Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices (SKLLMD), South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 117543, Singapore
3 NUSNNI-NanoCore, National University of Singapore, 117576, Singapore
4 e-mail: msxfjiang@scut.edu.cn
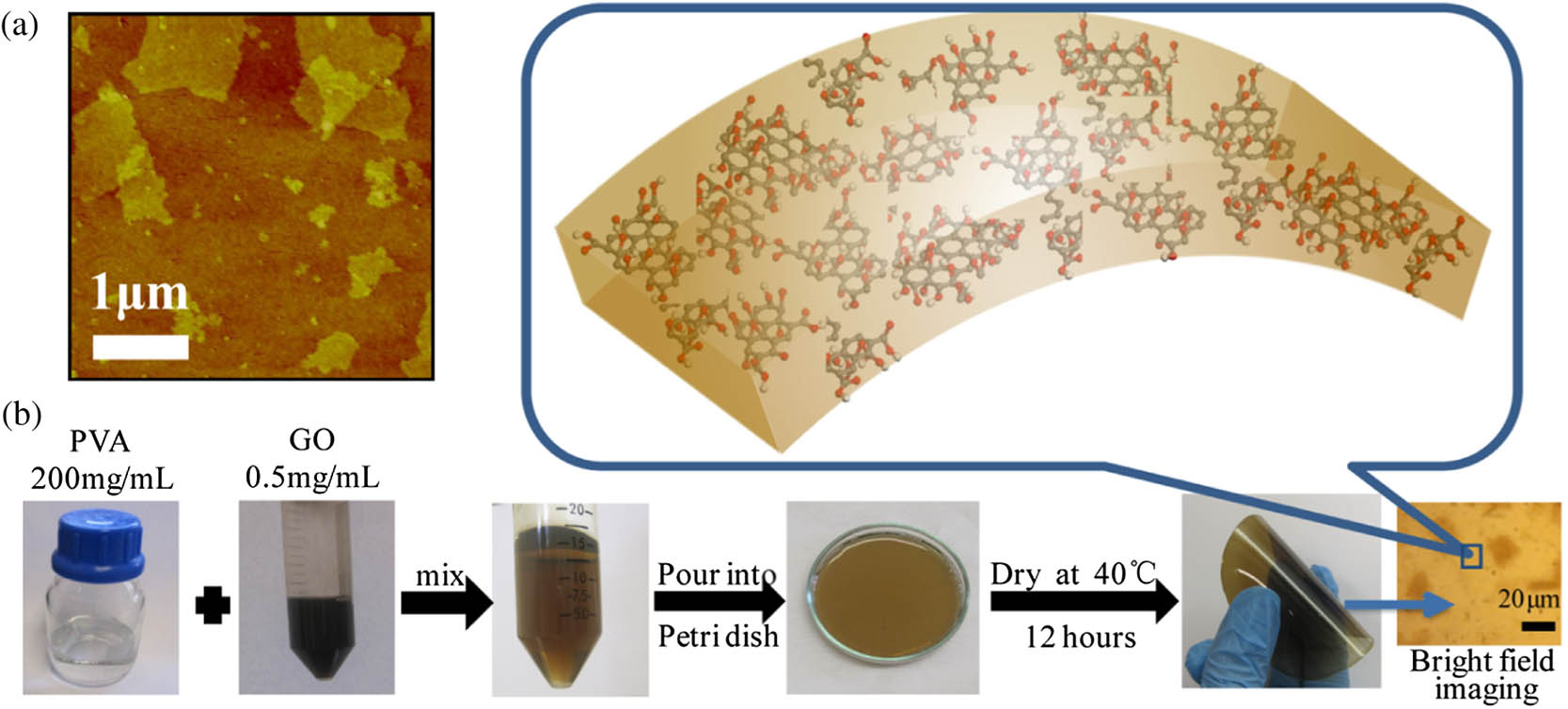
We report a simple solution-processed method for the fabrication of low-cost, flexible optical limiting materials based on graphene oxide (GO) impregnated polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) sheets. Such GO–PVA composite sheets display highly efficient broadband optical limiting activities for femtosecond laser pulses at 400, 800, and 1400 nm with very low limiting thresholds. Femtosecond pump–probe measurement results revealed that nonlinear absorption played an important role for the observed optical limiting activities. High flexibility and efficient optical limiting activities of these materials allow these composite sheets to be attached to nonplanar optical sensors in order to protect them from light-induced damage.
Thin films, optical properties Nonlinear optical materials Ultrafast nonlinear optics Spectroscopy, time-resolved Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A87
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials Chemistry and Physics of CAS, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, CAS, Fuzhou, Fujian 350002, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
3 Department of Photonics, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
4 Department of Applied Physics, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330013, China
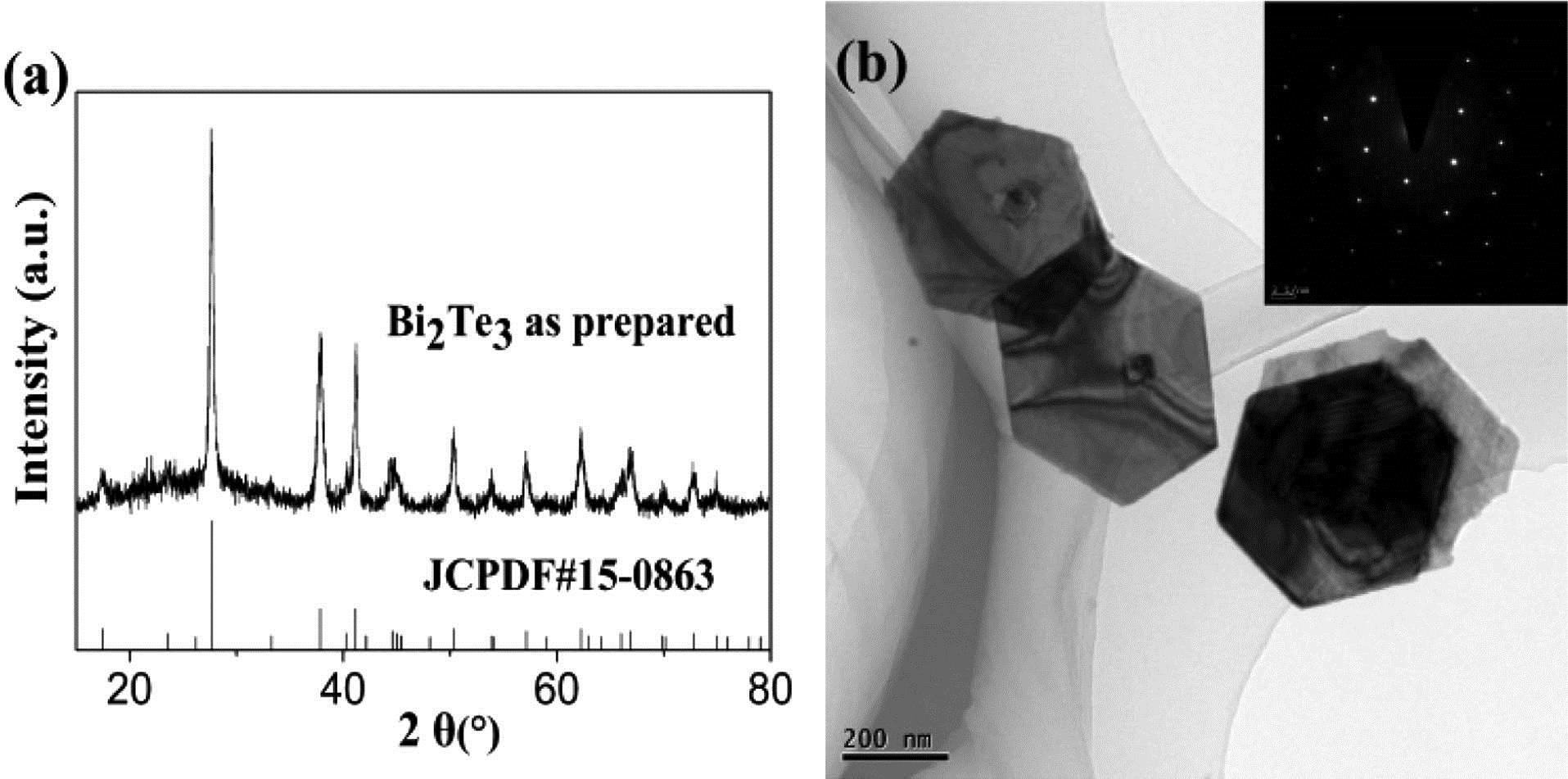
In this paper, we reported a multiwavelength passively Q-switched Yb3+:GdAl3(BO3)4 solid-state laser with topological insulator Bi2Te3 as a saturable absorber (SA) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Bi2Te3 nanosheets were prepared by the facile solvothermal method. The influence of three Bi2Te3 densities on the laser operation was compared. The maximum average output power was up to 57 mW with a pulse energy of 511.7 nJ. The shortest pulsewidth was measured to be 370 ns with 110 kHz pulse repetition rate and 40 mW average power. The laser operated at three wavelengths simultaneously at 1043.7, 1045.3, and 1046.2 nm, of which the frequency differences were within the terahertz wave band. Our work suggests that solvothermal synthesized Bi2Te3 is a promising SA for simultaneously multiwavelength laser operation.
Lasers, diode-pumped Lasers, Q-switched Lasers, solid-state Lasers, ytterbium Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A97
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Biomaterials, College of Materials, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
3 e-mail: jweng@xmu.edu.cn
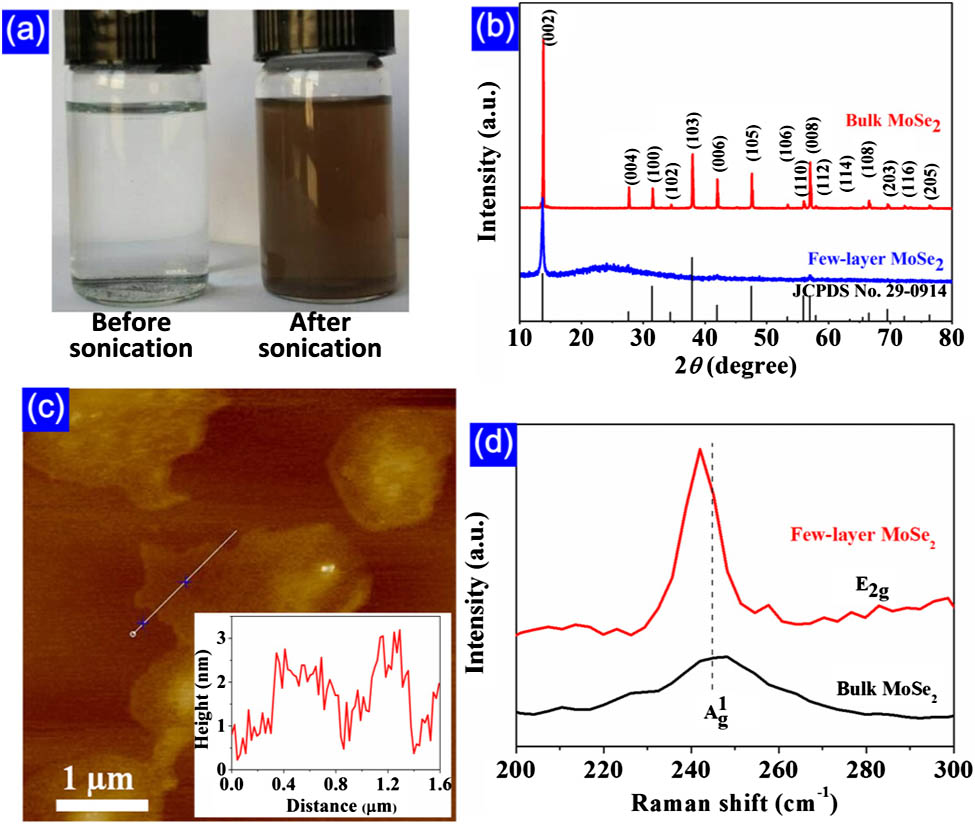
In this paper, both nonlinear saturable absorption and two-photon absorption (TPA) of few-layer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) were observed at 1.56 μm wavelength and further applied to mode-locked ultrafast fiber laser for the first time to our knowledge. Few-layer MoSe2 nanosheets were prepared by liquid-phase exfoliation method and characterized by x ray diffractometer, Raman spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The obtained few-layer MoSe2 dispersion is further composited with a polymer material for convenient fabrication of MoSe2 thin films. Then, we investigated the nonlinear optical (NLO) absorption property of the few-layer MoSe2 film using a balanced twin-detector measurement technique. Both the saturable absorption and TPA effects of the few-layer MoSe2 film were found by increasing the input optical intensity. The saturable absorption shows a modulation depth of 0.63% and a low nonsaturable loss of ~3.5%, corresponding to the relative modulation depth of 18%. The TPA effect occurred when the input optical intensity exceeds ~260 MW/cm2. Furthermore, we experimentally exploit the saturable absorption of few-layer MoSe2 film to mode lock an all-fiber erbium-doped fiber laser. Stable soliton mode locking at 1558 nm center wavelength is achieved with pulse duration of 1.45 ps. It was also observed that the TPA process suppresses the mode-locking operation in the case of higher optical intensity. Our results indicate that layered MoSe2, as another two-dimensional nanomaterial, can provide excellent NLO properties (e.g., saturable absorption and TPA) for potential applications in ultrashort pulse generation and optical limiting.
Nanomaterials Nonlinear optical materials Lasers, fiber Mode-locked lasers Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A79

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department of Electronic Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Key Laboratory of Materials for High-Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
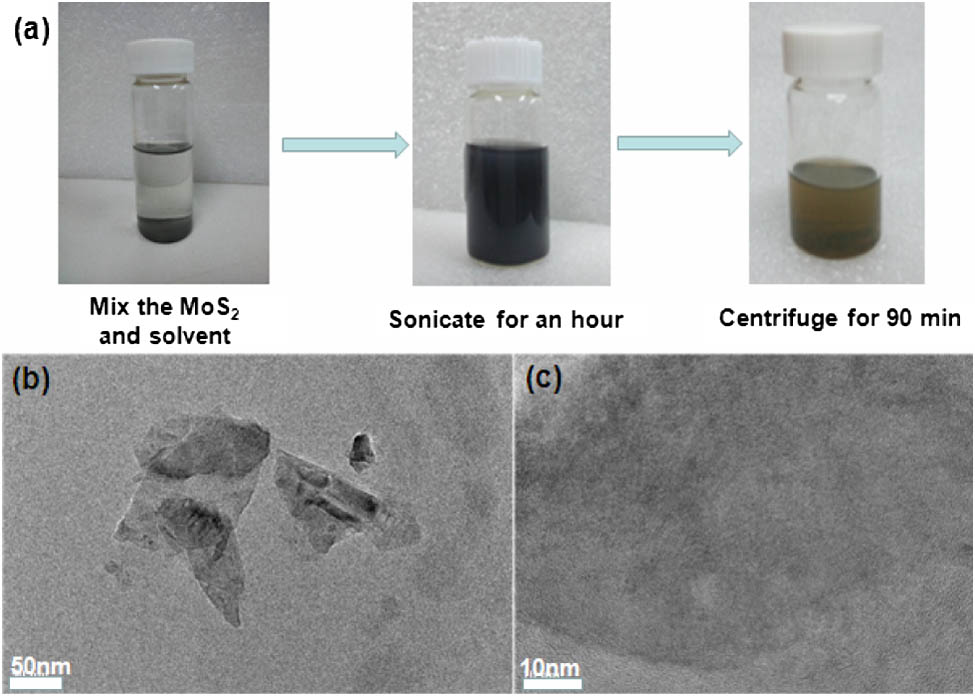
Deposition of two-dimensional (2D) MoS2 materials on the tapered fiber allows various photonic applications including saturable absorbers and four-wave mixing. Ethanol catalytic deposition (ECD) of MoS2 on the optical tapered fiber was proposed and demonstrated in this work. Different from the conventional optical driven deposition using water or organic solvent, the ECD method utilized the high volatility of the ethanol solvent, which significantly increased the movement speed of the MoS2 nanosheets and thus boosted the deposition rate and reduced the minimum power threshold to drive the deposition. We believe the ECD method should be able to be applied to other similar 2D materials such as other types of transition metal chalcogenides.
Nonlinear optical materials Deposition and fabrication Nonlinear optical devices Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 0300A102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
We report an erbium-doped fiber laser passively Q-switched by a few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) saturable absorber (SA). The few-layer MoS2 is grown by the chemical vapor deposition method and transferred onto the end-face of a fiber connector to form a fiber-compatible MoS2 SA. The laser cavity is constructed by using a three-port optical circulator and a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) as the two end-mirrors. Stable Q-switched pulses are obtained with a pulse duration of 1.92 μs at 1560.5 nm. By increasing the pump power from 42 to 204 mW, the pulse repetition rate can be widely changed from 28.6 to 114.8 kHz. Passive Q-switching operations with discrete lasing wavelengths ranging from 1529.8 to 1570.1 nm are also investigated by using FBGs with different central wavelengths. This work demonstrates that few-layer MoS2 can serve as a promising SA for wideband-tunable Q-switching laser operation.
Lasers, Q-switched Lasers, erbium Nanomaterials Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A92
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanophotonic Functional Materials and Devices, School of Information and Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510006, China
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have emerged as attractive mediums for fabricating versatile optoelectronic devices. Recently, few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), as a shining 2D material, has been discovered to possess both the saturable absorption effect and large nonlinear refractive index. Herein, taking advantage of the unique nonlinear optical properties of MoS2, we fabricated a highly nonlinear saturable absorption photonic device by depositing the few-layer MoS2 onto the microfiber. With the proposed MoS2 photonic device, apart from the conventional soliton patterns, the mode-locked pulses could be shaped into some new soliton patterns, namely, multiple soliton molecules, localized chaotic multipulses, and double-scale soliton clusters. Our findings indicate that the few-layer MoS2-deposited microfiber could operate as a promising highlynonlinear photonic device for the related nonlinear optics applications.
Nonlinear optical materials Nonlinear optical materials Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A69
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Education Ministry of China, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
3 Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Center (iNANO), Aarhus University, Aarhus C DK-8000, Denmark
4 Department of Electronic Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
A graphene-coated microfiber (GCM)-based hybrid waveguide structure formed by wrapping monolayer graphene around a microfiber with length of several millimeters is pumped by a nanosecond laser at ~1550 nm, and multiorder cascaded four-wave-mixing (FWM) is effectively generated. By optimizing both the detuning and the pump power, such a GCM device with high nonlinearity and compact size would have potential for a wide range ofFWM applications, such as phase-sensitive amplification, multi-wavelength filter, all-optical regeneration and frequency conversion, and so on.
Nonlinear wave mixing Nonlinear wave mixing Optical materials Optical materials Guided waves Guided waves Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A64
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The paper summarizes the recent achievements in the area of ultrafast fiber lasers mode-locked with so-called lowdimensional nanomaterials: graphene, topological insulators (Bi2Te3, Bi2Se3, Sb2Te3), and transition metal sulfide semiconductors, like molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). The most important experimental achievements are described and compared. Additionally, new original results on ultrashort pulse generation at 1.94 μm wavelength using graphene are presented. The designed Tm-doped fiber laser utilizes multilayer graphene as a saturable absorber and generates 654 fs pulses at 1940 nm wavelength, which are currently the shortest pulses generated from a Tm-doped fiber laser with a graphene-based saturable absorber.
Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A56
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High-Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 School of Physics and the Centre for Research on Adaptive Nanostructures and Nanodevices (CRANN),Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland
3 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
Liquid-phase-exfoliation technology was utilized to prepare layered MoS2, WS2, and MoSe2 nanosheets in cyclohexylpyrrolidone. The nonlinear optical response of these nanosheets in dispersions was investigated by observing spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) using a 488 nm continuous wave laser beam. The diffraction ring patterns of SSPM were found to be distorted along the vertical direction right after the laser traversing the nanosheet dispersions. The nonlinear refractive index of the three transition metal dichalcogenides dispersions n2 was measured to be ~10 7 cm2·W 1, and the third-order nonlinear susceptibility χ(3) ~ 10 9 esu. The relative change of effective nonlinear refractive index Δn2e∕n2e of the MoS2, WS2, and MoSe2 dispersions can be modulated 0.012– 0.240, 0.029–0.154, and 0.091–0.304, respectively, by changing the incident intensities. Our experimental results imply novel potential application of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides in nonlinear phase modulation devices.
Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics Nanomaterials Nanomaterials Nonlinear optical materials Nonlinear optical materials Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A51
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education), IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials and Institute of Crystal Materials,Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
With MoS2 as saturable absorber, passive Q-switching and Q-switched mode-locking operations of a Tm-doped calcium lithium niobium gallium garnet (Tm:CLNGG) laser were experimentally demonstrated. The Q-switched laser emitted a maximum average output power of 62 mW and highest pulse energy of 0.72 μJ. Q-switched mode locking was also obtained in the experiment. The research results will open up applications of MoS2 at the mid-infrared wavelength.
Lasers Lasers Q-switched Q-switched Lasers Lasers solid-state solid-state Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A47





