Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Key Laboratory for Biomedical Measurements and Ultrasound Imaging, National-Regional Key Technology Engineering Laboratory for Medical Ultrasound, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, US
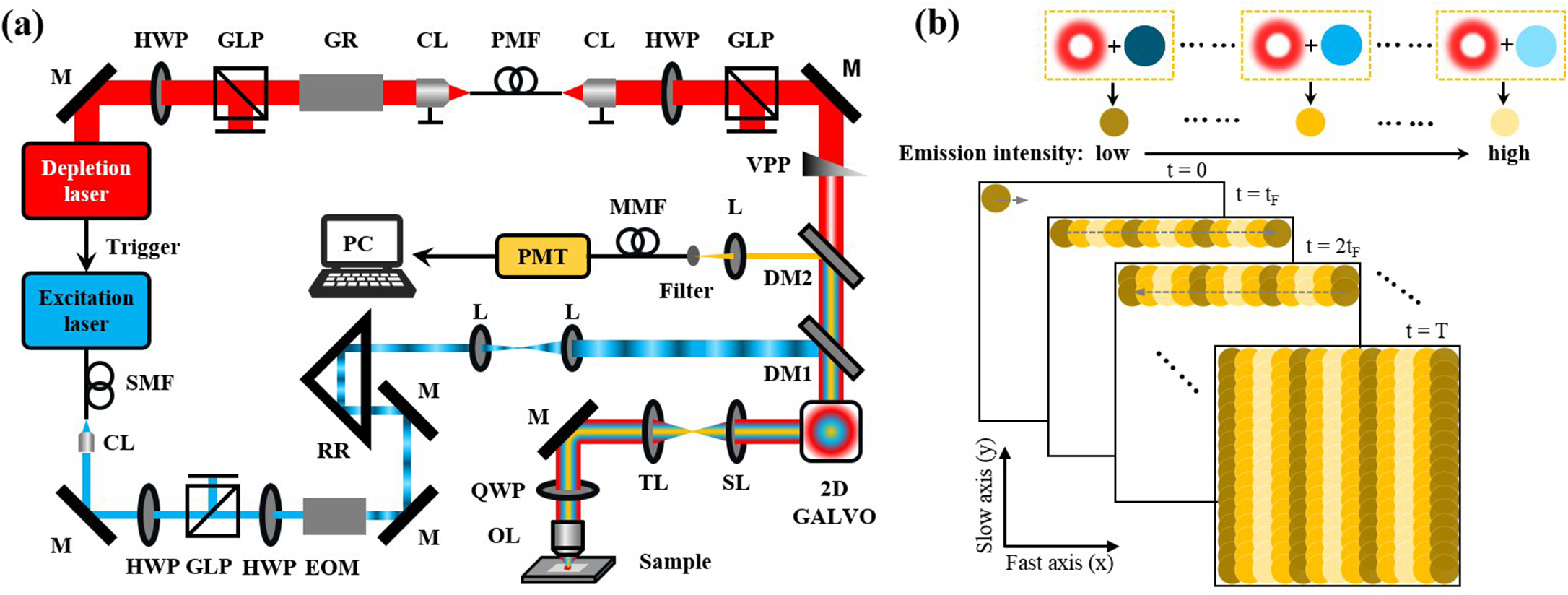
Wide-field linear structured illumination microscopy (LSIM) extends resolution beyond the diffraction limit by moving unresolvable high-frequency information into the passband of the microscopy in the form of moiré fringes. However, due to the diffraction limit, the spatial frequency of the structured illumination pattern cannot be larger than the microscopy cutoff frequency, which results in a twofold resolution improvement over wide-field microscopes. This Letter presents a novel approach in point-scanning LSIM, aimed at achieving higher-resolution improvement by combining stimulated emission depletion (STED) with point-scanning structured illumination microscopy (psSIM) (STED-psSIM). The according structured illumination pattern whose frequency exceeds the microscopy cutoff frequency is produced by scanning the focus of the sinusoidally modulated excitation beam of STED microscopy. The experimental results showed a 1.58-fold resolution improvement over conventional STED microscopy with the same depletion laser power.
stimulated emission depletion structured illumination microscopy superresolution microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031701
深圳大学光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
基于纳米材料的生物分子检测、光热治疗、光动力治疗和药物靶向输送等新方法,正逐渐成为生物医学领域中重要的诊疗手段。但由于传统纳米材料本身的局限性或治疗手段的缺陷,当前纳米医疗技术存在药物利用率低、毒副作用大和治疗效果低等问题。将纳米技术和光子学相结合,可以在纳米范围内精确控制光与物质的相互作用,从而使生物医学诊疗技术更加精准和稳定。从四个方面总结回顾了近年国内外面向精准化生物医学的多功能纳米光子学技术的发展状况,这四个方面分别为依靠光学技术改善纳米生物医学的稳定性、依靠光学技术实现对肿瘤纳米治疗过程的精准监控、依靠光学技术深入理解纳米生物医学的作用机制以及依靠新型光学技术获取前沿生物医学精细化研究新手段。
生物光学 功能监测和成像 纳米材料 光学诊断医学
1 广西师范大学物理科学与技术学院, 广西 桂林 541004
2 广西科学院生物物理实验室, 广西 南宁 530007
了解细胞生命活动途径并阐释其功能和分子机制是当前生命科学与物理科学交叉领域面临的重要科学挑战之一,而光学技术的创新与应用,能够通过监测单个细胞生理变化的细节来实现上述目标。细菌芽孢是一种特殊的休眠体,从休眠态转向营养生长的萌发过程是一种特别的细胞生理过程。光学技术和单细胞分析在芽孢萌发研究中的应用与发展,对认识芽孢萌发机理及其异质性发挥了极其重要的作用。就拉曼光谱、微分干涉差显微术、荧光成像和拉曼成像等技术的基本原理及其在细菌芽孢萌发中的应用与进展,前景与存在问题进行了简要述评。
生物光学 芽孢萌发机制 拉曼光谱 微分干涉差显微术 单细胞分析 激光与光电子学进展
2015, 52(10): 100002
广西师范大学物理科学与技术学院,桂林 541004
滤波器是通信中一种重要的器件,相移光纤光栅因其显著的滤波特性,可作为带阻滤波器应用于密集波分复用系统,实现光信号的解调。影响相移光纤光栅滤波特性的因素有很多,通过相移光纤光栅的耦合模理论分析,并利用MATLAB语言编程计算出相移光纤光栅的单波长、双波长和多波长滤波反射谱。结果发现:光栅参数的变化会使相移光纤光栅滤波特性发生改变;当进行双波长滤波时,反射谱将随着相移点位置由内向外的改变而向内塌缩;多波长滤波时,相移点位置不同可分别出现多透射窗口和超宽矩形透射窗口。
相移 反射谱 透射窗口 滤波器 phase shift reflective spectrum transmission window filter





