干涉偏差对四束圆偏振光干涉的影响  下载: 813次
下载: 813次
1 引言
激光干涉技术由于其制造过程用时短且能实现大面积均匀分布的周期性结构而被广泛地应用于制造光子晶体、光波导、滤光片等电子器件[1-15]。通过设置发生干涉光束的数目和曝光次数,可以得到多维的任意周期性结构。其中,四光束干涉技术仅利用单次曝光就能得到二维周期性结构,并已逐渐用于制造微纳米级的多维周期性结构[16-19]。近年来,文献[ 20-24]已研究干涉强度分布对入射光束偏振态的依赖性,发现了干涉光束的入射角和光强的偏差会影响干涉图形。为了可以更好地用四光束干涉技术实现微纳周期结构,有必要通过理论研究来认识四光束干涉原理,进一步分析干涉偏差对四光束干涉的影响。
本文对四束均为右旋圆偏振(RC)的干涉光的干涉现象进行理论计算和MATLAB模拟研究,并从入射角和方位角设置方面,详细讨论了当干涉光束对称分布和当其中一束干涉光存在偏差时对干涉强度分布产生的影响。
2 四束右旋圆偏振光干涉理论
式中:
干涉后强度分布为
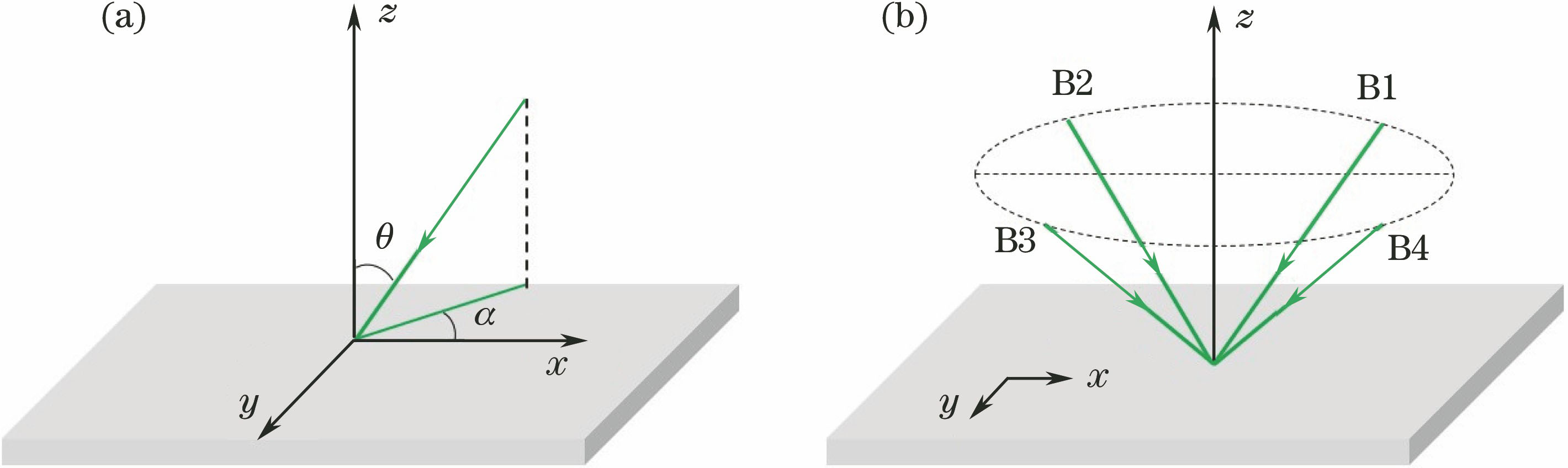
图 1. (a)干涉光束在直角坐标系中的位置表示;(b)四束光(B1,B2,B3,B4)干涉的示意图
Fig. 1. (a) Interference beam in rectangular coordinate system; (b) diagram of four beams (B1, B2, B3, B4) interference
沿
可得:干涉时,四束光的波矢和偏振态的单位矢量分别为
当四束干涉光对称分布于
从(6)式可得,四束对称分布的干涉光干涉后其强度分布与
3 干涉偏差分析
当入射光束中的一束干涉光发生偏差,即入射角和方位角分别为:

图 2. 利用MATLAB模拟得到四束对称分布的右旋圆偏振干涉光束干涉强度分布。(a)干涉强度分布的三维视图;(b)入射角为θ=10°时干涉强度在xy平面内的分布;(c)入射角为θ=15°时干涉强度在xy平面内的分布
Fig. 2. Interference intensity distributions of four symmetrical RC interference beams using MATLAB simulation. (a) 3-dimensional view of intensity distribution; (b) intensity distribution in xy-plane with the incidence angle θ=10° ; (c) intensity distribution in xy-plane with the incidence angle θ=15°
由(7)式可知,入射角

图 3. 四束干涉光沿xz轴和yz轴方向的干涉强度分布。(a1)、(a2)对称分布;(b1)、(b2)入射角发生偏差时; (c1)、(c2)方位角发生偏差时
Fig. 3. Interference intensity distributions along the xz-axis and yz-axis. (a1)(a2) Symmetrical distribution; (b1)(b2) under incidence deviation; (c1)(c2) under azimuth deviation
表 1. 干涉强度分布出现最大值的直线所对应的斜率和干涉周期
Table 1. Slope of lines and interference periods where the maximum interference intensity appears
| ||||||||||||||||||||
如
表 2. 当入射角或方位角发生偏差时,所对应的斜率和干涉周期
Table 2. Slope of lines and interference periods when there is a deviation in the incident angle or azimuth angle
|
应用MATLAB程序,得到一束干涉光出现偏差(

图 4. 干涉强度分布图。(a)入射角发生偏差时;(b)方位角发生偏差时;(c)入射角和方位角都发生偏差时
Fig. 4. Interference intensity distributions. (a) Under azimuth deviation; (b) under azimuth deviation; (c) under both incidence and azimuth deviations
4 结论
综上所述,研究了四束右旋圆偏振光的干涉过程,分析其中一束光的入射角和方位角发生偏差对干涉强度分布的影响。通过理论推导,得出对于四束对称分布的干涉光,干涉后得到均匀的二维周期性强度分布,且沿着
[10] 周兴平, 疏静, 卢斌杰, 等. 基于三角晶格光子晶体谐振腔的双通道解波分复用器[J]. 光学学报, 2013, 33(1): 0123001.
[12] 熊平新, 贾鑫, 贾天卿, 等. 三光束飞秒激光干涉在GaP, ZnSe表面诱导二维复合纳米-微米周期结构[J]. 物理学报, 2010, 59(1): 311-316.
Xiong P X, Jia X, Jia T Q, et al. Two-dimensional complex nano-micro patterning on GaP and ZnSe surface created by the interference of three femtosecond laser beams[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(1): 311-316.
[13] 杨宏道, 李晓红, 李国强, 等. 1064 nm纳秒脉冲激光诱导硅表面微结构研究[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60(2): 027901.
Yang H D, Li X H, Li G Q, et al. Silicon surface microstructures created by 1064 nm Nd∶YAG nanosecond laser[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(2): 027901.
[14] 李晨, 程光华, Stoian R. 飞秒激光诱导金属钨表面周期性自组织结构的研究[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(5): 0532001.
[15] 钟敏霖, 李焱. “超快激光加工与微纳制造”专题前言[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(1): 0102000.
Zhong M L, Li Y. Special introduction: ultra-fast laser processing and micro-nano manufacturing[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser, 2017, 44(1): 0102000.
[16] 张锦, 冯伯儒, 郭永康. 四激光束干涉光刻制造纳米级孔阵的理论分析[J]. 光子学报, 2003, 32(4): 398-401.
[17] 陈小军, 张自丽, 葛辉良. 四光束干涉单次曝光构造含平面缺陷三维周期性微纳结构[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(17): 174211.
Cheng X J, Zhang Z L, Ge H L. Fabricating three-dimensional periodic micro-structure with planar defects via a single exposure[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(17): 174211.
[18] 李艳, 陈辉, 代克杰. 飞秒四光束干涉技术加工石墨烯纳米网[J]. 微纳电子技术, 2013, 50(10): 662-666.
Li Y, Chen H, Dai K J. Fabrication of graphene nanomeshes by the femtosecond four-beam interference technique[J]. Micronanoelectronic Technology, 2013, 50(10): 662-666.
[19] 张锦, 冯伯儒, 郭永康. 双光束双曝光与四光束单曝光干涉光刻方法的比较[J]. 光电工程, 2005, 32(12): 21-24.
[20] 梁文耀, 何锐斌, 林灯荣, 等. 光束偏振对三角光子晶体全息制作影响的仿真研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2016, 53(9): 091601.
[21] 吴晓. 偏振态对三光束激光干涉分布的影响[J]. 光学学报, 2015, 35(10): 1012002.
[24] 马丽娜, 张锦, 蒋世磊, 等. 入射光束角度及强度偏差对多光束干涉光刻结果的影响[J]. 光子学报, 2015, 44(10): 1011003.
Article Outline
吴晓. 干涉偏差对四束圆偏振光干涉的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(6): 061405. Xiao Wu. Influence of Interference Deviation on Four-Beam Interference with Circular Polarization[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(6): 061405.






