Photonics Research, 2020, 8 (5): 05000648, Published Online: Apr. 20, 2020
Circular Dammann gratings for enhanced control of the ring profile of perfect optical vortices  Download: 581次
Download: 581次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 1. Schematic diagrams of the experimental scheme. (a) The proof-of-principle experimental setup. L 1 ∼ 2 PBS 1 ∼ 2 P 1 ∼ 2 λ / 4
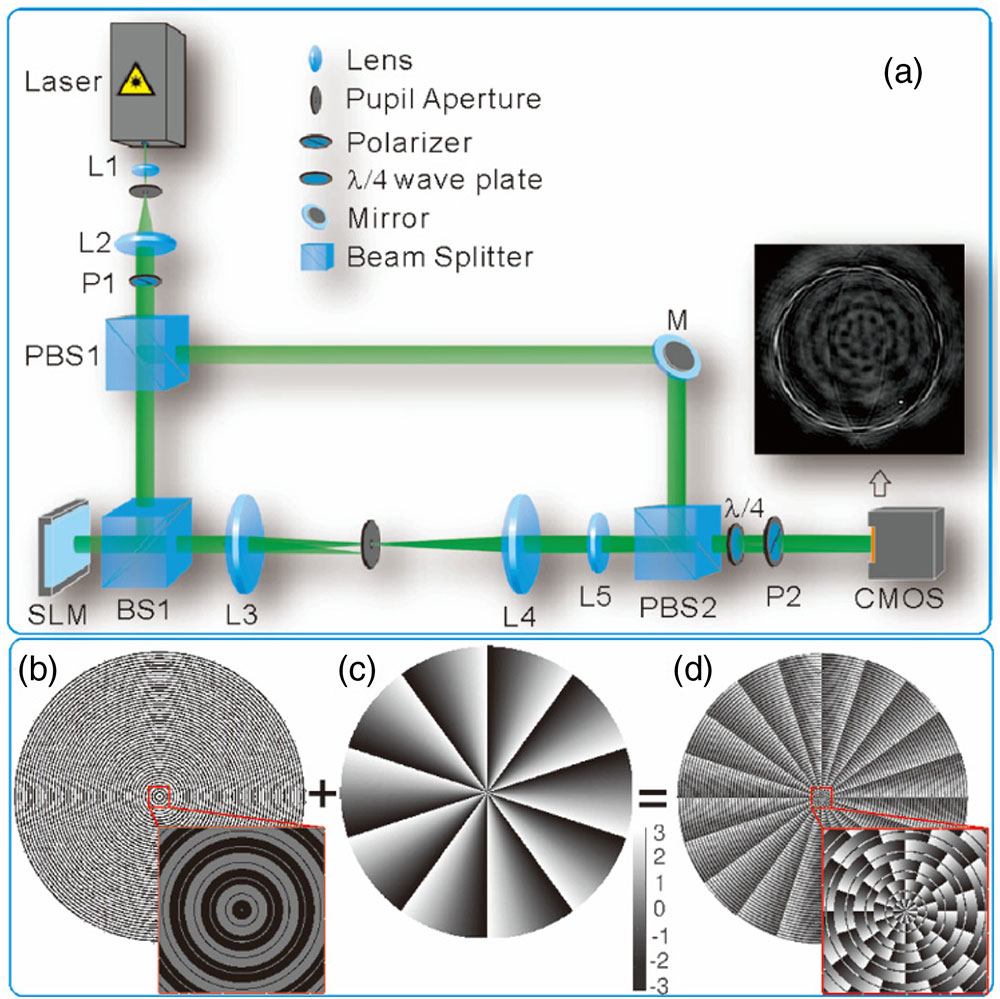
Fig. 2. Simulation and experimental results of dark POVs generated by CDGs embedded with spiral phases with charges of (a) l = 1 − 5

Fig. 3. Simulation and experimental results of interferograms on defocused planes (with defocus distance Δ d = 10 mm l = 10 − 5

Fig. 4. Simulation and experimental results of phase distributions on defocused planes (with defocus distance Δ d = 25 mm l = 10 l = − 5

Fig. 5. Simulation and experimental results of bright POVs generated by CDGs embedded with spiral phases with charges of (a) l = 1 − 5

Fig. 6. Simulation and experimental results of POVs with tunable ring profiles generated by CDGs (with period number of N = 30 l = 10 β δ ϕ

Fig. 7. Influences of topological charge and period number on performance parameters of POVs with bright and dark ring profiles generated by CDGs. (a) The ring radius, (b) the ring width, and (c) the side-lobe ratio as a function of the charge; (d) the ring radius, (e) the ring width, and (f) the side-lobe ratio versus the period number inside the aperture. In each sub-figure, the blue solid line denotes the simulation results of POVs with bright ring profiles (bright POVs) and the red broken line denotes the simulation results of POVs with dark ring profiles (dark POVs); the square denotes the experimental results of bright POVs, and the circle is the experimental results of dark POVs.

Junjie Yu, Chaofeng Miao, Jun Wu, Changhe Zhou. Circular Dammann gratings for enhanced control of the ring profile of perfect optical vortices[J]. Photonics Research, 2020, 8(5): 05000648.





