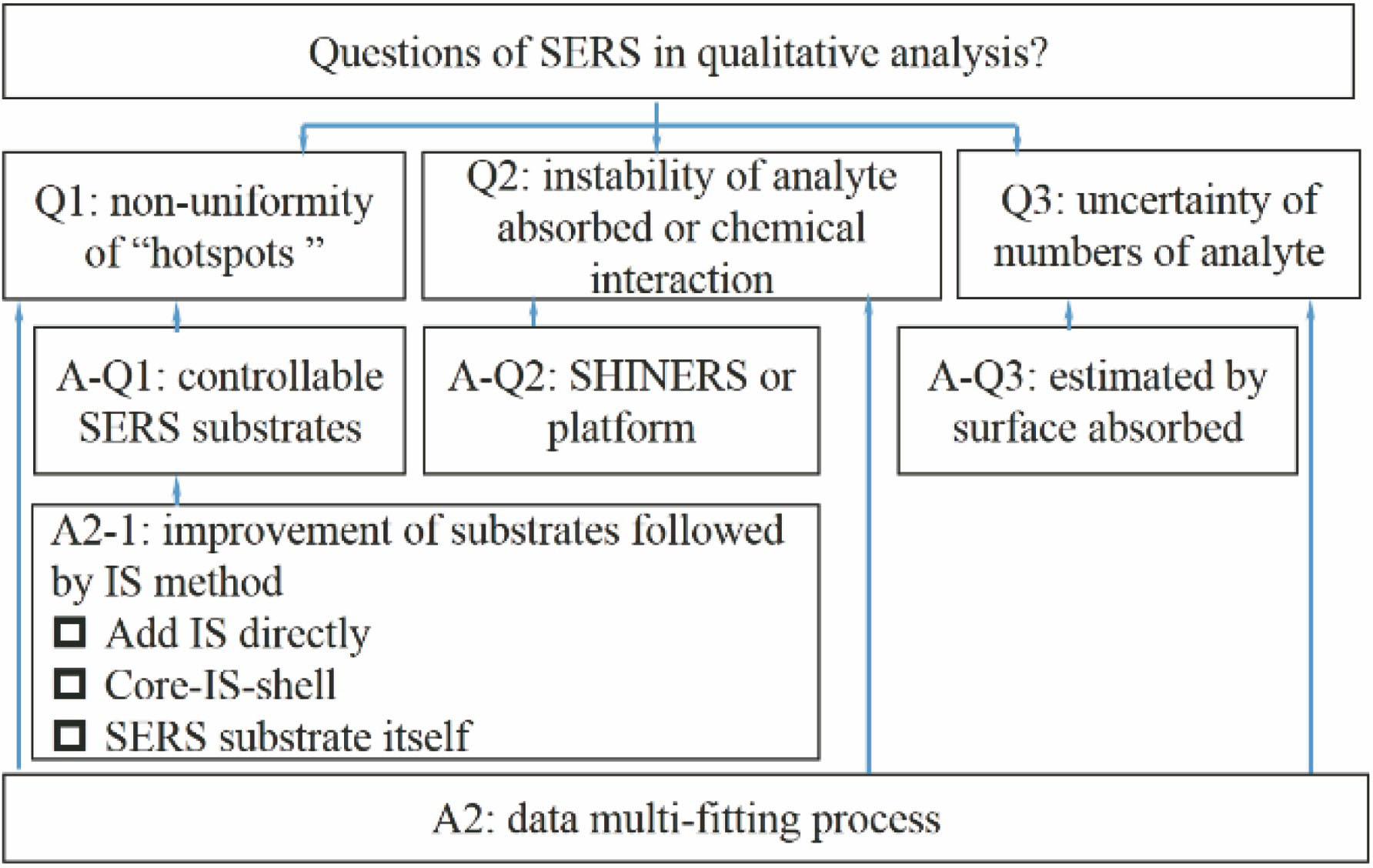
基于内标法的表面增强拉曼散射定量分析  下载: 1769次
下载: 1769次
邢豪健, 尹增鹤, 张洁, 朱永. 基于内标法的表面增强拉曼散射定量分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(3): 030002.
Haojian Xing, Zenghe Yin, Jie Zhang, Yong Zhu. Quantitative Analysis of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Based on Internal Standard Method[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(3): 030002.
[1] Fleischmann M, Hendra P J. McQuillan A J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1974, 26(2): 163-166.
[2] Ding S Y, Yi J, Li J F, et al. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2016, 1(6): 16021.
[3] Pitarke J M, Silkin V M, Chulkov E V, et al. Theory of surface plasmons and surface-plasmon polaritons[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2007, 70(1): 1-87.
[4] Jensen L, Aikens C M, Schatz G C. Electronic structure methods for studying surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(5): 1061-1073.
[5] Persson B N J, Zhao K, Zhang Z Y. Chemical contribution to surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(20): 207401.
[6] Zong C, Xu M X, Xu L J, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: reliability and challenges[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(10): 4946-4980.
[7] 赵畅, 李蓉, 杨荟楠, 等. 基于表面增强拉曼光谱测量尿液样本中血小板衍生生长因子-BB[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(8): 0811002.
[8] Freeman L M, Pang L, Fainman Y. Self-reference and random sampling approach for label-free identification of DNA composition using plasmonic nanomaterials[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 7398.
[9] Sharma B, Frontiera R R, Henry A I, et al. SERS: materials, applications, and the future[J]. Materials Today, 2012, 15(1/2): 16-25.
[10] 史晓凤, 张心敏, 严霞, 等. 基于三维表面增强拉曼基底的水中多环芳烃检测[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(7): 0724001.
[11] Li Y S, Church J S. Raman spectroscopy in the analysis of food and pharmaceutical nanomaterials[J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 2014, 22(1): 29-48.
[12] Li M, Cushing S K, Wu N Q. Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: a review[J]. The Analyst, 2015, 140(2): 386-406.
[13] 马海宽, 张旭, 钟石磊, 等. 基于静电富集-表面增强拉曼光谱联用技术的抗生素检测[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(2): 0207028.
[14] 卢树华, 王照明, 田方. 表面增强拉曼光谱技术在毒品检测中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(3): 030004.
[15] Geiman I, Leona M, Lombardi J R. Application of Raman spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman scattering to the analysis of synthetic dyes found in ballpoint pen inks[J]. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2009, 54(4): 947-952.
[16] Berger A G, White I M. Therapeutic drug monitoring of flucytosine in serum using a SERS-active membrane system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10081: 1008104.
[17] Li J F, Anema J R, Wandlowski T, et al. Dielectric shell isolated and graphene shell isolated nanoparticle enhanced Raman spectroscopies and their applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(23): 8399-8409.
[18] Tian Z Q, Ren B, Wu D Y. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: from noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(37): 9463-9483.
[19] Yoshida K, Itoh T, Tamaru H, et al. Quantitative evaluation of electromagnetic enhancement in surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering from plasmonic properties and morphologies of individual Ag nanostructures[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(11): 115406.
[20] Xu H X. Theoretical study of coated spherical metallic nanoparticles for single-molecule surface-enhanced spectroscopy[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(24): 5980-5982.
[21] Fang Y, Seong N H, Dlott D D. Measurement of the distribution of site enhancements in surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5887): 388-392.
[22] Le Ru E C, Etchegoin P G. Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 2012, 63(1): 65-87.
[23] Moskovits M. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a brief retrospective[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2005, 36(6/7): 485-496.
[24] Yamamoto Y S, Ozaki Y, Itoh T. Recent progress and frontiers in the electromagnetic mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 2014, 21: 81-104.
[25] Szlag V M, Rodriguez R S, He J Y, et al. Molecular affinity agents for intrinsic surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(38): 31825-31844.
[26] 尹增鹤. 碳纳米管/石墨烯/金属纳米复合结构增强拉曼散射自标定特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019.
Yin ZH. Carbon nanotubes/graphene/metal nanoparticles with self calibration for enhanced Raman scattering[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019.
[27] Bell S E, Sirimuthu N M. Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(5): 1012-1024.
[28] Su Y D, Han H L, Cai Q, et al. Polymer adsorption on graphite and CVD graphene surfaces studied by surface-specific vibrational spectroscopy[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(10): 6501-6505.
[29] Lazar P, Karlicky F, Jurecka P, et al. Adsorption of small organic molecules on graphene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(16): 6372-6377.
[30] Tian H H, Zhang N, Tong L M, et al. In situ quantitative graphene-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Small Methods, 2017, 1(6): 1700126.
[32] Patze S, Huebner U, Weber K, et al. TopUp SERS substrates with integrated internal standard[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(2): 325.
[33] Weatherston J D, Worstell N C, Wu H J. Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for kinetic analysis of aldol condensation using Ag-Au core-shell nanocubes[J]. The Analyst, 2016, 141(21): 6051-6060.
[34] Li J F, Huang Y F, Ding Y, et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7287): 392-395.
[35] Zhang J, Yin Z H, Zhang X L, et al. Quantitative SERS by electromagnetic enhancement normalization with carbon nanotube as an internal standard[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(18): 23534-23539.
[36] Tian ZQ, RenB, Li JF, et al. Expanding generality of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with borrowing SERS activity strategy[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2007( 34): 3514- 3534.
[37] Velleman L, Scarabelli L, Sikdar D, et al. Monitoring plasmon coupling and SERS enhancement through in situ nanoparticle spacing modulation[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2017, 205: 67-83.
[38] Gong T C, Luo Y F, Zhao C W, et al. Highly reproducible and stable surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates of graphene-Ag nanohole arrays fabricated by sub-diffraction plasmonic lithography[J]. OSA Continuum, 2019, 2(3): 582-594.
[39] Yan B, Boriskina S V, Reinhard B M. Design and implementation of noble metal nanoparticle cluster arrays for plasmon enhanced biosensing[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(50): 24437-24453.
[42] Bian X, Song Z L, Qian Y, et al. Fabrication of graphene-isolated-Au-nanocrystal nanostructures for multimodal cell imaging and photothermal-enhanced chemotherapy[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6093.
[43] Lai X F, Zou Y X, Wang S S, et al. Modulating the morphology of gold graphitic nanocapsules for plasmon resonance-enhanced multimodal imaging[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(10): 5385-5391.
[44] Qian X M, Peng X H, Ansari D O, et al. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2008, 26(1): 83-90.
[45] Chen L, Yu Z, Lee Y, et al. Quantitative evaluation of proteins with bicinchoninic acid (BCA): resonance Raman and surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering-based methods[J]. The Analyst, 2012, 137(24): 5834-5838.
[46] Dong N, Hu Y J, Yang K, et al. Development of aptamer-modified SERS nanosensor and oligonucleotide chip to quantitatively detect melamine in milk with high sensitivity[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 228: 85-93.
[48] Wu L, Wang Z Y, Zhang Y Z, et al. In situ probing of cell-cell communications with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanoprobes and microfluidic networks for screening of immunotherapeutic drugs[J]. Nano Research, 2017, 10(2): 584-594.
[51] Chen Y, Chen Z P, Jin J W, et al. Quantitative determination of ametryn in river water using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with an advanced chemometric model[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2015, 142: 166-171.
[52] Zhang D M, Xie Y, Deb S K, et al. Isotope edited internal standard method for quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 77(11): 3563-3569.
[53] Perera P N, Deb S K, Jo Davisson V, et al. Multiplexed concentration quantification using isotopic surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2010, 41(7): 752-757.
[54] Subaihi A, Xu Y, Muhamadali H, et al. Towards improved quantitative analysis using surface-enhanced Raman scattering incorporating internal isotope labelling[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(47): 6636-6644.
[55] Shen W, Lin X, Jiang C Y, et al. Reliable quantitative SERS analysis facilitated by core-shell nanoparticles with embedded internal standards[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2015, 54(25): 7308-7312.
[56] Wu S R, Tian X D, Liu S Y, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy solution and solid substrates with built-in calibration for quantitative applications[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2018, 49(4): 659-667.
[57] Zhang X Q, Li S X, Chen Z P, et al. Quantitative SERS analysis based on multiple-internal-standard embedded core-shell nanoparticles and spectral shape deformation quantitative theory[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2018, 177: 47-54.
[59] Zou Y X, Chen L, Song Z L, et al. Stable and unique graphitic Raman internal standard nanocapsules for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy quantitative analysis[J]. Nano Research, 2016, 9(5): 1418-1425.
[60] Zhang J, Yin Z H, Gong T C, et al. Graphene/Ag nanoholes composites for quantitative surface-enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(17): 22432-22439.
[61] Peksa V, Jahn M, Štolcova L, et al. Quantitative SERS analysis of azorubine (E 122) in sweet drinks[J]. Analytical chemistry, 2015, 87(5): 2840-2844.
[62] Wei H R. McCarthy A, Song J, et al. Quantitative SERS by hot spot normalization-surface enhanced Rayleigh band intensity as an alternative evaluation parameter for SERS substrate performance[J]. Faraday Discussions, 2017, 205: 491-504.
[63] Ryu Y, Kang G M, Lee C W, et al. Porous metallic nanocone arrays for high-density SERS hot spots via solvent-assisted nanoimprint lithography of block copolymer[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(93): 76085-76091.
邢豪健, 尹增鹤, 张洁, 朱永. 基于内标法的表面增强拉曼散射定量分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(3): 030002. Haojian Xing, Zenghe Yin, Jie Zhang, Yong Zhu. Quantitative Analysis of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Based on Internal Standard Method[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(3): 030002.