Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
We demonstrated the efficient plasmon-induced nonlinear absorption of liquid metal GaInSn nanospheres prepared by a facile liquid-phase method. With GaInSn as saturable absorbers, a passively Q-switching operation was obtained at both 1.3 and 2 μm. The pulse width of 32 ns was achieved at 1.3 μm with repetition rate of 44 kHz, single pulse energy of 51.9 μJ, and output power of 425 mW. Meanwhile, 510 ns and 92 kHz pulses with energy of 36.1 μJ and output power of 2.48 W were obtained at 2 μm. This work provides the potential of liquid metal for improving metal functions and flexible optical devices.
GaInSn nanosphere passively Q-switched lasers saturable absorber Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(11): 111901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Alloying in two-dimension has been a hot spot in the development of new, versatile systems of optics and electronics. Alloys have been demonstrated to be a fascinating strategy to modulate the chemical and electronic properties of two-dimensional nanosheets. We firstly reported ultra-broadband enhanced nonlinear saturable absorption of Mo0.53W0.47Te2 alloy at 0.6, 1.0, and 2.0 μm. The nonlinear saturable absorption of Mo0.53W0.47Te2 saturable absorber (SA) was measured by the open aperture Z-scan technique. Compared to MoTe2 and WTe2 SAs, the Mo0.53W0.47Te2 SA showed five times deeper modulation depth, 8.6% lower saturable intensity, and one order larger figure of merit. Thus, our research provides a method of alloys to find novel materials with more outstanding properties for optics and optoelectronic applications.
nonlinear optics transition metal dichalcogenides saturable absorption Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 021902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
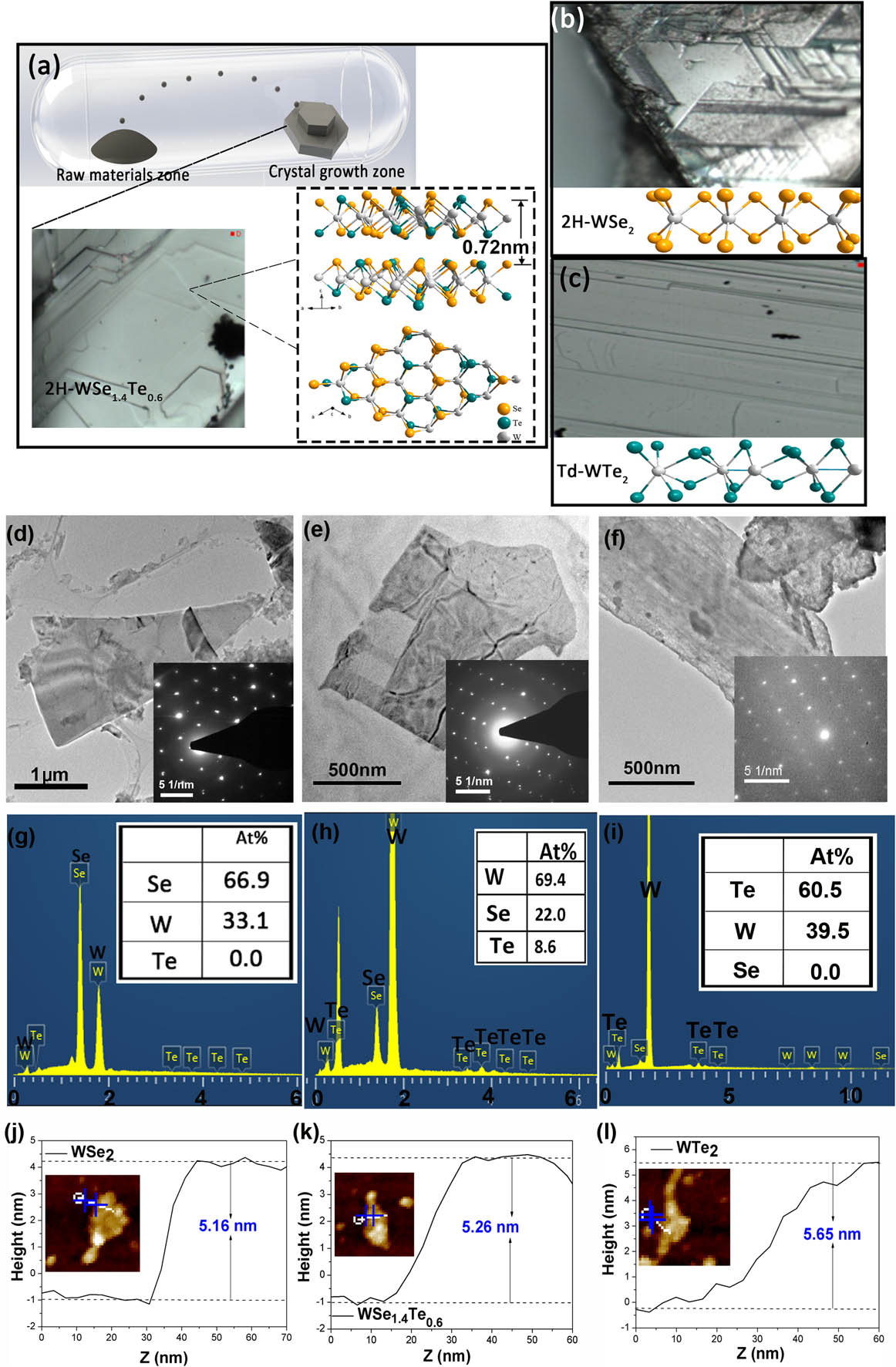
Due to the composition-dependent properties of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), alloying of existing dissimilar TMDs architecture is a novel and controllable route to tailor crystal structures with superior optical and optoelectronic properties. Here, we reported the hexagonal-phase WSe1.4Te0.6 alloy can enable great promise for enhanced saturable absorption response exceeding the parent component WSe2 and WTe2, with larger modulation depth and lower saturable intensity. These advantages allowed the 1064 nm passively Q-switched lasers based on WSe1.4Te0.6 to be more efficient, with pulse duration narrowed to 45%, and slope efficiency increased by 232%. Our findings highlighted the appropriate alloying of TMDs as an effective strategy for development of saturable absorbers.
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 121404

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 E-mail: xphu@nju.edu.cn
4 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
We report the fabrication of an MoS2 black phosphorus (BP) composite saturable absorber by liquid phase exfoliation and the spin-coating method and further exploitation to build a 2 μm passively Q-switched Tm:YAP laser. Such a composite based Q-switched laser with a duration of 488 ns and corresponding peak power of 85.9 W is obtained, which shows an improved saturable absorption effect than that of single MoS2 (616 ns, 68.7 W) and BP (932 ns, 22.4 W). The results indicate that simple and reasonable fabrication of the vertical composite from two-dimensional atomic layer materials opens up the possibility to create an unprecedented saturable absorber with exciting properties.
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(2): 020018
1 哈尔滨工业大学可调谐激光技术国家重点实验室, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
2 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
近些年,分布式布里渊光纤传感因具有分布式应变和温度的测量能力, 以及在结构健康监测领域的重要应用而受到广泛的研究。在多种传感方案中, 布里渊光时域分析(BOTDA)技术具有信噪比好、空间分辨率高、传感距离远等优点, 受到广泛关注。传统的BOTDA系统平均和扫频过程比较费时, 只适宜进行静态或缓慢的应变测量。通过分析BOTDA系统的分布式传感原理, 总结了限制其快速分布式传感测量的主要因素。针对这些限制因素, 综述了近期快速BOTDA系统取得的一系列的进展, 主要包括基于偏振补偿技术的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学捷变频技术的快速BOTDA系统、基于斜坡法的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学啁啾链的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学频率梳技术的快速BOTDA系统, 指出通过单一或者多个新技术组合而成的快速BOTDA系统具有更好的性能和更广阔的应用前景。
传感器 非线性光纤光学 受激布里渊散射 振动分析
1 济南大学物理科学与技术学院, 山东 济南 250022
2 山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室, 山东 济南 250100
3 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所, 福建 福州 350002
采用提拉法生长了Yb:NaY(WO4)2晶体,使用透射式半导体可饱和吸收镜(SESAM),实现了激光二极管(LD)抽运的连续波锁模飞秒激光运转。当最大抽运功率为8.6 W时,输出功率为164 mW,中心谱线为1035 nm,锁模脉冲的重复频率为35 MHz。经测量此时锁模脉冲宽度为246 fs。
激光器 钨酸钇钠晶体 半导体可饱和吸收镜 锁模 飞秒 中国激光
2012, 39(11): 1102002
山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室, 山东 济南 250100
石墨烯具有饱和恢复时间极短、导热性好、吸收带宽、损耗低、成本低廉且容易制备等优点,被认为是光电子应用中理想的半导体可饱和吸收体材料,近几年受到广泛的关注。介绍了本课题组最近在石墨烯锁模超快全固体激光器研究中取得的一些进展。在用液相剥离方法成功制备出尺寸大于20 μm的石墨烯薄片的基础上,将其应用于全固态NdGdVO4激光器,实现了脉宽16 ps、平均功率360 mW的锁模激光输出,单脉冲能量为8.4 nJ;继而在宽带增益介质YbKGW晶体中又实现了脉宽为489 fs的超快激光,平均功率564 mW。
激光器 全固态激光器 锁模 石墨烯
1 济南大学 理学院,山东 济南 250022
2 山东大学 晶体材料国家重点实验室,山东 济南 250100
使用透射式半导体可饱和吸收镜(SESAM),实现了光纤耦合半导体激光抽运Nd:YAG晶体的连续波锁模运转。根据ABCD矩阵传输理论,对激光器谐振腔的像散、稳定性与腔参数的关系进行了理论计算。在此基础上,设计了Z型折叠激光谐振腔,获得了稳定的1064 nm皮秒锁模激光输出。当抽运功率为7.7 W时,最大输出功率为372 mW。重复频率为54 MHz。经测量此时锁模脉冲宽度为8.9 ps。
激光技术 半导体可饱和吸收镜 连续锁模 皮秒脉冲 Nd:YAG激光器





