
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Microcomb generation with simultaneous χ(2) and χ(3) nonlinearities brings new possibilities for ultrabroadband and potentially self-referenced integrated comb sources. However, the evolution of the intracavity field involving multiple nonlinear processes shows complex dynamics that are still poorly understood. Here, we report on strong soliton regulation induced by fundamental–second-harmonic (FD-SH) mode coupling. The formation of solitons from chaos is extensively investigated based on coupled Lugiato–Lefever equations. The soliton generation shows more deterministic behaviors in the presence of FD-SH mode interaction, which is in sharp contrast with the usual cases where the soliton number and relative locations are stochastic. Deterministic single soliton transition, soliton binding, and prohibition are observed, depending on the phase-matching condition and coupling coefficient between the fundamental and second-harmonic waves. Our finding provides important new insights into the soliton dynamics in microcavities with simultaneous χ(2) and χ(3) nonlinearities and can be immediate guidance for broadband soliton comb generation with such platforms.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Harmonic generation and mixing Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Microcavities Photonics Research
2018, 6(10): 10000948

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, C2N Marcoussis, 91460 Marcoussis, France
2 Thales Research and Technology France, 1 avenue Augustin Fresnel, 91120 Palaiseau, France
3 Université Paris Diderot, Sorbone Paris Cité, 75013 Paris, France
We introduce a nanoscale photonic platform based on gallium phosphide. Owing to the favorable material properties, peak power intensity levels of 50 GW/cm2 are safely reached in a suspended membrane. Consequently, the field enhancement is exploited to a far greater extent to achieve efficient and strong light–matter interaction. As an example, parametric interactions are shown to reach a deeply nonlinear regime, revealing cascaded four-wave mixing leading to comb generation and high-order soliton dynamics.
Kerr effect Nonlinear wave mixing Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Integrated optics materials Photonic crystals Microwaves Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000B43
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, Staudtstrasse 2, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Spectral anti-crossings between the fundamental guided mode and core-wall resonances alter the dispersion in hollow-core anti-resonant-reflection photonic crystal fibers. Here we study the effect of this dispersion change on the nonlinear propagation and dynamics of ultrashort pulses. We find that it causes emission of narrow spectral peaks through a combination of four-wave mixing and dispersive wave emission. We further investigate the influence of the anti-crossings on nonlinear pulse propagation and show that their impact can be minimized by adjusting the core-wall thickness in such a way that the anti-crossings lie spectrally distant from the pump wavelength.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Photonic crystal fibers Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000084
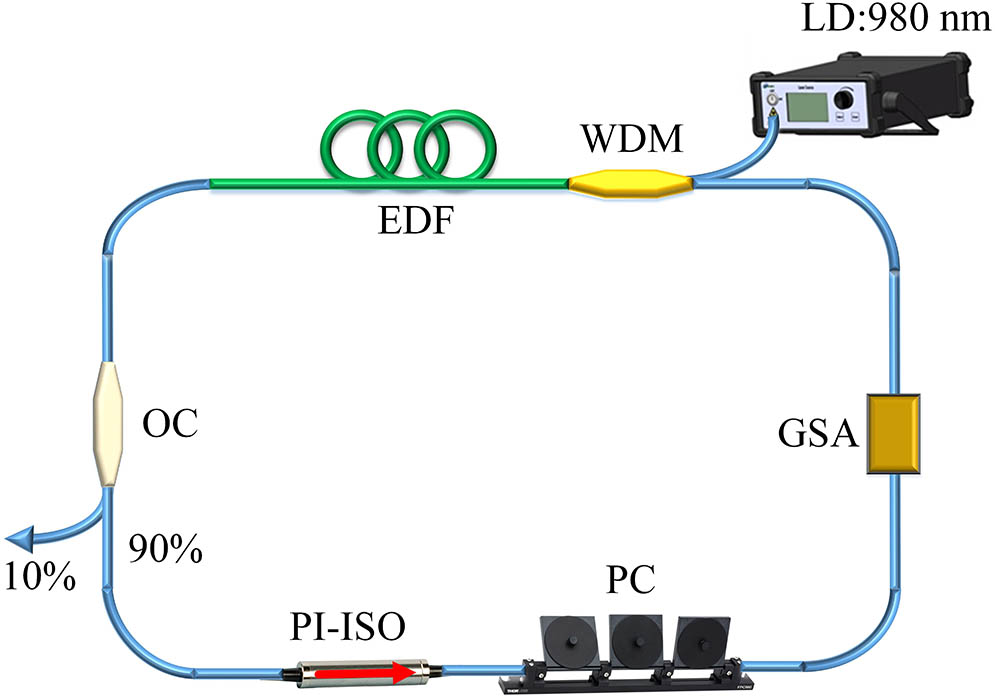
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Information and Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, and Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
We report a regime of the loose soliton bunch in an erbium-doped passively mode-locked fiber laser. In this state, every soliton bunch consists of multiple pulses. The amount of multiple pulses inside the soliton bunch increase as the pump power rises. Moreover, the temporal average pulse-to-pulse separation decreases in general with the increase of the pump power. Further, the spatial-temporal sequences based on the dispersive Fourier transformation technique show that pulse-to-pulse interactions and time jitter can result in pulse forking inside the soliton bunch. Finally, we theoretically demonstrate the soliton bunch with different pulse-to-pulse separations.
060.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3500 Lasers, erbium Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 080605

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Electronic Engineering Department, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
4 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Quantum Engineering and Quantum Materials, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
Temporal cavity solitons (CSs) have excellent properties that can sustain their shape in a temporal profile and with a broadband, smooth-frequency spectrum. We propose a method for controllable frequency line spacing soliton formation in a microresonator using two continuous-wave (CW) pumps with multi-free-spectral-range (FSR) spacing. The method we propose has better control over the amount and location of the solitons traveling in the cavity compared to the tuning pump method. We also find that by introducing a second pump with frequency N FSR from the first pump, solitons with N FSR comb spacing can be generated.
190.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 230.5750 Resonators 190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 121903

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Science, P. O. Box 91, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
Tungsten disulfide (WS2) is a type of anisotropic-layered compound and has broadband saturable absorption features as saturable absorbers (SAs). With WS2-based SAs, dark solitons in erbium-doped fiber (EDF) lasers are first obtained. For the generated dark solitons, the center wavelength is measured to be 1530 nm, and the repetition rateis about 116.5 MHz. A series of optical spectra is exhibited. The electrical signal-to-noise ratio is better than 94 dB. Results in this paper demonstrate that WS2-based SAs are the promising SAs for generating dark solitons in EDF lasers.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Modelocked lasers Modelocked lasers Photonics Research
2016, 4(3): 03000111
Author Affiliations
Abstract
I3N—Institute of Nanostructures, Nanomodelling and Nanofabrication, Department of Physics, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
This publisher’s note reports corrections to three of the figures in [Photon. Res. 4, 49 (2016)].
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers Photonics Research
2016, 4(3): 03000101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
I3N—Institute of Nanostructures, Nanomodelling and Nanofabrication, Department of Physics, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
In this work, new plain and composite high-energy solitons of the cubic–quintic Swift–Hohenberg equation were numerically found. Starting from a composite pulse found by Soto-Crespo and Akhmediev and changing some parameter values allowed us to find these high energy pulses. We also found the region in the parameter space in which these solutions exist. Some pulse characteristics, namely, temporal and spectral profiles and chirp, are presented. The study of the pulse energy shows its independence of the dispersion parameter but its dependence on the nonlinear gain. An extreme amplitude pulse has also been found.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers Photonics Research
2016, 4(2): 02000049

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 e-mail: jiangtian198611@163.com
3 e-mail: houjing25@sina.com
We reported diverse soliton operations in a thulium/holmium-doped fiber laser by taking advantage of a tapered fiber-based topological insulator (TI) Bi2Te3 saturable absorber (SA). The SA had a nonsaturable loss of ~53.5% and a modulation depth of 9.8%. Stable fundamentally mode-locked solitons at 1909.5 nm with distinct Kelly sidebands on the output spectrum, a pulse repetition rate of 21.5 MHz, and a measured pulse width of 1.26 ps were observed in the work. By increasing the pump power, both bunched solitons with soliton number up to 15 and harmonically mode-locked solitons with harmonic order up to 10 were obtained. To our knowledge, this is the first report of both bunched solitons and harmonically mode-locked solitons in a fiber laser at 2 μm region incorporated with TIs.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Ultrafast lasers Lasers and laser optics Mode-locked lasers Nonlinear optical materials Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000072
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanophotonic Functional Materials and Devices, School of Information and Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510006, China
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have emerged as attractive mediums for fabricating versatile optoelectronic devices. Recently, few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), as a shining 2D material, has been discovered to possess both the saturable absorption effect and large nonlinear refractive index. Herein, taking advantage of the unique nonlinear optical properties of MoS2, we fabricated a highly nonlinear saturable absorption photonic device by depositing the few-layer MoS2 onto the microfiber. With the proposed MoS2 photonic device, apart from the conventional soliton patterns, the mode-locked pulses could be shaped into some new soliton patterns, namely, multiple soliton molecules, localized chaotic multipulses, and double-scale soliton clusters. Our findings indicate that the few-layer MoS2-deposited microfiber could operate as a promising highlynonlinear photonic device for the related nonlinear optics applications.
Nonlinear optical materials Nonlinear optical materials Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Photonics Research
2015, 3(2): 02000A69





