基于双色LED芯片的双波长像面数字全息显微术  下载: 1051次
下载: 1051次
1 引言
数字全息显微术是一种能够快速、定量地获取被测物场复振幅信息的新型显微技术,具有非接触、全场测量、高精度等特点,因而在材料分析[1]、生物医学观测[2]、流场测量[3]等方面得到了广泛的应用。
双波长数字全息显微术首先记录两个不同波长下的两幅数字全息图,然后分别通过数值再现算法获得其对应波长的包裹相位图,并求得两者的包裹相位差,最后得到等效波长的相位分布。该方法解决了单波长数字全息显微术所面临的相位解包裹问题,而且适用于被测样品表面结构梯度变化很大或受噪声严重影响的情况[4-7]。
传统双波长数字全息显微术通常采用单色光电记录器件获取两个分立光源照明下的多幅数字全息图,这种方式极易受到光源稳定性不佳、外界环境振动、气流扰动等因素的影响[8-9]。曾雅楠等[10]利用两个分立光源并结合像面数字全息显微术实现了对台阶型透明样品的高精度测量,但其实验装置较为复杂。Wada[11]利用可调谐激光器实现了对大深度台阶的形貌测量,但由于该方法需要依次获取被测样品在不同波长下的全息图,因此无法进行实时测量。Rinehart等[12]首先通过实验证明了彩色电荷耦合器件(CCD)的色串扰对双波长数字全息相位测量精度的影响很小。而后,Min等[13]利用彩色光电记录器件CMOS并结合角分复用技术,实现了单帧采集双波长数字全息图,但实验中依然采用两个独立光源,易受光源稳定性及外界环境因素影响。Jeon等[14]采用两种不同中心波长的窄带滤光片对宽带发光二极管(LED)光源进行滤色,依次获得不同照明光波下的数字全息图,但是滤光片的引入使得实验中的影响因素增多,如光能损耗、滤色效果都会影响该方案的有效性,同时也降低了测量的实时性。
针对上述问题,本文提出了一种基于双色LED芯片的双波长像面数字全息显微测量方法,该方法通过在LED中封装两种波长的芯片实现双色光场的同时输出,而后利用彩色CCD记录的双色场数字全息图,并结合两步相移迭代技术,重构出被测样品的相位分布及面型分布。与现有系统相比,本文方法能够有效地简化光路,降低光源稳定性,减小外界环境因素扰动对系统稳定性的影响。
2 原理
在像面数字全息显微术中,记录两幅含有相移量
式中
通过(1)式获取的+1级再现像
通过模拟产生数字参考光波
获取实际相移量后,利用(2)式及(3)式就可以准确得到+1级再现像
式中Im
在双波长数字全息显微术中,将记录光波
式中
获取等效波长下的去噪声物光波相位分布后,依据被测样品结构的不同,分别得到被测样品的面型分布。
对于反射型被测样品,其面型分布
对于透射型被测样品,其面型分布
式中
3 实验
3.1 双色LED芯片的封装结构
利用固晶、焊线、灌胶等传统封装工艺,将台湾晶元光电股份有限公司生产的红光芯片(1.13 mm×1.13 mm)、绿光芯片(1.52 mm×1.52 mm)封装成双色LED芯片,其结构尺寸及实物如
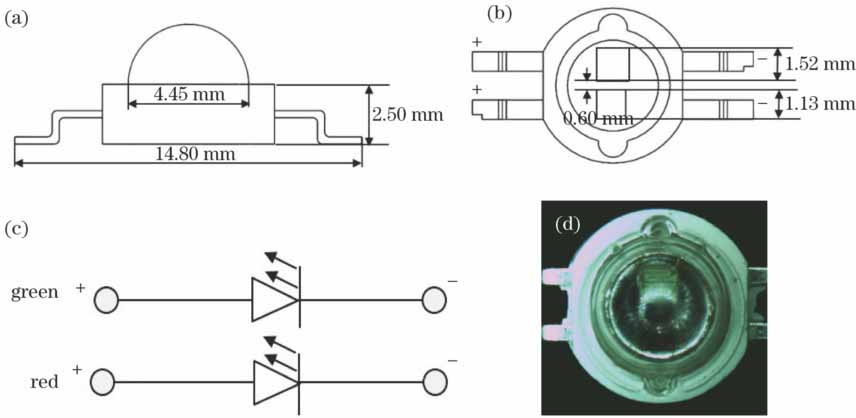
图 1. 双色LED芯片的封装结构图。 (a)正视图;(b)俯视图;(c)电路图;(d)实物图
Fig. 1. Packaging structure of bi-color LED chips. (a) Front view; (b) top view; (c) circuit; (d) physical map
采用杭州灵彩科技有限公司生产的LMS-0315光源光电色测试系统,对封装后的双色LED芯片进行功率谱测量。当直流输入电压为3.2 V,电流为350 mA时,其结果如
从双色LED芯片的功率谱可以获取封装后LED的中心波长
3.2 实验装置
实验装置的光路如
在
表 1. 封装后双色LED芯片的光学性质
Table 1. Optical properties of the utilized bi-color LED chips
|

图 4. 彩色数字全息图。 (a)相移前;(b)相移后
Fig. 4. Colorful digital holograms. (a) Without phase shift; (b) with phase shift
利用彩色CCD的不同颜色通道将获取的两幅彩色相移数字全息图进行颜色分离,得到两组分别对应于670 nm(红光通道)和521 nm(绿光通道)的相移数字全息图,如

图 5. 两种波长的相移数字全息图。(a) 670 nm波长相移前;(b) 670 nm波长相移后;(c) 521 nm波长相移前;(d) 521 nm波长相移后
Fig. 5. Phase shifting digital holograms with two wavelengths. (a) Without phase shift at 670 nm; (b) with phase shift at 670 nm; (c) without phase shift at 521 nm; (d) with phase shift at 521 nm
对获取的两组像面相移数字全息图,采用以再现参考光的峰值信噪比为判断条件的两步相移迭代算法,降低相移误差,优化迭代过程[17-18]。通过该方法,获取670 nm及521 nm照明波长下的实际相移量分别为1.5567 rad和1.9523 rad。结合(1)式和(2)式,利用实际相移量及两步相移算法,重构被测样品在两个波长下的包裹相位,如

图 6. 通过两步相移算法重构的包裹相位图。 (a) 670 nm; (b) 521 nm
Fig. 6. Reconstructed wrap phase maps using two-step phase shifting algorithm. (a) 670 nm; (b) 521 nm
利用被测样品在两个波长下的包裹相位分布并结合(5)式即可获取被测样品的无包裹相位分布,如

图 7. 实验结果。 (a)含有相位畸变的双波长合成相位;(b)去除相位畸变的双波长合成相位;(c)被测样品的三维面型分布;(d)对比实验结果
Fig. 7. Experimental results. (a) Dual-wavelength phase map with phase distortion; (b) dual wavelength phase map without phase distortion; (c) 3D surface profile of the tested sample; (d) comparison of the measurement data
为了证明本文方法与分立光源相比具有更好的系统稳定性,分别利用双色LED芯片以及与双色LED芯片波长相同的分立LED光源对被测样品进行了30 min连续测量,间隔时间为1 min。而后,针对

图 8. 本文系统与分立光源测量系统的稳定性对比
Fig. 8. Comparison of stability between the proposed system and the system with two individual light sources
4 结论
结合双色LED封装技术、彩色全息图分离技术及双波长相位提取技术,提出了一种基于双色LED芯片的双波长像面数字全息显微测量系统,并进行了实验验证。结果表明,该系统可以有效地获取被测样品真实的相位分布和面型分布。该系统与其他双波长数字全息记录系统相比,避免了多个独立光源、可调谐光源或滤光元件的使用,这能够有效地简化实验光路和实验过程,降低光源稳定性要求及外界环境因素扰动对测量系统稳定性的影响,提高系统稳定性。
[1] 袁飞, 袁操今, 聂守平, 等. 双Lloyd镜数字全息显微测量术[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(10): 104207.
袁飞, 袁操今, 聂守平, 等. 双Lloyd镜数字全息显微测量术[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(10): 104207.
袁飞, 袁操今, 聂守平, 等. 双Lloyd镜数字全息显微测量术[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(10): 104207.
Yuan F, Yuan C J, Nie S P, et al. Digital holographic microscopy employing dual-Lloyd's mirror[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(10): 104207.
[2] 赵洁, 王大勇, 李艳, 等. 数字全息显微术应用于生物样品相衬成像的实验研究[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(11): 2906-2911.
赵洁, 王大勇, 李艳, 等. 数字全息显微术应用于生物样品相衬成像的实验研究[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(11): 2906-2911.
赵洁, 王大勇, 李艳, 等. 数字全息显微术应用于生物样品相衬成像的实验研究[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(11): 2906-2911.
[5] 邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于双波长数字全息术的微光学元件折射率分布及面形测量[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(3): 0312006.
邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于双波长数字全息术的微光学元件折射率分布及面形测量[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(3): 0312006.
邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于双波长数字全息术的微光学元件折射率分布及面形测量[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(3): 0312006.
[6] 王羽佳, 江竹青, 高志瑞, 等. 双波长数字全息相位解包裹方法研究[J]. 光学学报, 2012, 32(10): 1009001.
王羽佳, 江竹青, 高志瑞, 等. 双波长数字全息相位解包裹方法研究[J]. 光学学报, 2012, 32(10): 1009001.
王羽佳, 江竹青, 高志瑞, 等. 双波长数字全息相位解包裹方法研究[J]. 光学学报, 2012, 32(10): 1009001.
[9] 寇云莉, 李恩普, 邸江磊, 等. 利用双波长数字全息显微术测量微小物体表面形貌[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209010.
寇云莉, 李恩普, 邸江磊, 等. 利用双波长数字全息显微术测量微小物体表面形貌[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209010.
寇云莉, 李恩普, 邸江磊, 等. 利用双波长数字全息显微术测量微小物体表面形貌[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209010.
[10] 曾雅楠, 汪飞, 雷海, 等. 双波长数字显微像面全息术测量微结构表面形貌[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(10): 1009001.
曾雅楠, 汪飞, 雷海, 等. 双波长数字显微像面全息术测量微结构表面形貌[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(10): 1009001.
曾雅楠, 汪飞, 雷海, 等. 双波长数字显微像面全息术测量微结构表面形貌[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(10): 1009001.
[16] 潘卫青, 龚国芳, 范玉峰. 低噪声双波长数字全息及在超精密加工表面检测中的应用[J]. 光电工程, 2015, 42(1): 25-31.
潘卫青, 龚国芳, 范玉峰. 低噪声双波长数字全息及在超精密加工表面检测中的应用[J]. 光电工程, 2015, 42(1): 25-31.
潘卫青, 龚国芳, 范玉峰. 低噪声双波长数字全息及在超精密加工表面检测中的应用[J]. 光电工程, 2015, 42(1): 25-31.
[17] 邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于相移量提取的两步相移数字全息术[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209014.
邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于相移量提取的两步相移数字全息术[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209014.
邓丽军, 杨勇, 石炳川, 等. 基于相移量提取的两步相移数字全息术[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209014.
[18] 巩琼, 秦怡. 二步相移数字全息中实际相移角的获取[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(7): 1807-1811.
巩琼, 秦怡. 二步相移数字全息中实际相移角的获取[J]. 中国激光, 2010, 37(7): 1807-1811.
邓丽军, 黄星艳, 曾吕明, 黄振, 刘国栋. 基于双色LED芯片的双波长像面数字全息显微术[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(1): 0111004. Lijun Deng, Xingyan Huang, Lüming Zeng, Zhen Huang, Guodong Liu. Dual-Wavelength Image-Plane Digital Holographic Microscopy Based on Bi-Color LED Chips[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0111004.