
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information Materials and Intelligent Sensing Laboratory of Anhui Province, Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronic Information Acquisition and Manipulation of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Opto-electronics Engineering, Anhui University, Hefei 230601, China
2 School of Instrument Science and Opto-electronics Engineering, Laboratory of Optical Fibers and Micro-nano Photonics, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
3 School of Opto-electronic Engineering, Zaozhuang University, Zaozhuang 277160, China
Random lasers are a type of lasers that lack typical resonator structures, offering benefits such as easy integration, low cost, and low spatial coherence. These features make them popular for speckle-free imaging and random number generation. However, due to their high threshold and phase instability, the production of picosecond random lasers has still been a challenge. In this work, we have developed three dyes incorporating polymer optical fibers doped with various scattering nanoparticles to produce short-pulsed random fiber lasers. Notably, stable picosecond random laser emission lasting 600 ps is observed at a low pump energy of 50 µJ, indicating the gain-switching mechanism. Population inversion and gain undergo an abrupt surge as the intensity of the continuously pumped light nears the threshold level. When the intensity of the continuously pumped light reaches a specific value, the number of inversion populations in the “scattering cavity” surpasses the threshold rapidly. Simulation results based on a model that considers power-dependent gain saturation confirmed the above phenomenon. This research helps expand the understanding of the dynamics behind random medium-stimulated emission in random lasers and opens up possibilities for mode locking in these systems.
random laser polymer optical fiber gain-switched laser picosecond pulse Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 040603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Advanced Photonic Technology Laboratory, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
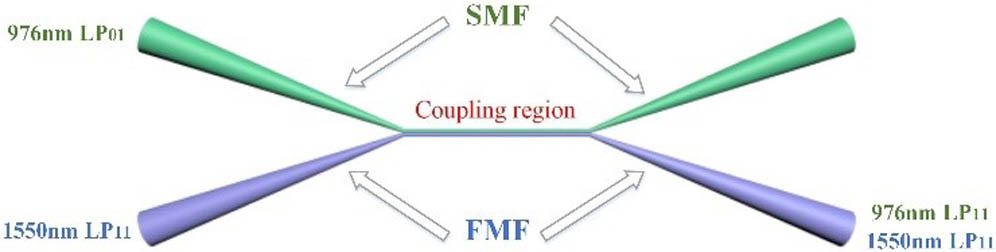
Experimental generation of stable mode-locked pulses and cylindrical vector beams (CVBs), from an all few-mode fiber (FMF) ring laser is first reported, to the best of our knowledge. In this laser, a section of few-mode erbium-doped fiber (FM-EDF) is used as the gain medium. The FM-EDF is pumped by 976 nm laser with LP11 mode, which is simultaneously converted and multiplexed through a homemade hybrid device, i.e., wavelength division multiplexing-mode selection coupler (WDM-MSC). All the components in our experiment are connected using FMF. The resulted CVB pulses have a spectral width of 0.33 nm with a repetition rate of 30.58 MHz under the pump power of 340 mW. Moreover, both azimuthally and radially polarized CVBs were achieved with a high purity of >95%. This mode-locked CVB fiber laser with an all FMF configuration opens the way to manipulate the transverse mode in mode-locked fiber lasers.
140.3300 Laser beam shaping 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 121405
1 中国科学院光电研究院, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100049
电荷耦合器件(CCD)是成像系统的关键器件,CCD器件的点扩展函数(PSF)是整个成像系统PSF的重要部分。采用背部入射、部分耗尽CCD,分析了载流子在CCD中的运动过程,推导了计算CCD的PSF的解析公式。对CCD进行物理建模,用蒙特卡罗方法进行粒子跟踪模拟计算得到了PSF,并能和解析公式计算得到的PSF很好的吻合。系统分析计算了CCD的主要特性参数,如响应度、线性度和调制传递函数(MTF)等。模拟研究了入射光波长和CCD自由层宽度对CCD的PSF的影响,结果表明较窄自由层宽度和长波易得到较好的PSF。
光计算 电荷耦合器件 点扩散函数 蒙特卡罗方法 自由层





