Author Affiliations
Abstract
Small particle light scattering can produce light with polarization characteristics different from those of the incident beam. An analytical solution to the scattering by a spheroid with inclusion for an on-axis polarized Gaussian beam incidence is provided within the generalized Lorenz-Mie theory framework. The shapes of the inclusion can be spherical, confocal spheroid, or non-confocal spheroid. The Muller scattering matrix elements are computed for plane wave incidence or Gaussian light beam incidence. The effect of the size and shape of the inclusion or the coating on the polarized Gaussian light scattering characteristics by a spheroidal water coating aerosol particle are computed and analyzed.
290.1090 Aerosol and cloud effects 290.1350 Backscattering 290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5855 Scattering, polarization Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(1): 012901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Electronic Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
A method of chromatic polarization imaging is presented for the online detection of colorless plastic contaminants from ginned cotton in an industrial setting. To understand the experimental results, we consider a realistic microscopic model, including the multiple scattering of anisotropic fibers and the light propagation in anisotropic slabs. A Monte Carlo code, based on the extended Jones matrix, is developed to simulate photon migration with polarization states, and phase information followed. Using simulations and experiments, we analyze the underlying mechanisms and evaluate the performance of this method with different layer thicknesses. Our approaches proposed in this Letter also have the potential to be applied in tissue imaging, remote sensing, and other scenarios.
290.5855 Scattering, polarization 290.7050 Turbid media 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(9): 092901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu 610068, China
2 Department of Physics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
The far-zone scattered spectral density of a light wave on the scattering from a collection of particles is investigated, and the relationship between the character of the collection and the distribution of the scattered spectral density is discussed. It is shown that both the number of particles and their locations in the collection play roles in the distribution of the far-zone scattered spectral density. This phenomenon may provide a potential method to reconstruct the structure character of a collection of particles from measurements of the far-zone scattered spectral density.
290.2558 Forward scattering 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 102901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center on Atmospheric Environment and Equipment Technology, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
3 School of Electronic & Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
4 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Meteorological Observation and Signal Processing, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
In order to improve the inversion precision of aerosol mass concentrations based on the particle group light scattering method, the concept that particles through a laser beam are equivalent to an aggregate is proposed. A fractal model for aerosol mass concentration using the signal amplitude distribution of aggregates is presented, and then the subsection calibration method is given. The experimental results show that the mass concentrations inversed by this model agree well with those measured by the norm-referenced instrument. The average relative errors of the two experiments are 5.6% and 6.0%, respectively, which are less than those obtained by the conventional inversion model.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 120.5820 Scattering measurements 010.1100 Aerosol detection Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 112901
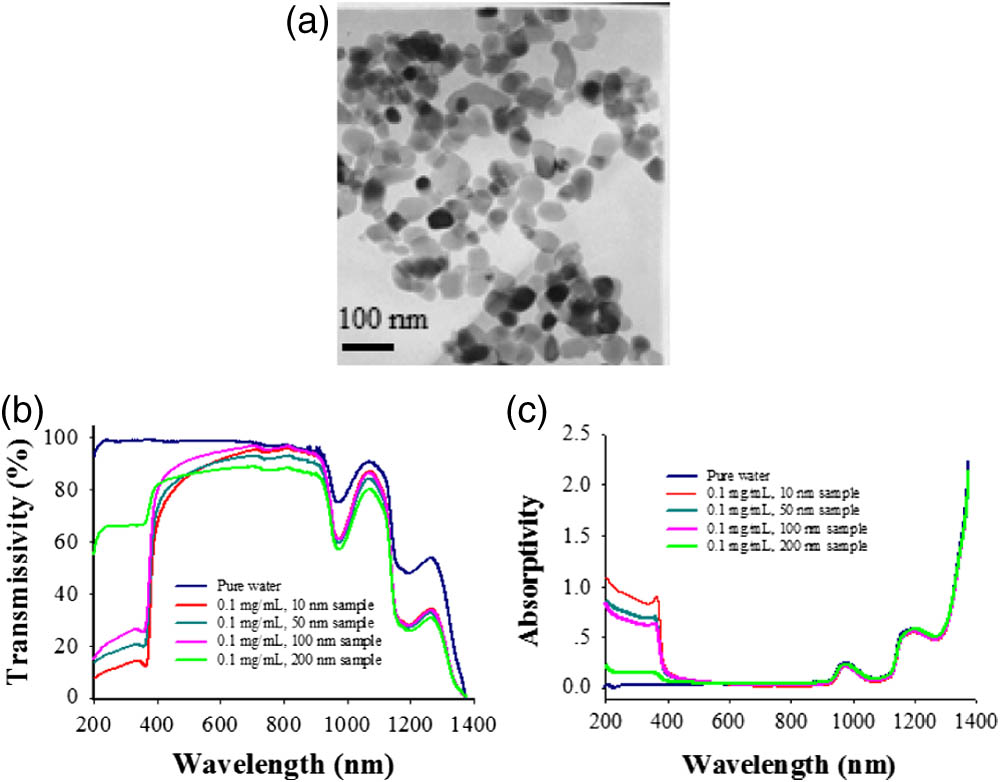
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory for Optoelectronics Testing Technology, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
2 National Engineering Laboratory for Nondestructive testing and Optoelectric Sensing Technology and Application, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres with four different particle diameters of 10, 50, 100, and 200 nm suspended in water are investigated theoretical and experimentally in the spectral range of the entire visible range and part of the near-infrared region. The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres suspended in water are described by employing three main parameters: the angular distribution of the scattering intensity I, the scattering extinction coefficient αscat, and the scattering cross section σscat. The results indicate that (i) at a certain wavelength, the angular distribution of the scattering intensity appears as an obviously forward-propagating feature, and the forward-scattering intensity is dominant gradually when the particle diameter increases from 10 to 200 nm, and (ii) the scattering extinction coefficient and cross section can be determined by using the measured transmittance changes of a pure water sample and a given ZnO sample; they all are shown to be dependent on the particle size and incident wavelength. The experimental results of four different scattering samples agree well with the theoretical predictions within the given wavelength range.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5825 Scattering theory Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 012901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Lab of Clean Energy Utilization, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 CNRS UMR 6614/CORIA, Saint Etienne du Rouvray BP12 76801, France
Calibration of the relationship between the scattering angle and the CCD pixel is a key part of achieving accurate measurements of rainbow refractometry. A novel self-calibrated global rainbow refractometry system based on illumination by two lasers of different wavelengths is proposed. The angular calibration and refractive index measurement of two wavelengths can be completed simultaneously without extra measurement devices. The numerical and experimental results show the feasibility and high precision of the self-calibration method, which enables the rainbow refractometry to be implemented in a more powerful and convenient way. The self-calibrated rainbow system is successfully applied to measure the refractive indices of ethanol-water solutions with volume concentrations of 10% to 60%.
290.5820 Scattering measurements 120.4820 Optical systems 120.6780 Temperature 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.3030 Index measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(4): 042902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
The Brillouin gain properties in a double-clad As2Se3 photonic crystal fiber (PCF) are simulated based on the finite-element method (FEM). The results indicate that the Brillouin gain spectrum (BGS) of our proposed chalcogenide PCF exhibits a multipeaked behavior and has a high Brillouin gain coefficient. We also find that a larger size of inner cladding air holes will lead to a more pronounced second peak in the BGS. On the other hand, the size of the outer cladding has nearly no effect on the BGS behavior. Through these results, one can tailor the Stimulated Brillouin scattering effect in PCFs for a wide range of applications.
290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin 190.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers 060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(4): 042901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Physics and Engineering,Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
2 Institute of Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Institute of Solid State Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
The angle dependence of optical phonon modes of an AlN bulk single crystal from the m-plane (1100) and c-plane (0001) surfaces, respectively, is investigated by polarized Raman spectroscopy in a backscattering configuration at room temperature. Corresponding Raman selection rules are derived according to measured scattering geometries to illustrate the angle dependence. The angle-dependent intensities of phonon modes are discussed and compared to theoretical scattering intensities, yielding the Raman tensor elements of A1(TO), E22 , E1(TO), and A1(LO) phonon modes and the relative phase difference between the two complex elements of A1_TO_. Furthermore, the Raman tensor of wurtzite AlN is compared with that of wurtzite ZnO reported in previous work, revealing the intrinsic differences of lattice vibration dynamics between AlN and ZnO.
Semiconductor materials Semiconductor materials Scattering Scattering Raman Raman Scattering Scattering polarization polarization Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000038
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu 610068, China
The spectrum of an electromagnetic light wave on scattering from a semisoft boundary medium is discussed within the accuracy of the first-order Born approximation. It is shown that spectral shifts and spectral switches are affected both by the polarization of the incident light wave and by the characters of the scattering medium. Moreover, numerical results show that the direction at which the spectral switch occurs is governed by the characters of the scattering medium, whereas the magnitude of the spectral switch is affected by the polarization of the incident light wave.
290.5825 Scattering theory 260.2110 Electromagnetic optics 300.6170 Spectra Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 122901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Koc University, Microphotonics Research Laboratory, Department of Physics, Rumelifeneri Yolu, Sariyer, Istanbul 34450, Turkey
2 Istanbul Technical University, Faculty of Sciences and Letters, Department of Physics, Maslak, Sariyer, Istanbul 34469, Turkey
The polarization behavior of elastic scattering at 1473 nm is analyzed from a silicon microsphere on an optical fiber half-coupler. The 0.27 nm angular mode spacing of the resonances correlates well with the optical size of the silicon sphere. The spectral linewidths of the resonances are on the order of 10-3 nm, which corresponds to quality factors on the order of 106. The transverse magnetically polarized elastic scattering signal has higher resonance to modulation depth and background ratio than the transverse electrically polarized elastic scattering signal and is suitable for high-resolution optical filtering applications such as optical monitoring and sensing.
Infrared Microcavities Resonators Scattering particles Scattering polarization Photonics Research
2014, 2(2): 02000045





