Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 International Research Institute for Multidisciplinary Science, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
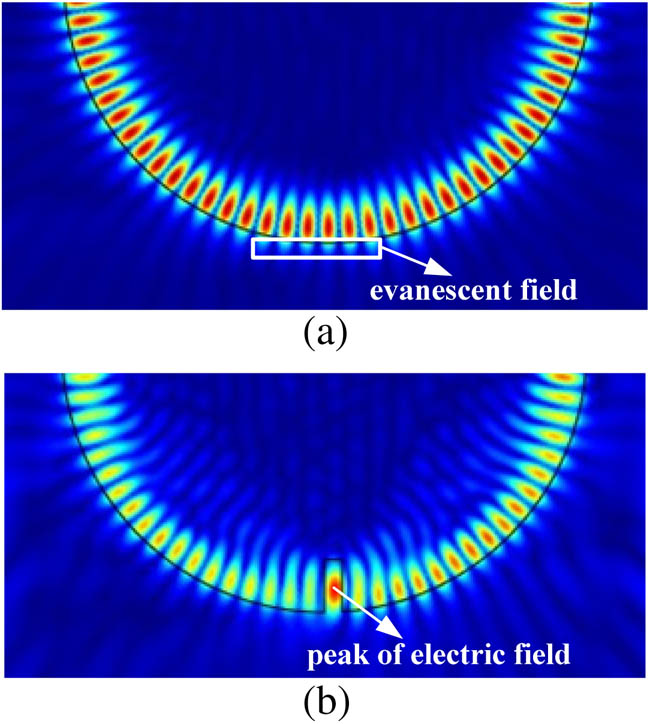
A novel slotted optical microdisk resonator, which significantly enhances light–matter interaction and provides a promising approach for increasing the sensitivity of sensors, is theoretically and numerically investigated. In this slotted resonator, the mode splitting is generated due to reflection of the slot. Remarkably, effects of the slot width and angular position on the mode splitting are mainly studied. The results reveal that the mode splitting is a second function of the slot width, and the maximum mode splitting induced by the slot deformation is achieved with 2.7853×109 Hz/nm. Therefore, the slotted resonator is an excellent candidate for pressure and force sensing. Besides, the influence of the slot angular position on the mode splitting is a cosine curve with the highest sensitivity of 1.23×1011 Hz/deg ; thus, the optical characteristic demonstrates that the slotted resonator can be used for inertial measurements.
Resonators Optical devices Fiber optics components Fiber optics Fiber optics and optical communications Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000194
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences,Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Department of Physics, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, Arkansas 72701, USA
We experimentally demonstrate high optical quality factor silica microdisk resonators on a silicon chip with large wedge angles by reactive ion etching. For 2-μm-thick microresonators, we have achieved wedge angles of 59°, 63°, 70°, and 79° with optical quality factors of 2.4 × 107, 8.1 × 106, 5.9 × 106, and 7.4 × 106, respectively, from ~80 μmdiameter microresonators in the 1550 nm wavelength band. Also, for 1-μm-thick microresonators, we have obtained an optical quality factor of 7.3 × 106 with a wedge angle of 74°.
Optical resonators Optical resonators Microcavity devices Microcavity devices Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000279
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026, China
2 Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China
An efficient method to mount a coupled silica microsphere and tapered fiber system is proposed and demonstrated experimentally. For the purpose of optomechanical studies, high-quality-factor optical (Qo ~ 108) and mechanical modes (Qm ~ 0.87 × 104<)sup>) are maintained after the mounting process. For the mounted microsphere, the coupling system is more stable and compact and, thus, is beneficial for future studies and applications based on optomechanical interactions. Especially, the packaged optomechanical system, which is tested in a vacuum chamber, paves the way toward quantum optomechanics research in cryostat.
Resonators Resonators Micro-optical devices Micro-optical devices Optomechanics Optomechanics Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000243





