工型超材料共振研究  下载: 749次
下载: 749次
1 引言
表面等离子体激元(SPP)是位于金属与电介质界面的电荷密度振荡,其被局限在界面上,沿着金属与电介质界面传播[1-4]。1902年,Wood[5]发现了SPP;1971年,Kretschmann[6]提出了表面等离子体传感器;1998年,Ebbesen等[1]发现SPP共振会导致亚波长超强透射现象。表面等离子体共振(SPR)在许多领域具有应用前景,如亚波长集成[7-8]、生物传感[9]、化学反应控制[10]等。最新的研究发现,SPR技术可以用于微弱磁场探测[11]、热致折射率变化[12]以及宽波段纳米超材料太阳能吸收器的设计[13]等。
在原子系统中,在光的照射下,连续态与离散态的耦合会导致量子干涉,从而在较宽的吸收带中形成一条新的反射模式,称为电磁诱导反射(EIR)模[14]。在光学中,两个共振模式之间的耦合会导致反射谱中出现新的模式,类似于原子系统中的EIR模。超材料是一种人工复合材料,由金属和电介质的亚波长周期结构组成。由于能激发SPP和SPR,因此超材料具有天然材料所不具备的独特的电磁性质,如非常高的介电常数和磁导率[15-16]。研究发现,超材料中存在的EIR模是由结构中等离子体的共振导致的,并在超材料中产生了慢光效应[17-18]和负折射率现象[19-21]。几种不同单元结构的超材料中出现了EIR模,如:工型结构单元产生电磁感应透明效应[22],十字架型结构单元产生近红外局部SPR效应[16],H-II型结构单元产生表面等离子体诱导出新的反射模式[23]等。Vafapour等[24]发现:在工型超材料中,当结构对称时,只出现一个反射模;当结构的对称性破缺后,会出现新的EIR模。
本文利用时域有限差分法研究工型结构超材料时发现,非对称工型结构中存在5个特殊的反射模式,出现了新的EIR模。结合理论模型和近场分布分析了5个反射模产生的物理机制。
2 研究结构
在玻璃衬底上镀厚度为40 nm的金属银,在银层上刻蚀周期性工型结构,结构单元如
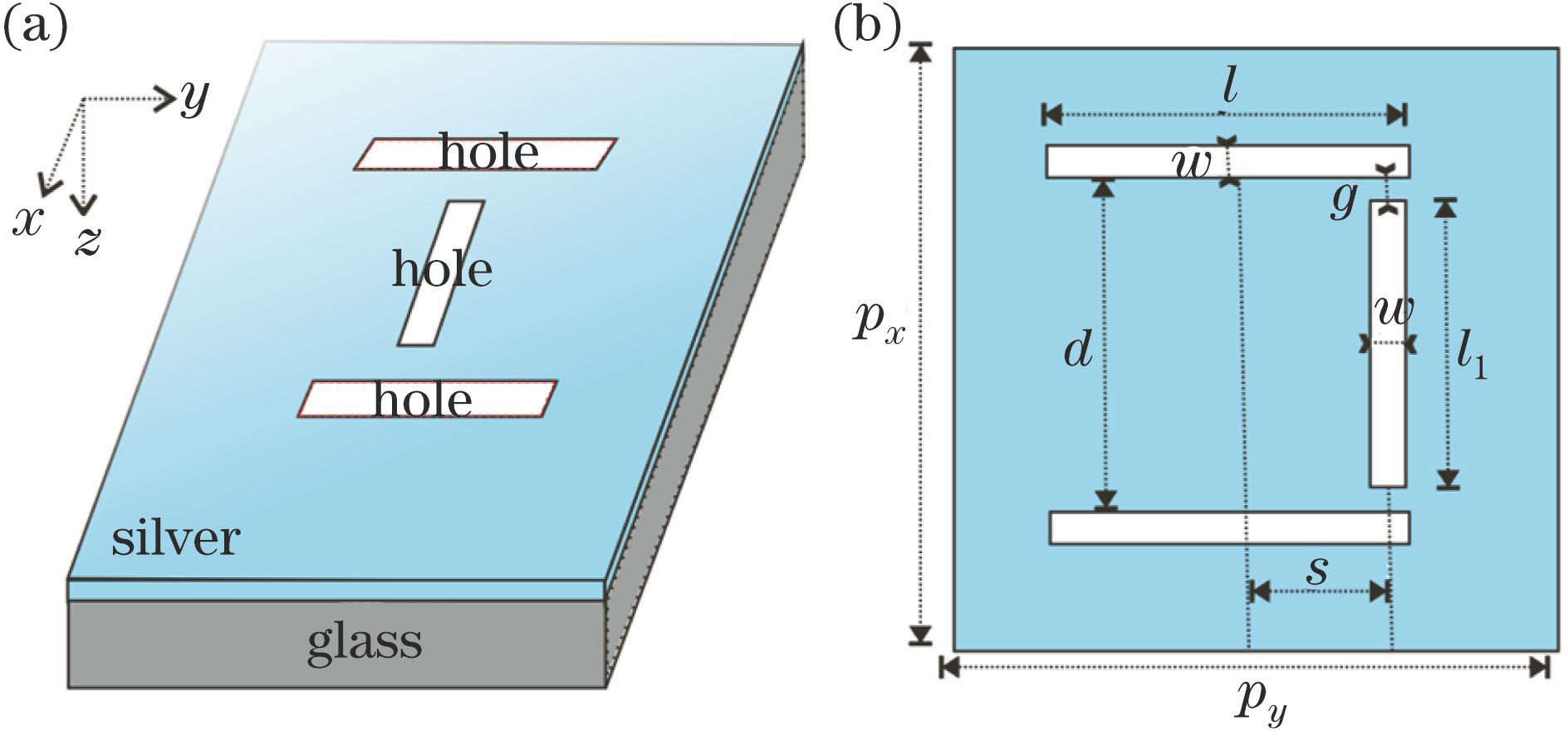
图 1. 结构模型示意图。(a)三维立体图;(b)二维平面图
Fig. 1. Schematic of structure model. (a) Three-dimensional stereogram; (b) two-dimensional plane picture
利用时域有限差分模拟得到频率在70~250 THz范围内的反射谱。光波沿
式中金属的SPR频率
两条横向狭缝的长度
竖向狭缝与两条横向狭缝的最右端对齐。此时向左延长两条横向狭缝,分别延长到

图 2. (a)横向狭缝为460 nm时的反射光谱;(b)横向狭缝延长后的反射光谱
Fig. 2. (a) Reflection spectra with horizontal slits of 460 nm; (b) reflection spectra after stretching two horizontal slits
3 物理机制分析
反射谱中反射模的产生主要是由狭缝中电磁场的共振引起的。设沿
式中
联立(2)~(6)式得到
当满足(8)式时,
式中
根据(9)式可得
式中
对于横向狭缝左边的部分,通过求解(2)~(6)式可得当满足(8)式时,
根据(10)式可得
式中
对于竖向狭缝,当达到稳定之后,
式中
在竖向狭缝中,
根据(10)式可以得到当满足(15)式时,竖向狭缝中的场达到最大。即
式中
当(15)式满足时,竖向狭缝共振,自由空间入射的电磁场被耦合到金属结构内。当(8)、(10)、(12)、(15)式满足时,在横向狭缝中能产生共振。横向狭缝和竖向狭缝共振耦合,导致EIR反射模出现。通过狭缝的共振,电磁波能量被散射和被金属吸收。
通过模拟得到各个反射模对应的电场分布,结合上面的理论分析模产生的机制。对于对称结构(

图 4. 对称状态下的电场分布图。(a)模1 ;(b)模2;(c)模3
Fig. 4. Electric field distribution in symmetrical state. (a) Mode 1; (b) mode 2; (c) mode 3
当结构的对称性破缺时,产生了1个新模。当横向狭缝长度增加时,也产生了1个新模,共出现5个模式,如

图 5. 非对称状态下的电场分布图。(a)模1;(b)模2;(c)模3;(d)模4;(e)模5
Fig. 5. Electric field distribution in asymmetric state. (a) Mode 1; (b) mode 2; (c) mode 3; (d) mode 4; (e) mode 5
在
下面结合理论和模拟结果分析各模随周期和竖向狭缝长度的变化规律。在

图 6. (a)增加周期后的反射光谱;(b)增加中间凹槽后的反射光谱
Fig. 6. (a) Reflection spectra after increasing period; (b) reflection spectra after increasing middle groove
反射谱随竖向狭缝
4 结论
利用时域有限差分法对工型结构超材料进行模拟研究。当结构对称时,存在简并,非对称工型结构超材料具有异常的电磁性质,存在5个特殊的反射模。分析其近场和随参数变化的特性,认为表面等离子体在工型结构单元内的不同共振位置、模式阶数和结构的周期性导致了这5个特殊的反射模。竖向狭缝1阶共振、横向狭缝左侧部分的1阶共振、右侧部分1阶共振和整个横向狭缝的2阶共振,以及周期结构间金属银表面部分的共振导致了这5个反射模。当结构的对称性破缺时,出现新的共振模式。研究结果表明工型超材料的特异性质是由不同的共振引起的。
[3] 陆云清, 成心怡, 许敏, 等. 基于TPPs-SPPs混合模式的激发以增强单纳米缝异常透射[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(20): 204207.
陆云清, 成心怡, 许敏, 等. 基于TPPs-SPPs混合模式的激发以增强单纳米缝异常透射[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(20): 204207.
Lu Y Q, Cheng X Y, Xu M, et al. Extraordinary transmission of light enhanced by exciting hybrid states of Tamm and surface plasmon polaritions in a single nano-slit[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(20): 204207.
[4] 张国浩, 陈跃刚. 激发双线波导中的对称和反对称等离子体波导模式的新型耦合器[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(11): 1113003.
张国浩, 陈跃刚. 激发双线波导中的对称和反对称等离子体波导模式的新型耦合器[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(11): 1113003.
[7] 付康印, 陈跃刚. 金属亚波长波导阵列的聚焦和分束[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(5): 0523003.
付康印, 陈跃刚. 金属亚波长波导阵列的聚焦和分束[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(5): 0523003.
[8] 陈跃刚, 杨兴. 基于表面等离子体腔的波分复用器件设计[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 29(4): 12-16.
陈跃刚, 杨兴. 基于表面等离子体腔的波分复用器件设计[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 29(4): 12-16.
Chen Y G, Yang X. Design of multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on surface plasma resonant cavity[J]. Journal of Guizhou University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2012, 29(4): 12-16.
[10] 李风华, 单长胜, 杨贵福, 等. 表面等离子体共振技术在电化学反应过程研究中的应用[J]. 分析化学, 2007, 35(5): 754-759.
李风华, 单长胜, 杨贵福, 等. 表面等离子体共振技术在电化学反应过程研究中的应用[J]. 分析化学, 2007, 35(5): 754-759.
Li F H, Shan C S, Yang G F, et al. Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and its applications for the studies on electrochemical processes[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 35(5): 754-759.
[12] 刘晓菲, 张学如, 兰国强, 等. 表面等离子体共振的热致折射率[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(5): 0524001.
刘晓菲, 张学如, 兰国强, 等. 表面等离子体共振的热致折射率[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(5): 0524001.
[13] 朱路, 王杨, 熊广, 等. 宽波段纳米超材料太阳吸收器的设计及其吸收特性[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(9): 0923001.
朱路, 王杨, 熊广, 等. 宽波段纳米超材料太阳吸收器的设计及其吸收特性[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(9): 0923001.
[19] Smith D R, Pendry J B. Wiltshire M C K. Metamaterials and negative refractive index[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5685): 788-792.
Smith D R, Pendry J B. Wiltshire M C K. Metamaterials and negative refractive index[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5685): 788-792.
[25] 钱景仁. 耦合模理论及其在光纤光学中的应用[J]. 光学学报, 2009, 29(5): 1188-1192.
刘瑶, 陈跃刚. 工型超材料共振研究[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(3): 0324001. Liu Yao, Chen Yuegang. Resonance of I-Shaped Metamaterials[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 0324001.







