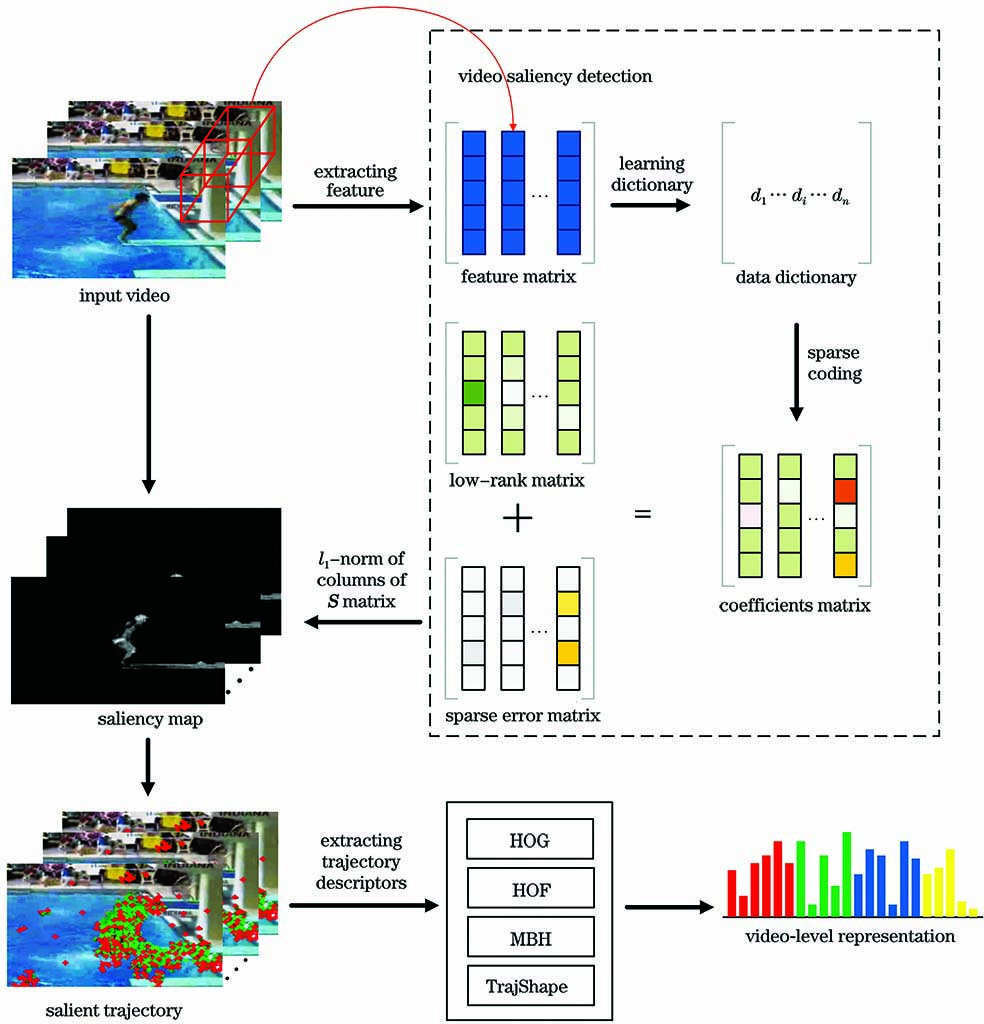
结合稠密轨迹与视频显著性特征的人体动作识别  下载: 1003次
下载: 1003次
高德勇, 康自兵, 王松, 王阳萍. 结合稠密轨迹与视频显著性特征的人体动作识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(24): 241003.
Deyong Gao, Zibing Kang, Song Wang, Yangping Wang. Human-Body Action Recognition Based on Dense Trajectories and Video Saliency[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(24): 241003.
[1] 罗会兰, 王婵娟, 卢飞. 视频行为识别综述[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(6): 169-180.
Luo H L, Wang C J, Lu F. Survey of video behavior recognition[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(6): 169-180.
[2] Bobick A F, Davis J W. The recognition of human movement using temporal templates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(3): 257-267.
[3] Laptev I. On space-time interest points[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2005, 64(2/3): 107-123.
[4] DollarP, RabaudV, CottrellG, et al.Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal features[C]∥2005 IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, October 15-16, 2005, Beijing, China.New York: IEEE Press, 2005: 65- 72.
[6] WangH, SchmidC. Action recognition with improved trajectories[C]∥2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, December 1-8, 2013, Sydney, NSW, Australia.New York: IEEE Press, 2013: 3551- 3558.
[7] Liu X, Zhao G Y, Yao J W, et al. Background subtraction based on low-rank and structured sparse decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(8): 2502-2514.
[9] 李艳荻, 徐熙平. 基于超像素时空特征的视频显著性检测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(1): 0110001.
[10] Duan L J, Xi T, Cui S, et al. A spatiotemporal weighted dissimilarity-based method for video saliency detection[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2015, 38: 45-56.
[11] 李庆武, 周亚琴, 马云鹏, 等. 基于双目视觉的显著性目标检测方法[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(3): 0315002.
[12] WangL, Zhao DB. Recognizing actions using salient features[C]∥2011 IEEE 13th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, October 17-19, 2011, Hangzhou, China.New York: IEEE Press, 2011: 1- 6.
[13] Yi Y, Lin Y K. Human action recognition with salient trajectories[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(11): 2932-2941.
[14] Somasundaram G, Cherian A, Morellas V, et al. Action recognition using global spatio-temporal features derived from sparse representations[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2014, 123: 1-13.
[15] Li Q, Cheng H, Zhou Y, et al. Human action recognition using improved salient dense trajectories[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 2016: 6750459.
[16] Yi Y, Zheng Z X, Lin M Q. Realistic action recognition with salient foreground trajectories[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2017, 75: 44-55.
[17] Wang X F, Qi C. Saliency-based dense trajectories for action recognition using low-rank matrix decomposition[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2016, 41: 361-374.
[18] Wang X F, Qi C, Lin F. Combined trajectories for action recognition based on saliency detection and motion boundary[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2017, 57: 91-102.
[19] Rodriguez MD, AhmedJ, ShahM. Action MACH a spatio-temporal Maximum Average Correlation Height filter for action recognition[C]∥2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 23-28, 2008, Anchorage, AK, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2008: 1- 8.
[20] Liu JG, Luo JB, ShahM. Recognizing realistic actions from videos “in the wild”[C]∥2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 20-25, 2009, Miami, FL, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2009: 1996- 2003.
[21] Cho J, Lee M, Chang H J, et al. Robust action recognition using local motion and group sparsity[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(5): 1813-1825.
[22] Yang XD, Tian YL. Action recognition using super sparse coding vector with spatio-temporal awareness[C]∥ Fleet D, Pajdla T, Schiele B, et al. Computer Vision-ECCV 2014. Cham: Springer, 2014: 727- 741.
[24] Guo YN, MaW, Duan LJ, et al.Human action recognition based on discriminative supervoxels[C]∥2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), July 24-29, 2016, Vancouver, BC, Canada.New York: IEEE Press, 2016: 3863- 3869.
[25] 段立娟, 郭亚楠, 乔元华, 等. 基于判别性区域提取的视频人体动作识别方法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2017, 43(10): 1480-1487.
Duan L J, Guo Y N, Qiao Y H, et al. Human action recognition based on extracted discriminative regions[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2017, 43(10): 1480-1487.
[26] Wang LM, QiaoY, Tang XO. Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors[C]∥2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 7-12, 2015, Boston, MA, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2015: 4305- 4314.
[27] 李庆辉, 李艾华, 王涛, 等. 结合有序光流图和双流卷积网络的行为识别[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(6): 0615002.
高德勇, 康自兵, 王松, 王阳萍. 结合稠密轨迹与视频显著性特征的人体动作识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(24): 241003. Deyong Gao, Zibing Kang, Song Wang, Yangping Wang. Human-Body Action Recognition Based on Dense Trajectories and Video Saliency[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(24): 241003.