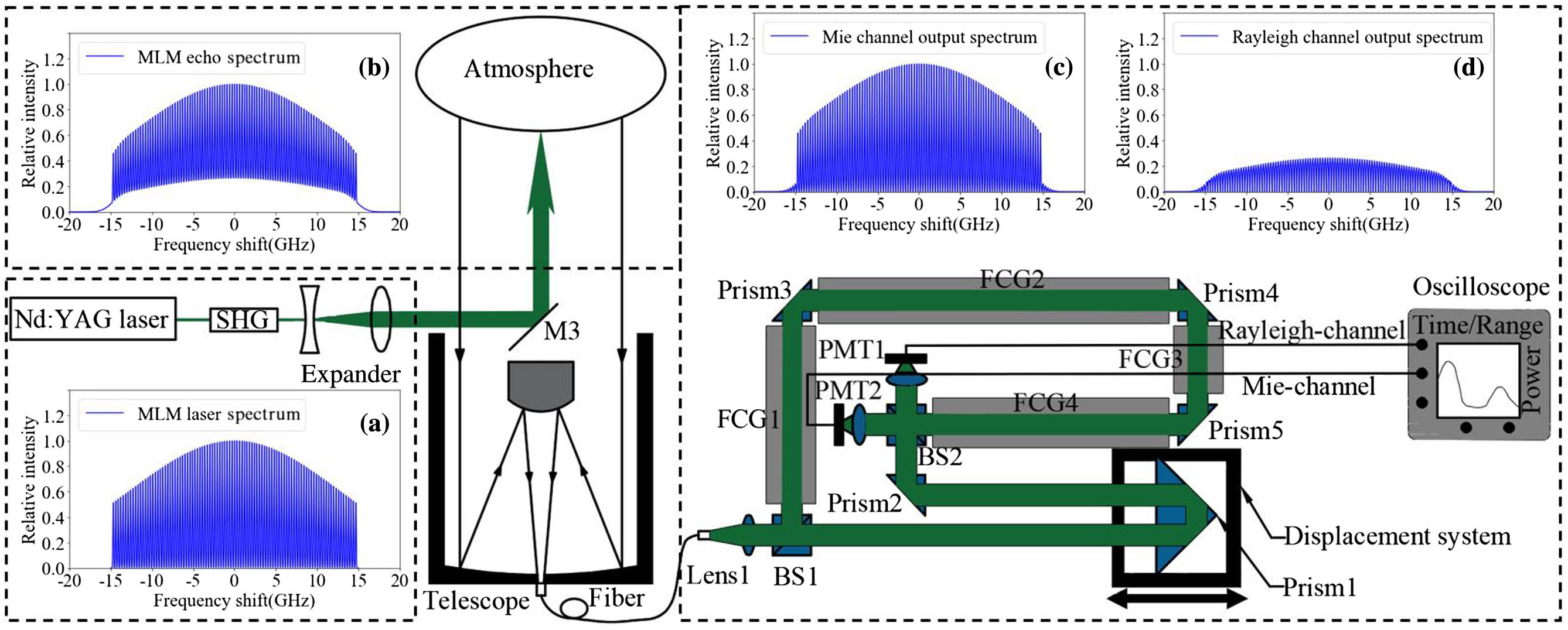
The multilongitudinal mode (MLM) high-spectral-resolution lidar (HSRL) based on the Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) is constructed in Xi’an for accurate measurements of aerosol optical properties. The critical requirement of the optimal match between the free spectral range of MZI and the longitudinal mode interval of the MLM laser is influenced by the laboratory temperature, pressure, and vibration. To realize the optimal separation of aerosol Mie scattering signals and molecular Rayleigh scattering signals excited by the MLM laser, a self-tuning technique to dynamically adjust the optical path difference (OPD) of the MZI is proposed, which utilizes the maximum ratio between the received power of the Mie channel and Rayleigh channel as the criterion of the OPD displacement. The preliminary experiments show the feasibility of the MLM-HSRL with self-tuning MZI and the stable performance in the separation of aerosol Mie scattering signals and molecular Rayleigh scattering signals.
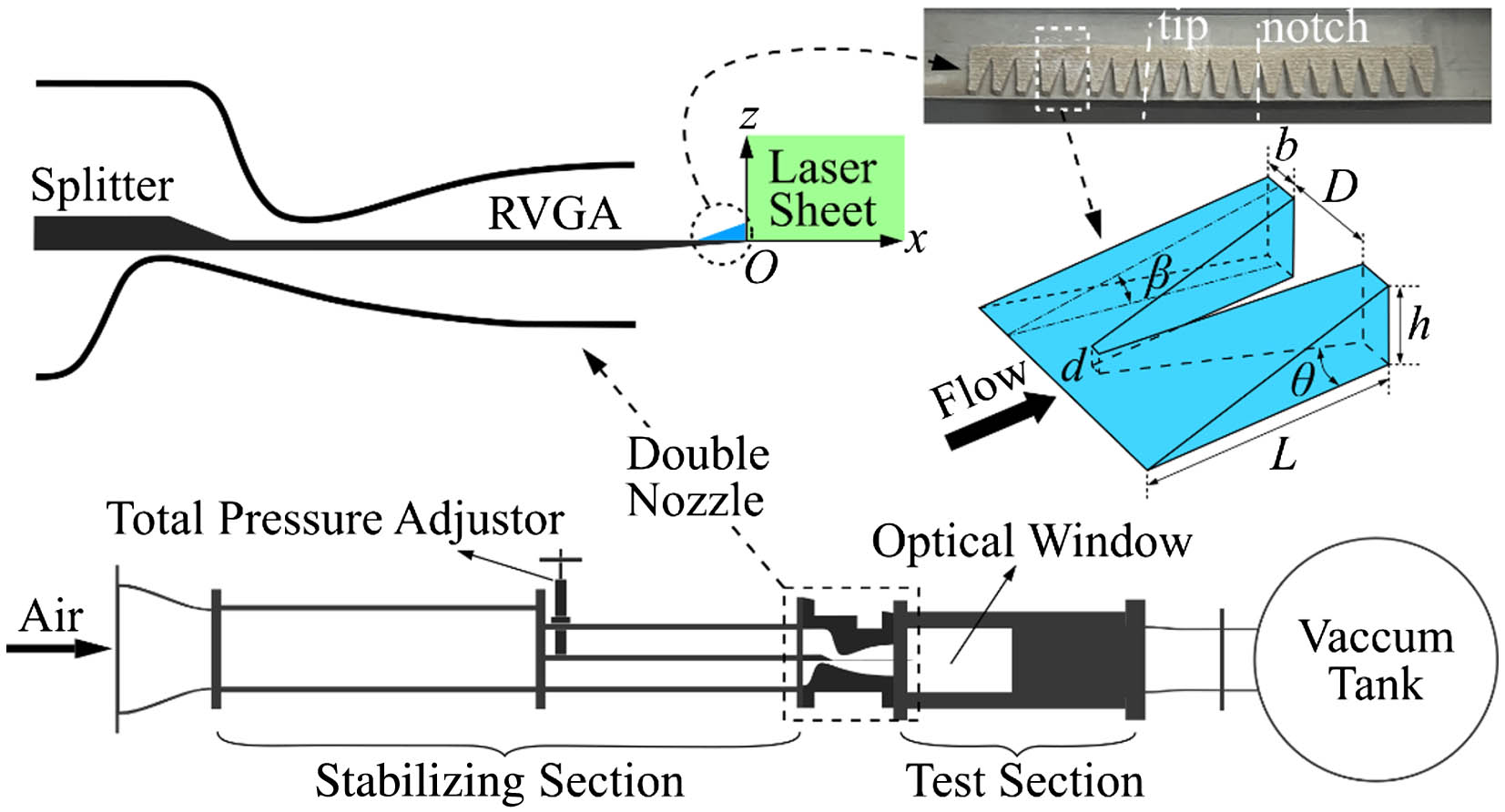
high-spectral-resolution lidar aerosol optical properties multilongitudinal mode laser self-tuning Mach–Zehnder interferometer The infrared imaging windows of the hyper/supersonic optical dome are encountering severe aero-optical effects (AOEs), so a flow control device, the ramp vortex generator array (RVGA) is proposed based on the ramp vortex generator to inhibit the supersonic mixing layers’ AOE, which is done by the nanotracer-based planar laser scattering technique and ray-tracing method. The experiments prove that under different pressure conditions, RVGA can reduce the mean and standard deviation of the root mean square of the optical path difference (
aero-optical effects supersonic mixing layer RVGA OPDrms flow control The converging lens is one of the key components in high-resolution terahertz imaging. In this Letter, a binary diffractive lens is proposed for the scanning imaging system working at 278.6 GHz, in which a convergent beam with a waist diameter of 0.65 mm is generated, and 1 mm lateral imaging resolution is realized. This low-cost terahertz lens, constituted by concentric rings with different radii, is optimized by stimulated annealing algorithm and fabricated by three-dimensional printing. Compared with the conventional transmissive convex lens, higher resolution and enhanced imaging quality are achieved via smaller focal spot of the illumination beam. This type of lens would promote terahertz imaging closer to practical applications such as nondestructive testing and other scenarios.
terahertz imaging binary diffractive lens phase modulation three-dimensional printing Self-healing in optics generally refers to the ability to reconstruct itself and restore the original state after encountering obstacles in the propagation of the light field. In this research, we observe the processes of the wave fields from perfect to defect in front of the focal plane of the 4f system, finally returning to an intact situation after the plane. According to simulations and experimental results, there is a minimum self-healing distance for the moiré lattice field that positively associates with the radius of the defect (obstacle) in the nondiffracting transmission range. Furthermore, it is observed that the defect self-healing is a process of “repairing the center and then repairing the edges.” These findings can be applied in areas such as optical imaging, capture, and information processing.
moiré lattice nondiffraction self-healing wave field Speckle backpropagation for compensation of nonlinear effects in few-mode optical fibers Download:642次
Download:642次
 Download:642次
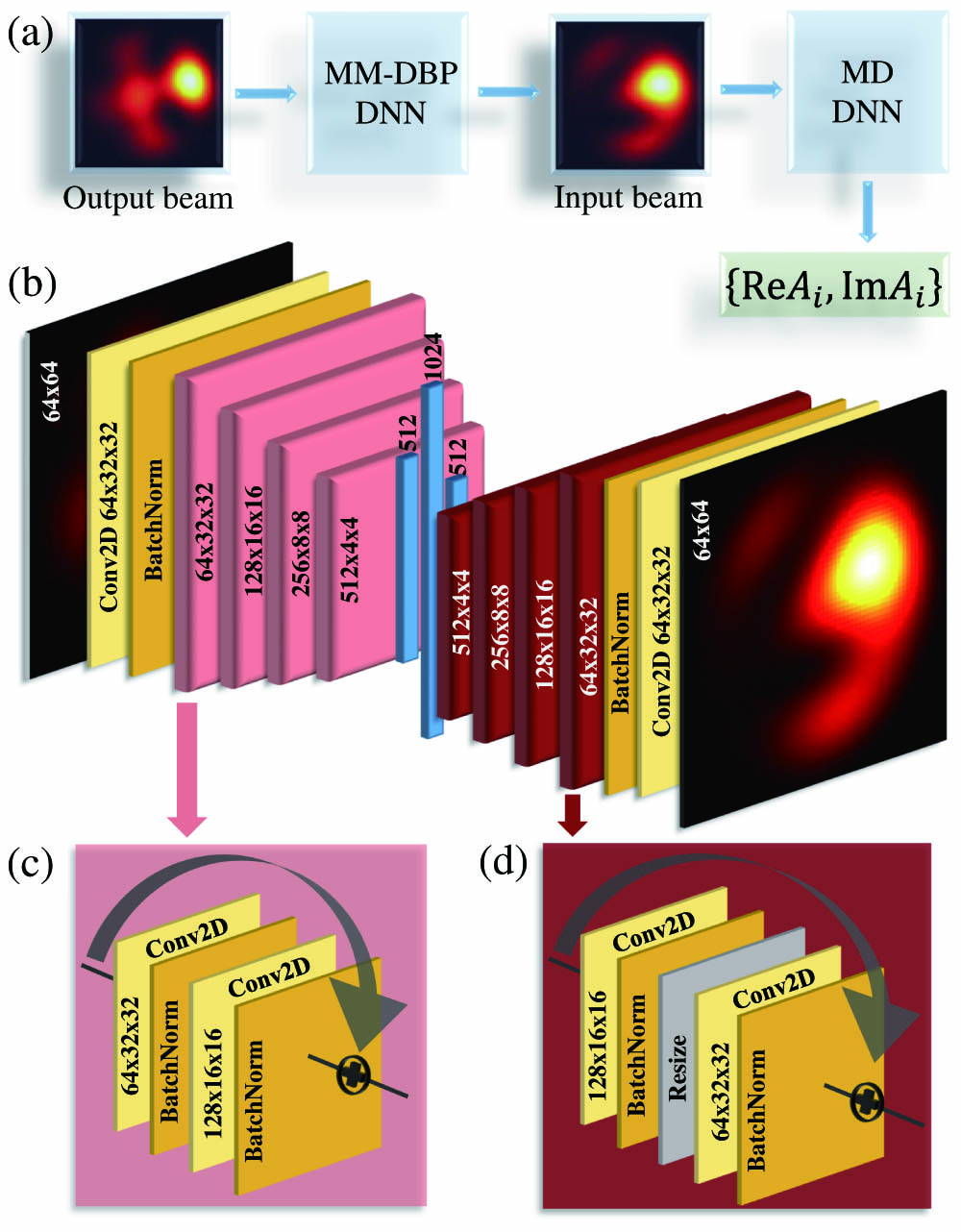
Download:642次We propose an alternative approach to compensation of intermodal interactions in few-mode optical fibers by means of digital backpropagation. Instead of solving the inverse generalized multimode nonlinear Schrödinger equation, we accomplish backpropagation of the multimode signals with help of their near-field intensity distributions captured by a camera. We demonstrate that this task can successfully be handled by a deep neural network and provide a proof of concept by training an autoencoder for backpropagation of six linearly polarized (LP) modes of a step-index fiber.
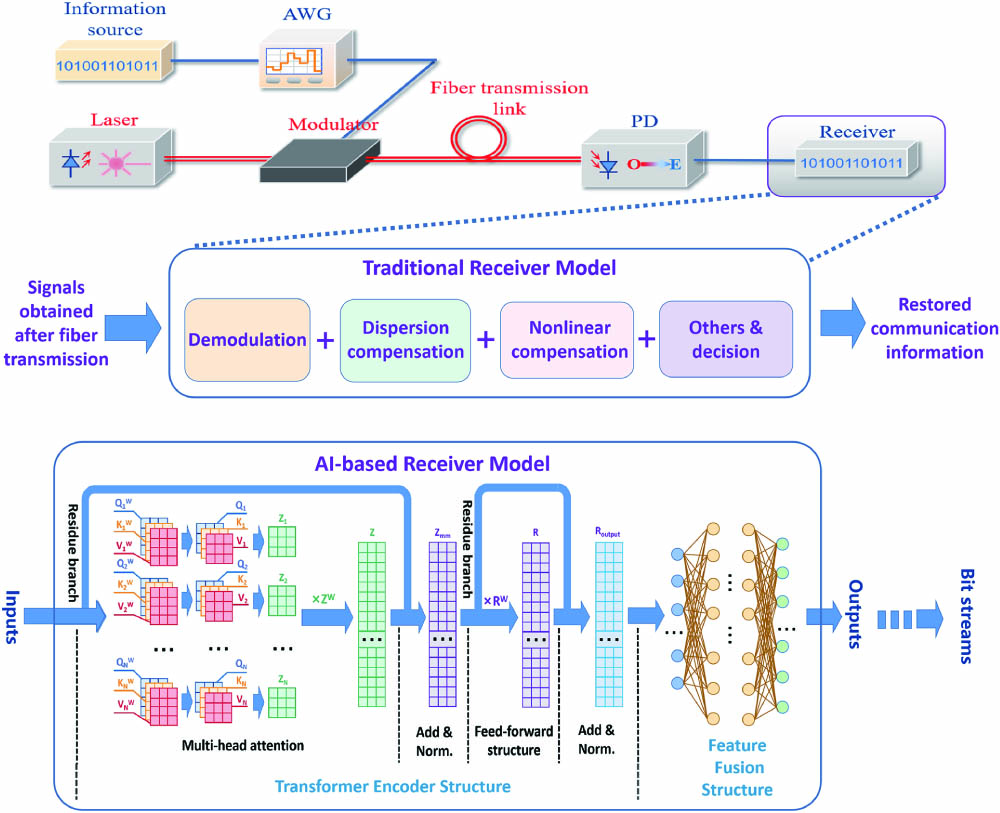
optical fibers multimode fibers few-mode fibers digital signal processing space division multiplexing mode division multiplexing mode decomposition In this paper, an artificial-intelligence-based fiber communication receiver model is put forward. With the multi-head attention mechanism it contains, this model can extract crucial patterns and map the transmitted signals into the bit stream. Once appropriately trained, it can obtain the ability to restore the information from the signals whose transmission distances range from 0 to 100 km, signal-to-noise ratios range from 0 to 20 dB, modulation formats range from OOK to PAM4, and symbol rates range from 10 to 40 GBaud. The validity of the model is numerically demonstrated via MATLAB and Pytorch scenarios and compared with traditional communication receivers.
fiber receiver model neural networks multi-head attention mechanism This paper utilizes uniquely decodable codes (UDCs) in an M-to-1 free-space optical (FSO) system. Benefiting from UDCs’ nonorthogonal nature, the sum throughput is improved. We first prove that the uniquely decodable property still holds, even in optical fading channels. It is further discovered that the receiver can extract each source’s data from superimposed symbols with only one processing unit. According to theoretical analysis and simulation results, the throughput gain is up to the normalized UDC’s sum rate in high signal-to-noise ratio cases. An equivalent desktop experiment is also implemented to show the feasibility of the UDC-FSO structure.
free-space optics throughput enhancement uniquely decodable code For speckle-correlation-based scattering imaging, an iris is generally used next to the diffuser to magnify the speckle size and enhance the speckle contrast, which limits the light flux and makes the setup cooperative. Here, we experimentally demonstrate a non-iris speckle-correlation imaging method associated with an image resizing process. The experimental results demonstrate that, by estimating an appropriate resizing factor, our method can achieve high-fidelity noncooperative speckle-correlation imaging by digital resizing of the raw captions or on-chip pixel binning without iris. The method opens a new door for noncooperative high-frame-rate speckle-correlation imaging and benefits scattering imaging for dynamic objects hidden behind opaque barriers.
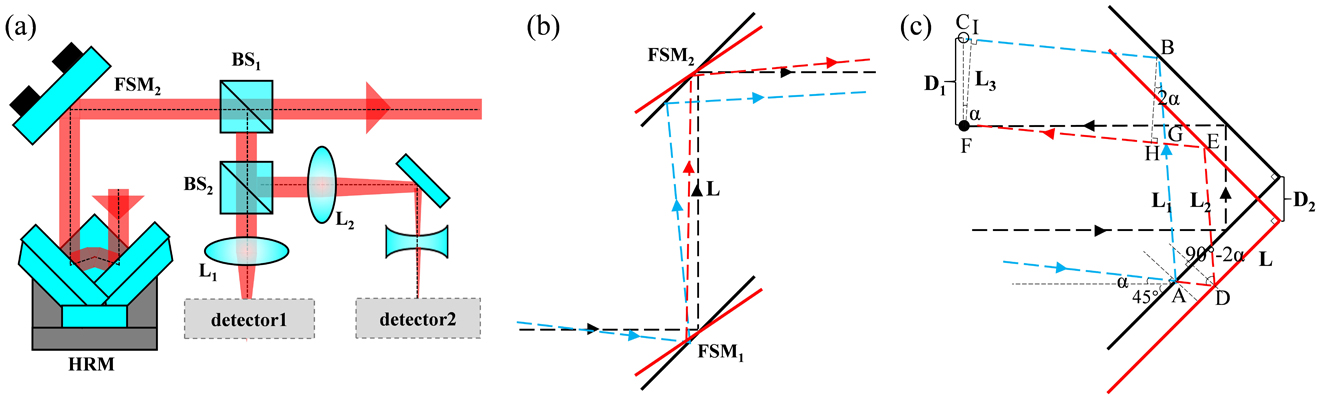
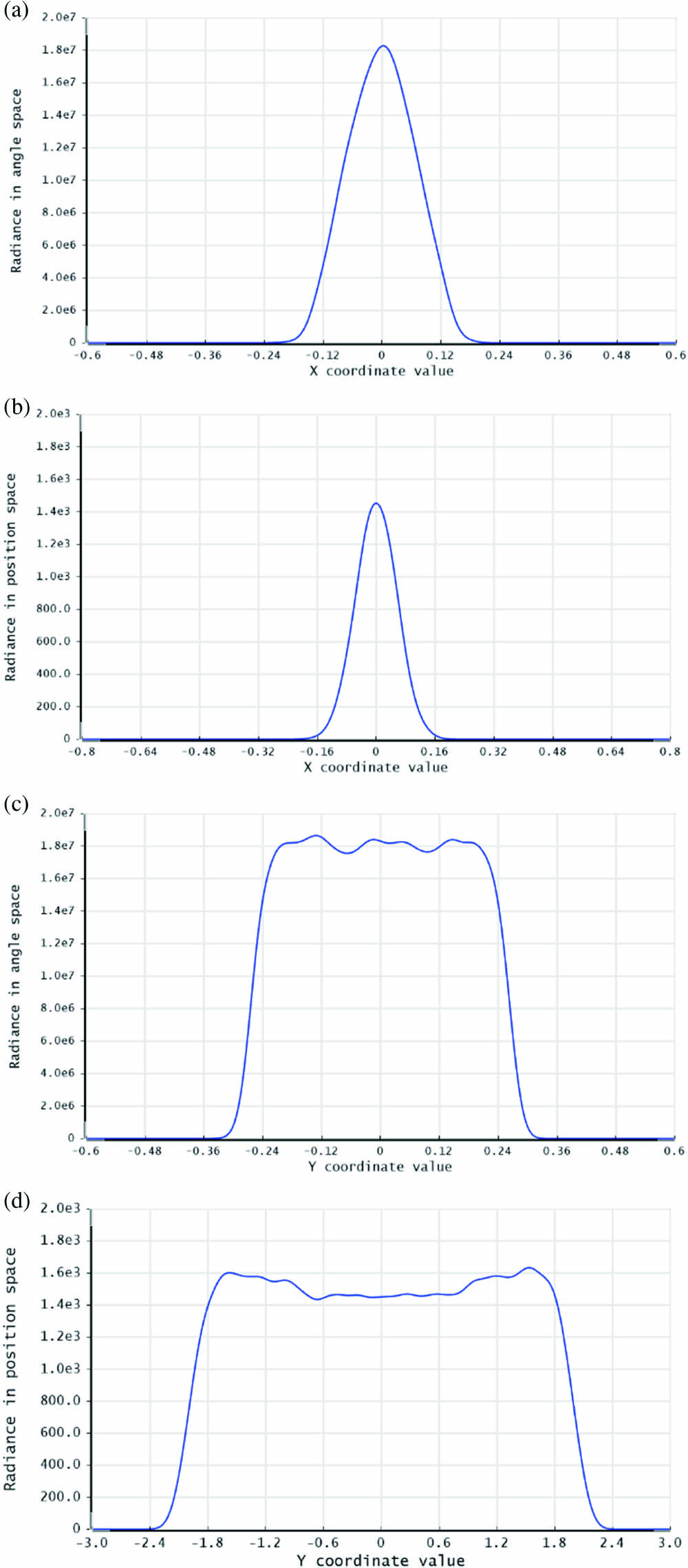
speckle correlation image resizing pixel binning We propose a new method for the development of multi-beam systems for the spatial alignment and stability of beams based on the error separation technique. This method avoids alignment errors caused by coupling effect of piezoelectric devices, inaccurate correction calculations, and detection mode of the angular deviation. According to the results by external detectors, the error value of spatial alignment and the root mean square (RMS) of deviations under control during 1 h can be equivalent to approximately 0.87 and 1.06 nm at the sample plane under an oil immersion lens (focal length f
Although previously reported terahertz absorbers can achieve high-sensitivity refractive index sensing, the resonant peak is too broad, which leads to a low figure of merit (FOM). Transmissive sensors based on bound states in the continuum (BIC) can achieve high FOM, but they have some limitations in high sensitivity. Herein, we propose a periodic triple parallel metal bars structure to obtain high quality, a strong field, and multiple hot spots by the Friedrich–Wintgen BIC. Numerical results show the sensitivity and FOM can reach 1877 GHz/RIU and 665, respectively. Compared to the previously reported transmissive sensors based on BIC, the sensitivity has been greatly improved.
Fano resonance bound states in the continuum terahertz high-sensitivity sensing More durable (with high impact force), lighter, and more compact flexible azo dye micropolarizers are attractive candidates for low-cost, simple polarization imaging systems. The liquid crystal polymer (LCP), as an emerging material developed by photo-alignment technology, is a potential material for organizing the long-range ordered structure of azo dyes. However, little research has been done on LCP aligned azo dyes. This paper points out and solves a key problem that restricts the fabrication of high-precision arrays in guest (azo dye)-host (LCP) systems: the doping of dyes leads to disorder of the LCP during curing. After solving the problem, the relationship between the thickness of the LCP and the extinction ratio of the polarizing film was investigated, which effectively improved the extinction ratio. Alignment of azo dye molecules in the range of 2 µm (0°–180°) and arrays of micropolarizers (0°, 45°, 90°,
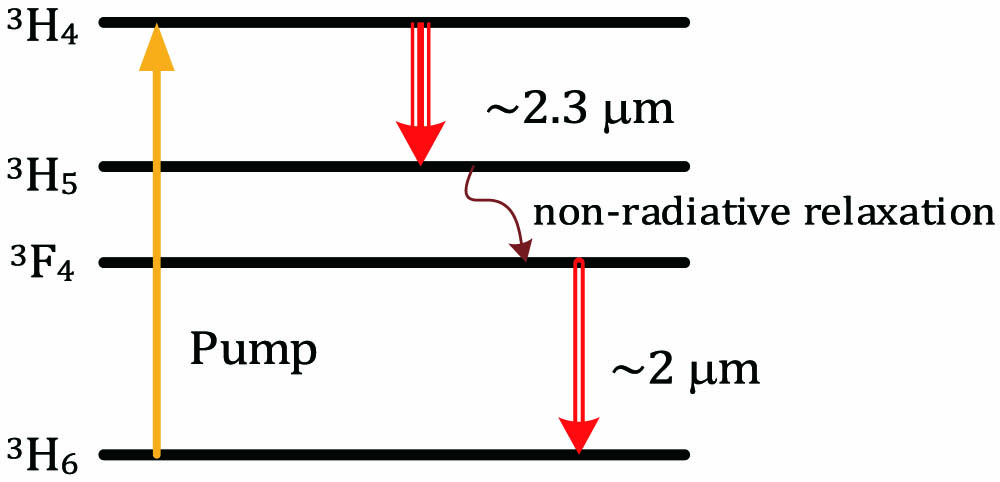
micropolarizer polarimetric imaging polarimetry azo dye polarization-sensitive devices A diode-pumped continuous-wave
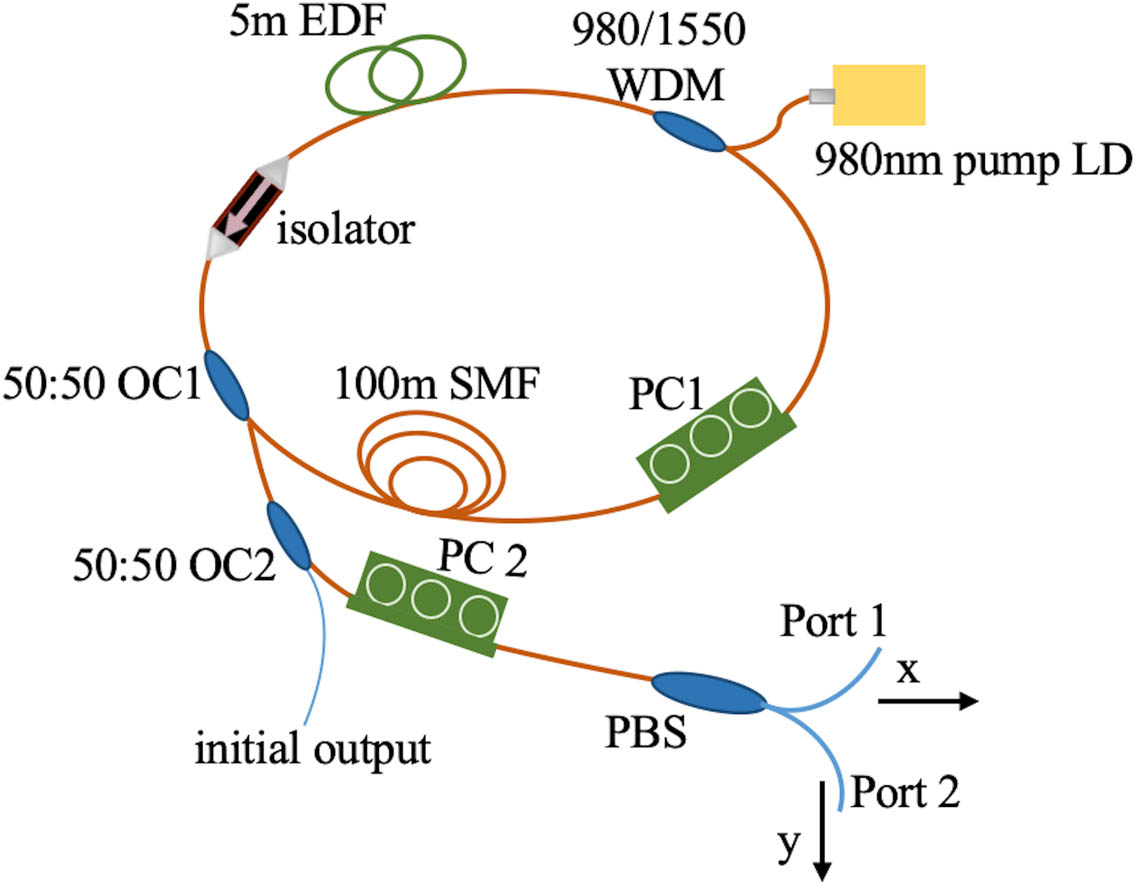
Tm:YVO4 crystal three-wavelength 3H4 → 3H5 transition We have observed various polarization domains and a giant self-mode-locked pulse in a 130 m long erbium-doped fiber laser without any mode-locking devices. By adjusting the intracavity polarization controller, we investigated the evolution process of the polarization domain with the varying cavity birefringence. When the birefringence was close to zero, the polarization domains split into multidomains, and finally a giant self-mode-locked pulse formed for the first time. We analyzed that the generation of the self-mode-locked pulse was related to the multiple subdomains ascribed to the strong coherent cross coupling between the orthogonal polarization light components in the long fiber cavity.
fiber lasers polarization domains self-mode-locked pulse nonlinear optics Serrated periodic electrode for high energy efficiency and large bandwidth acousto-optic modulators Download:633次
Download:633次
 Download:633次
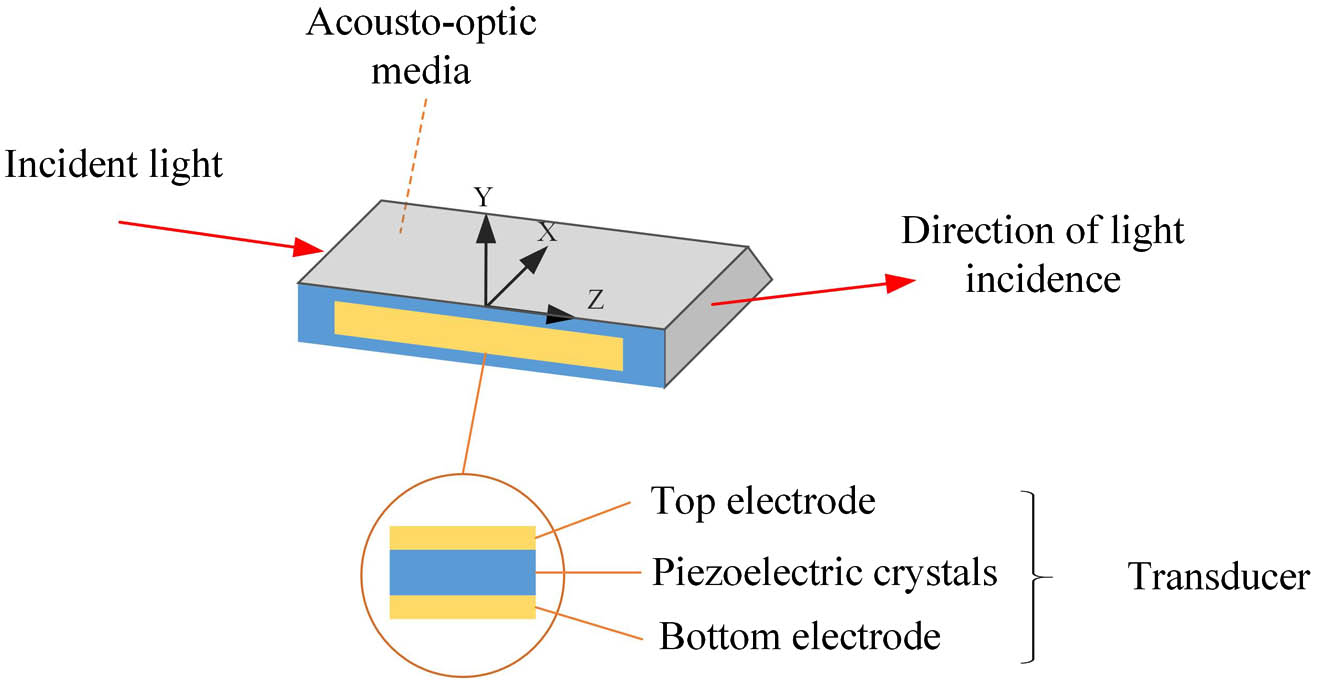
Download:633次In an acousto-optic modulator, the electrode shape plays an important role in performance, since it affects the distribution of the acoustic field. The acousto-optic modulator based on the conventional rectangular electrode has the problems of low energy efficiency and small modulation bandwidth due to an imperfect acoustic field. In this paper, a new serrated periodic electrode has been proposed for using acousto-optic modulator transducers. The proposed electrode has the following advantages. By using serrated periodic electrodes to suppress the sidelobes, the collimation of the acoustic field in the direction perpendicular to the light incidence is improved. This makes the acousto-optic modulator have a stable diffraction efficiency fluctuation and high energy efficiency. In addition, the electrode has a large divergence angle in the direction of light incidence, so a large bandwidth can be obtained. The simulations and experiments demonstrate that the serrated periodic electrode has an increased bandwidth and high energy efficiency.
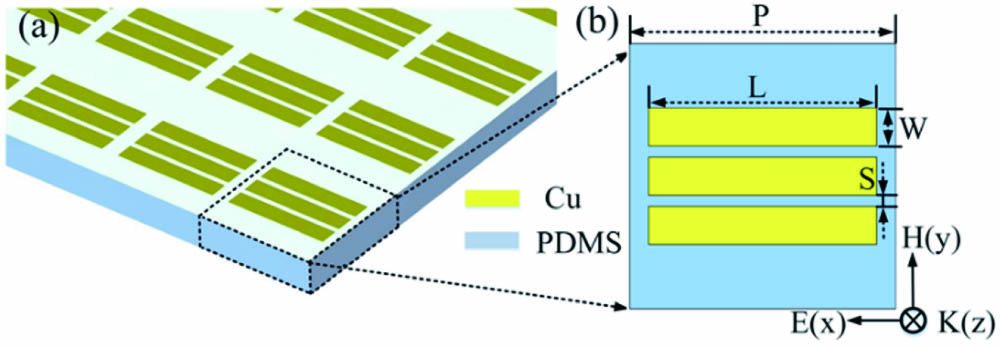
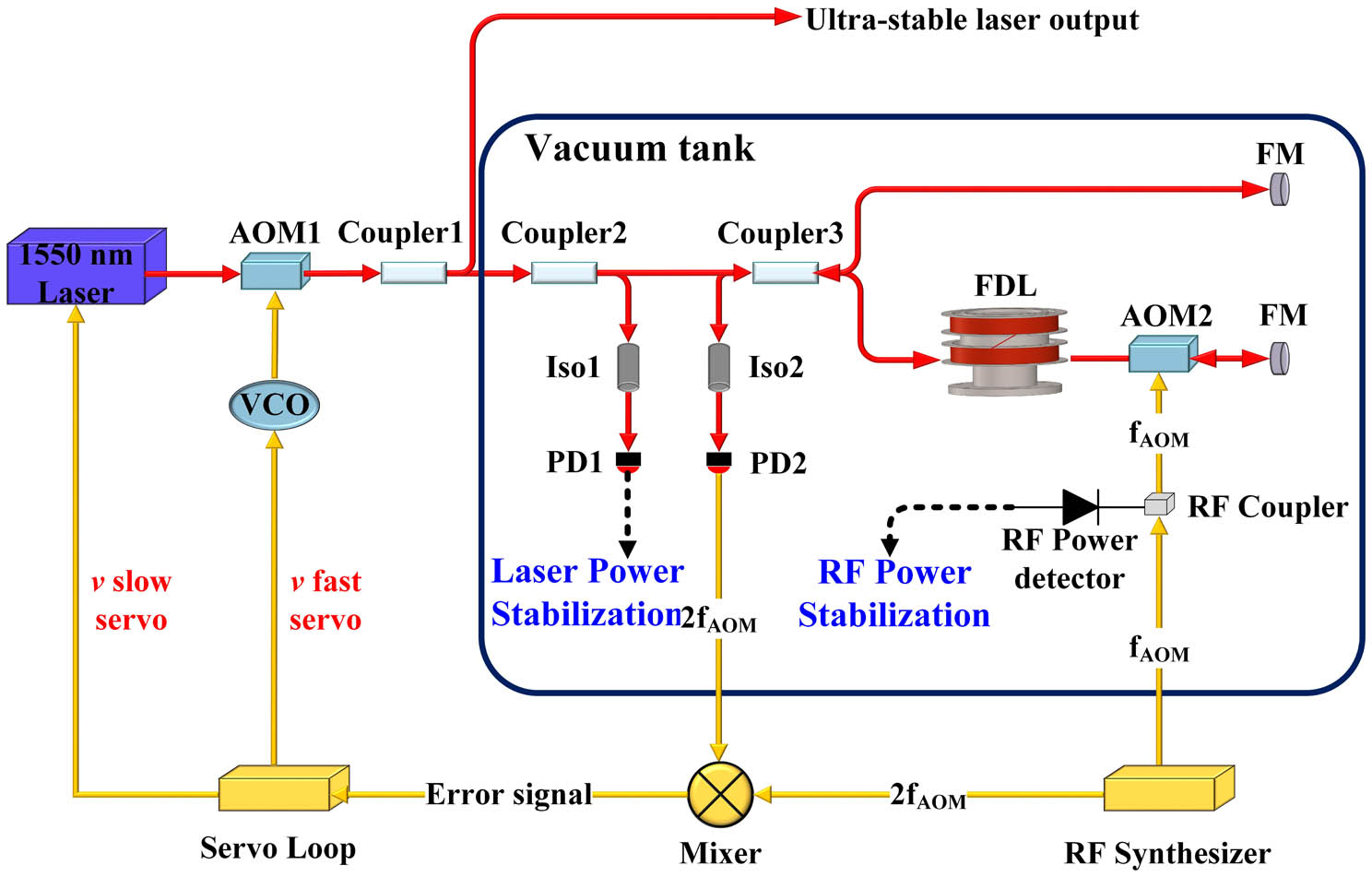
acousto-optic modulator serrated periodic electrode large bandwidth low power consumption We demonstrate an ultrastable miniaturized transportable laser system at 1550 nm by locking it to an optical fiber delay line (FDL). To achieve optimized long-term frequency stability, the FDL was placed into a vacuum chamber with a five-layer thermal shield, and a delicate two-stage active temperature stabilization, an optical power stabilization, and an RF power stabilization were applied in the system. A fractional frequency stability of better than
fiber delay line frequency stability ultrastable laser Beam homogenization structure for a laser illuminator design based on diode laser beam combining technology Download:579次
Download:579次
 Download:579次
Download:579次With the rapid development of laser technology, laser as the light source of night vision illuminating can realize long-distance and clear imaging, which has been widely used in laser active illuminating field. A high-power diode laser with a wavelength of 808 nm was designed as the laser active illuminating source, and the output power of no less than 100 W was obtained by spatial beam multiplexing, polarization multiplexing, and high efficiency fiber coupling techniques. In view of the beam homogenization of illuminating source, a novel beam homogenization system based on waveguide is proposed in this work. A square spot with a horizontal divergence angle of 40°, a vertical divergence angle of 10°, and an illuminating power ratio of 4:1 was obtained by a collimating lens. Comparing with the traditional circular illuminating beam, the square illuminating beam can match the illuminating angle of CCD camera better, and the energy utilization rate is higher. In addition, by optimizing the structure of waveguide and collimating lens, the illuminating angle can be changed to meet the illuminating requirements under different conditions theoretically.
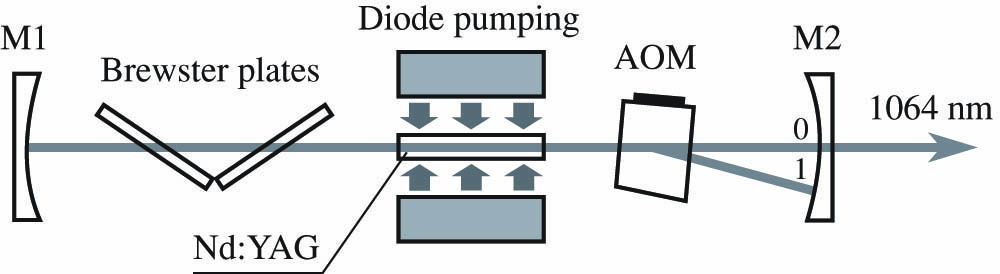
laser illumination spatial multiplexing polarization multiplexing beam homogenization waveguide A Q-switched Nd:YAG laser has been actively mode-locked at a subharmonic frequency for the first time, to the authors’ knowledge. The laser operation mode is provided by a combination of a traveling wave acousto-optic modulator and a spherical cavity mirror. The dynamics of laser generation is investigated. Pulses with a duration of 70 ps and a peak power of about 10 MW were obtained. Also presented are new results on obtaining high-power (
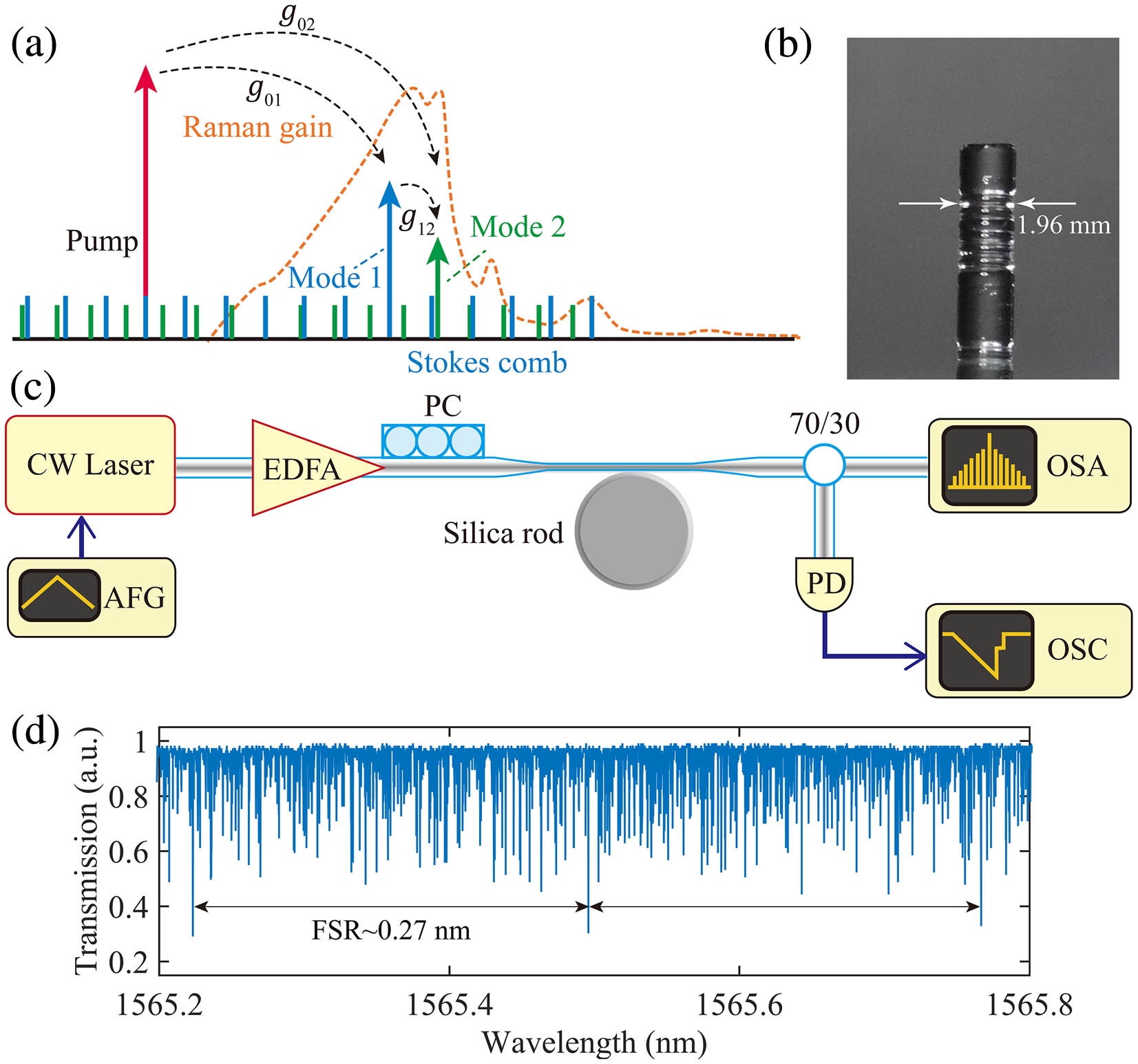
Nd:YAG laser diode pumping Q switching mode locking parametric light generators We investigate the mechanisms to realize the Raman laser switching in a silica rod microresonator with mode-interaction-assisted excitation. The laser switching can be triggered between two whispering gallery modes (WGMs) with either the same or distinct mode families, depending on the pumping conditions. The experimental observations are in excellent agreement with a theoretical analysis based on coupled-mode equations with intermodal interaction terms involved. Additionally, we also demonstrate switching of a single-mode Raman laser and a wideband spectral tuning range up to
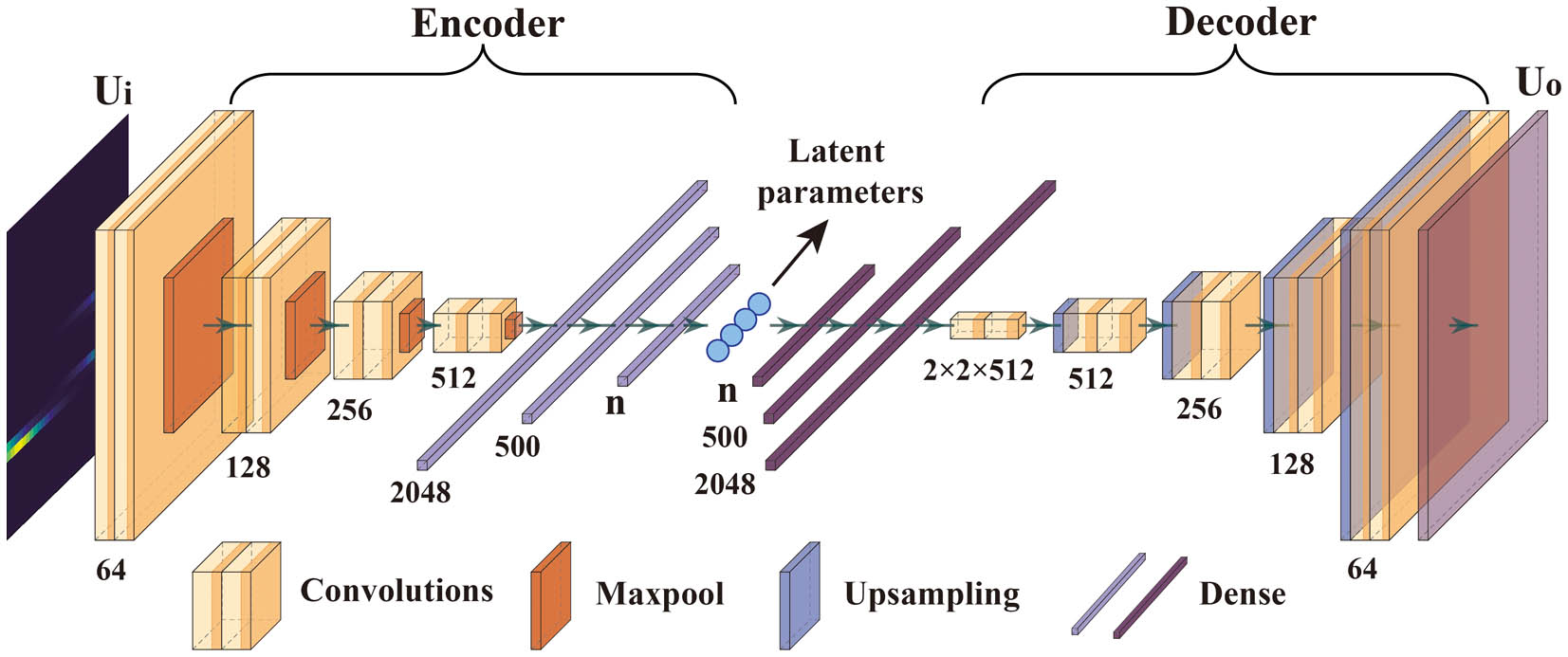
nonlinear optics devices Raman laser microresonators In this article, we use a convolutional autoencoder neural network to reduce data dimensioning and rebuild soliton dynamics in a passively mode-locked fiber laser. Based on the particle characteristic in double solitons and triple solitons interactions, we found that there is a strict correspondence between the number of minimum compression parameters and the number of independent parameters of soliton interaction. This shows that our network effectively coarsens the high-dimensional data in nonlinear systems. Our work not only introduces new prospects for the laser self-optimization algorithm, but also brings new insights into the modeling of nonlinear systems and description of soliton interactions.
fiber lasers optical solitons convolutional autoencoder neural network An exceptionally high stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) conversion efficiency to the first Stokes component associated with the secondary (low-frequency and low intensity) vibrational mode
stimulated Raman scattering secondary vibrational mode self-phase modulation ultrashort laser pulses transient phenomena High-uniformity 2 × 64 silicon avalanche photodiode arrays with silicon multiple epitaxy technology Download:559次
Download:559次
 Download:559次
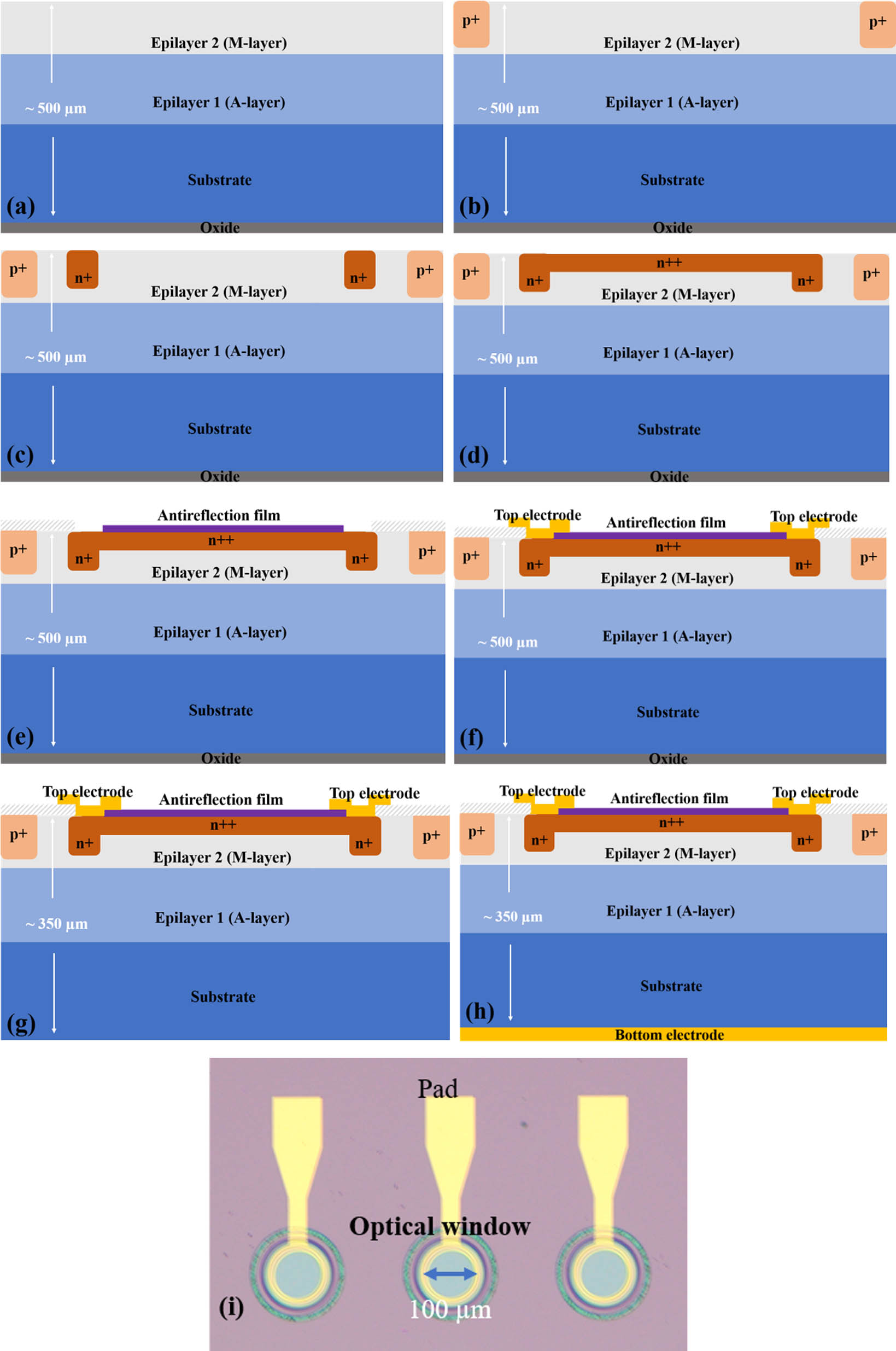
Download:559次In this paper, high-uniformity
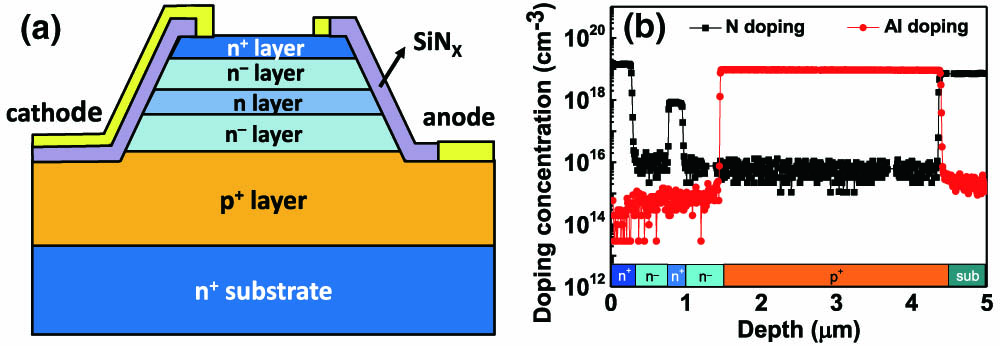
avalanche photodiode arrays silicon multiple epitaxy technology dark current In this work, high-stability 4H-SiC avalanche photodiodes (APDs) for ultraviolet (UV) detection at high temperatures are fabricated and investigated. With the temperature increasing from room temperature to 150°C, a very small temperature coefficient of 7.4 mV/°C is achieved for the avalanche breakdown voltage of devices. For the first time, the stability of 4H-SiC APDs is verified based on an accelerated aging test with harsh stress conditions. Three different stress conditions are selected with the temperatures and reverse currents of 175°C/100 µA, 200°C/100 µA, and 200°C/500 µA, respectively. The results show that our 4H-SiC APD exhibits robust high-temperature performance and can even endure more than 120 hours at the harsh aging condition of 200°C/500 µA, which indicates that 4H-SiC APDs are very stable and reliable for applications at high temperatures.
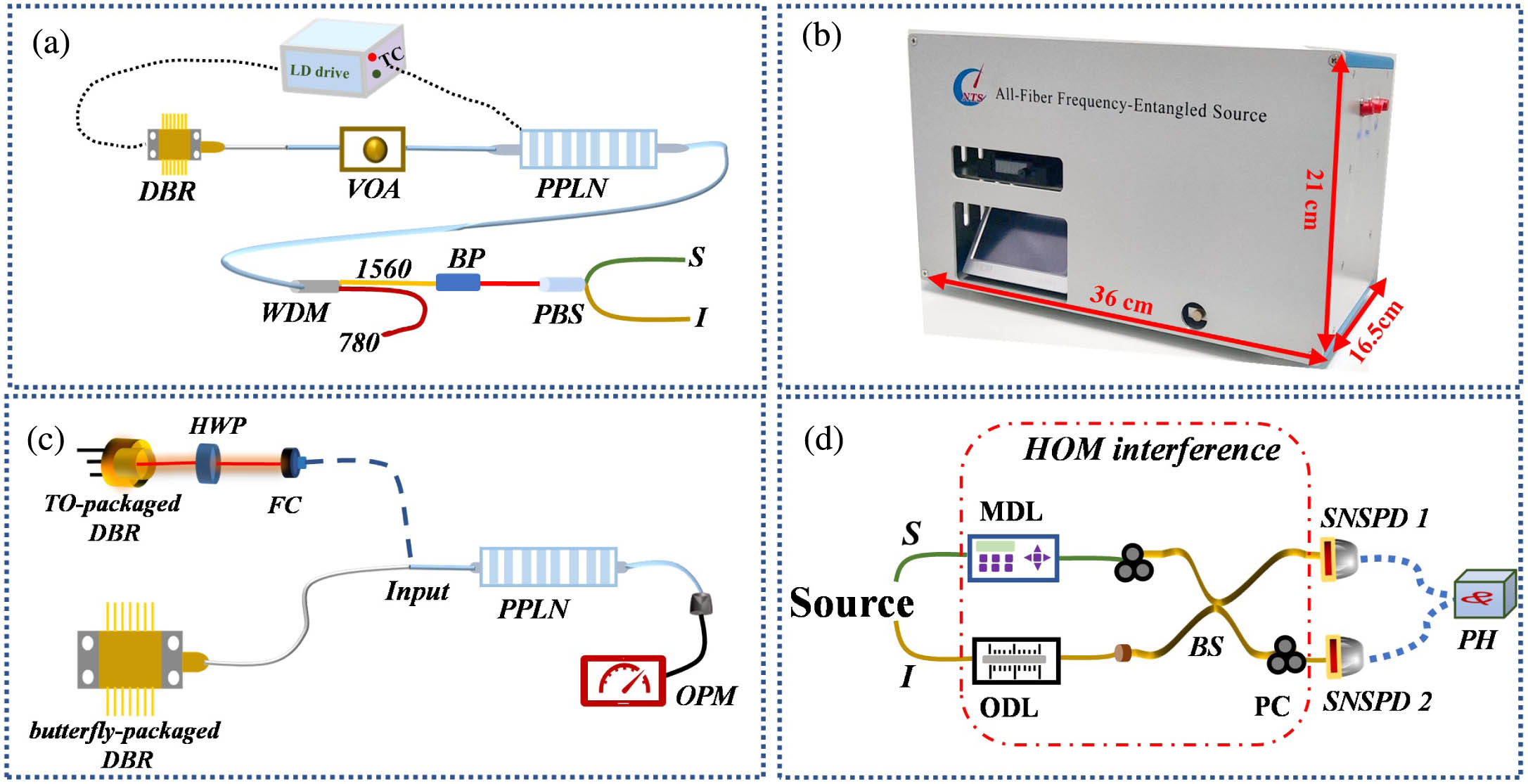
silicon carbide photodiode UV detector high temperature avalanche Geiger mode We report an all-fiber telecom-band energy-time entangled biphoton source with all physical elements integrated into a compact cabinet. At a pump power of 800 µW, the photon pairs generation rate reaches 6.9 MHz with the coincidence-to-accidental ratio (CAR) better than 1150. The long-term stability of the biphoton source is characterized by measuring the Hong–Ou–Mandel interference visibility and CAR within a continuous operation period of more than 10 h. Benefiting from the advantages of compact size, light weight, and high stability, this device provides a convenient resource for various field turnkey quantum communication and metrology applications.
energy–time entanglement all-fiber biphoton source Hong–Ou–Mandel interference Advances in multipass cell for absorption spectroscopy-based trace gas sensing technology [Invited] Download:605次
Download:605次
 Download:605次
Download:605次In the field of absorption spectroscopy, the multipass cell (MPC) is one of the key elements. It has the advantages of simple structure, easy adjustment, and high spectral coverage, which is an effective way to improve the detection sensitivity of gas sensing systems such as tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. This invited paper summarizes the design theory and the research results of some mainstream types of MPCs based on two mirrors and more than two mirrors in recent years, and briefly introduces the application of some processed products. The design theory of modified ABCD matrix and vector reflection principle are explained in detail. Finally, trends in its development are predicted.
multipass cell tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy gas sensing optical path length Cylindrical vector beam generator on photonic crystal cavity integrated with metal split ring nanoresonators Download:551次
Download:551次
 Download:551次
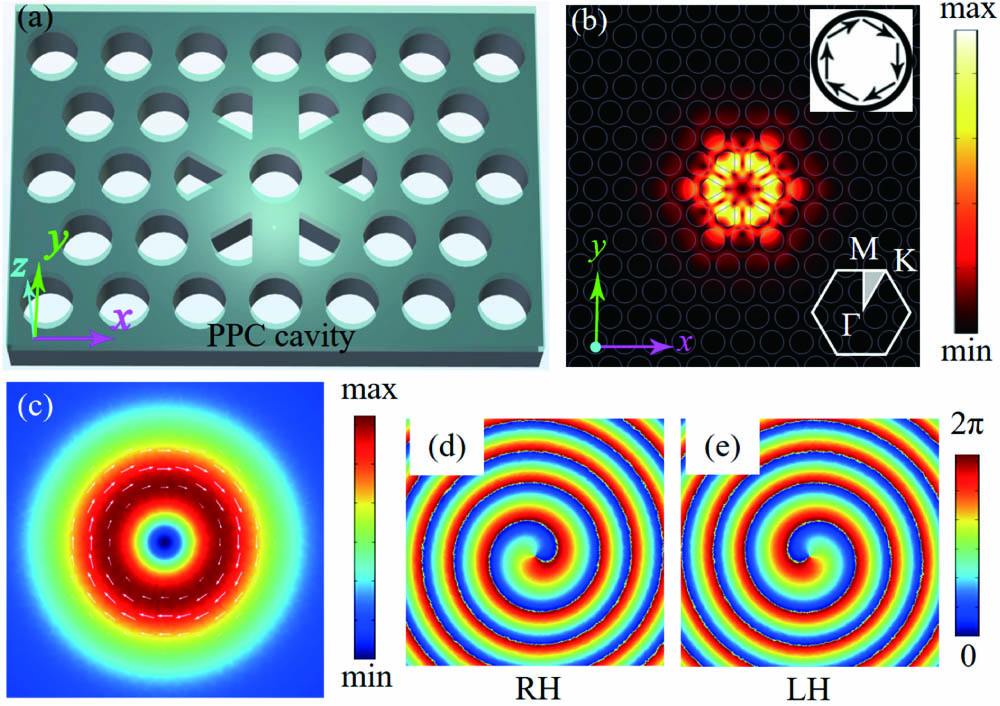
Download:551次We propose a chip-integratable cylindrical vector (CV) beam generator by integrating six plasmonic split ring resonators (SRRs) on a planar photonic crystal (PPC) cavity. The employed PPC cavity is formed by cutting six adjacent air holes in the PPC center, which could generate a CV beam with azimuthally symmetric polarizations. By further integrating six SRRs on the structure defects of the PPC cavity, the polarizations of the CV beam could be tailored by controlling the opening angles of the SRRs, e.g., from azimuthal to radial symmetry. The mechanism is governed by the coupling between the resonance modes in SRRs and PPC cavity, which modifies the far-field radiation of the resonance mode of the PPC cavity with the SRR as the nano-antenna. The integration of SRRs also increases the coupling of the generated CV beam with the free-space optics, such as an objective lens, promising its further applications in optical communication, optical tweezer, imaging, etc.
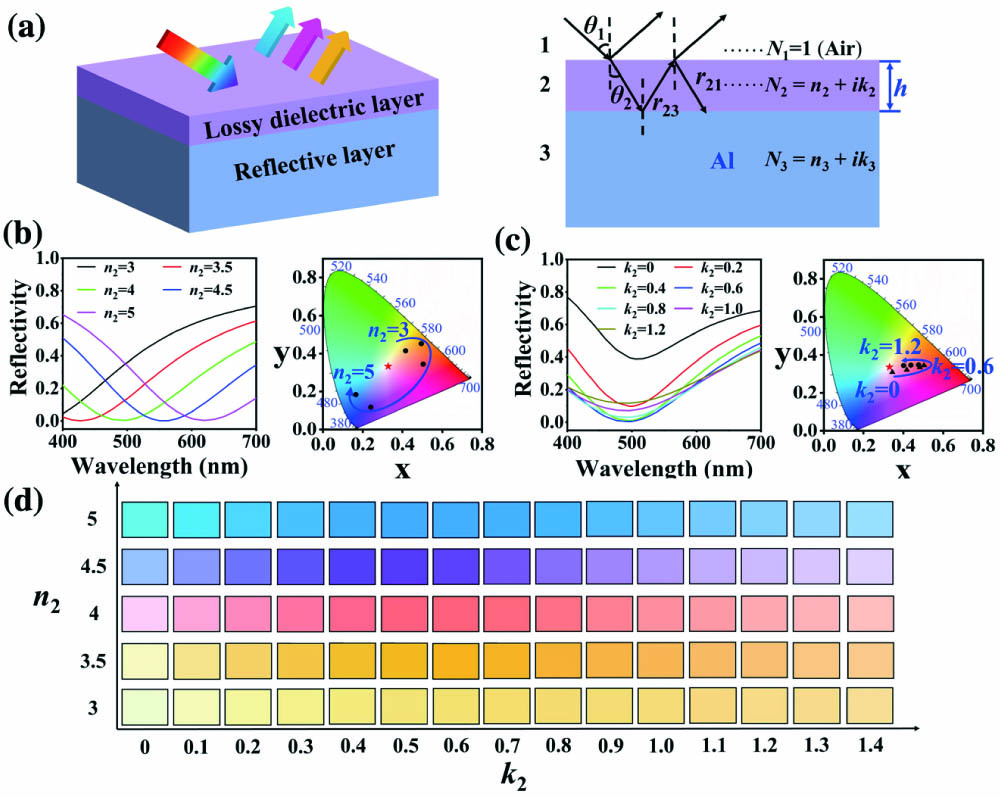
vector beams photonic crystal plasmonics integrated photonics An ultrathin angle-insensitive color filter enabling high color saturation and a wide color gamut is proposed by relying on a magnesium hydride-hydrogenated amorphous silicon (MgH2-a-Si:H) lossy dielectric layer. Based on effective medium theory, the MgH2-a-Si:H layer with an ultrathin thickness can be equivalent to a quasi-homogeneous dielectric layer with an effective complex refractive index, which can be tuned by altering the thickness of MgH2 to obtain the targeted value of the imaginary part, corresponding to the realization of high color saturation. It is verified that the proposed color filter offers highly enhanced color saturation in conjunction with a wide color gamut by introducing a few-nanometer thick MgH2 layer. As the MgH2-a-Si:H layer retains the advantages of high refractive index and tiny thickness, the proposed color filter exhibits large angular tolerance up to
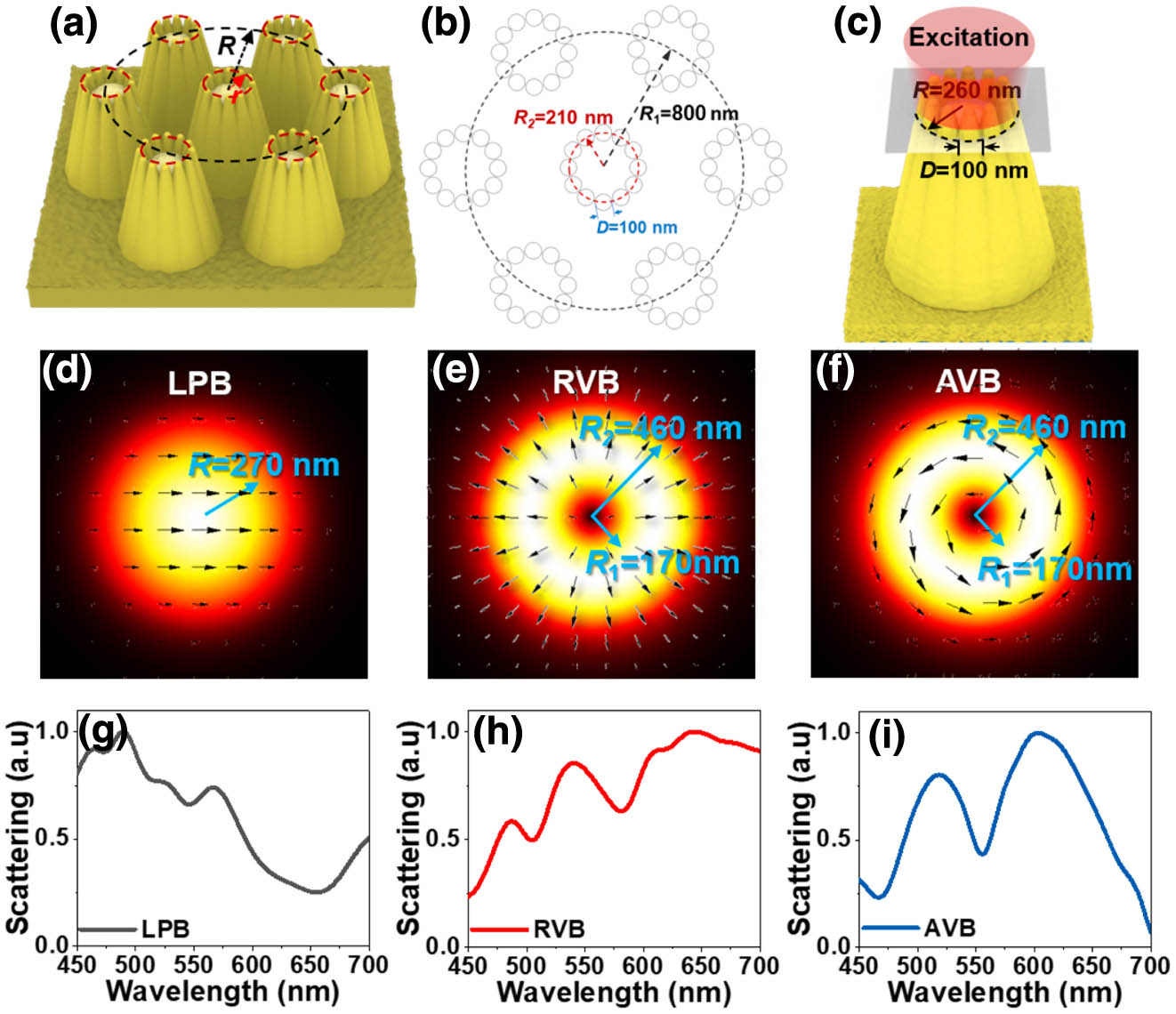
color filter effective medium theory lossy dielectric layer color saturation angle insensitivity Noble metallic nanostructures with strong electric near-field enhancement can significantly improve nanoscale light–matter interactions and are critical for high-sensitivity surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Here, we use an azimuthal vector beam (AVB) to illuminate the plasmonic tips circular cluster (PTCC) array to enhance the electric near-field intensity of the PTCC array, and then use it to improve SERS sensitivity. The PTCC array was prepared based on the self-assembled and inductive coupled plasmon (ICP) etching methods. The calculation results show that, compared with the linearly polarized beam (LPB) and radial vector beam excitations, the AVB excitation can obtain stronger electric near-field enhancement due to the strong resonant responses formed in the nanogap between adjacent plasmonic tips. Subsequently, our experimental results proved that AVB excitation increased SERS sensitivity to 10-13 mol/L, which is two orders of magnitude higher than that of LPB excitation. Meanwhile, the PTCC array had excellent uniformity with the Raman enhancement factor calculated to be
surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy plasmonic tips circular cluster array azimuthal vector beam surface plasmon polaritons 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦