1 西安电子科技大学光电工程学院,陕西 西安 710071
2 西安电子科技大学杭州研究院,浙江 杭州 311231
针对场景偏振三维成像中光照不均匀、色彩、材料复杂和大视场下观测方向变化等原因造成的偏振法线梯度不准确和真实三维信息获取困难的问题,提出一种基于方向感知卷积神经网络的场景偏振三维成像新方法。首先,搭建具有方向感知能力的场景深度估计网络结构;其次,利用卷积神经网络所估计的场景深度对偏振法线梯度进行校正;最后,利用校正后的梯度通过基于梯度的积分算法进行三维重建。实验结果表明,所提方法解决了偏振固有的方位角模糊,提高了在光照不均匀、大视场范围场景条件下获取的法线梯度的准确性,最终在恢复场景真实三维形状的同时保留了丰富的纹理细节信息。实验结果证明了所提技术的有效性与优越性。
偏振三维成像 深度估计 梯度场校正 神经网络 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(2): 0211029
哈尔滨工业大学物理学院微纳光电信息系统理论与技术工业和信息化部重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
无衍射光束近年来广受关注,其无衍射、自修复和自加速的传播特性在微观成像应用中显示出潜在的优势。无衍射特性可抑制光束在传播过程中的衍射,有助于提升成像的分辨率。自修复特性可使光束在透过强散射介质后快速恢复波前,提高成像景深和信噪比。自加速特性可增加光场信息的有效探测维度,实现多维重构成像。本综述结合几类生物显微成像技术特点,介绍以贝塞尔光束、艾里光束为代表的无衍射光束在高分辨生物显微成像中的应用研究进展。
无衍射光束 生物显微成像 三维成像技术 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(20): 2000001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Technische Universität Ilmenau, Fachgebiet Technische Optik, Postfach 100565, 98684 Ilmenau, Germany
2 Iba Heiligenstadt, 37308 Heilbad Heiligenstadt, Germany
Light sheet fluorescence microscope with single light sheet illumination enables rapid 3D imaging of living cells. In this paper we show the design, fabrication and characterization of a diffractive optical element producing several light sheets along a 45° inclined tube. The element, which is based on a multi-focal diffractive lens and a linear grating, generates five thin light sheets with equal intensities when combined with a refractive cylindrical lens. The generated uniform light sheets can be applied for the scanning of samples in tubes enabling flow-driven 3-dimensional imaging.
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy Diffractive optical elements Multi-plane imaging 3D imaging Multi-focal lens Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2023022
基于主动散斑投射的双目立体视觉成像技术仅需一次投影拍摄即可实现三维重建,适合于动态成像,但在水下应用时,存在小孔模型失效、极线约束匹配条件不满足,以及投射散斑左右图像因受水下环境吸收、散射影响产生退化等问题。本文重新建立了基于主动投射散斑图案的水下双目视觉成像模型,分析了散斑图案对水下双目对应点匹配精度的影响,搭建了主动散斑水下双目视觉动态三维成像系统实验装置。实验结果表明,基于主动散斑投射的水下双目立体视觉技术具有较好的动态3D成像效果,动态误差在该双目立体视觉实验装置本身结构和系统参数决定的静态误差之内。
成像系统 水下双目立体视觉 动态三维成像 水下三维重建 主动散斑投射 光学学报
2023, 43(14): 1411003
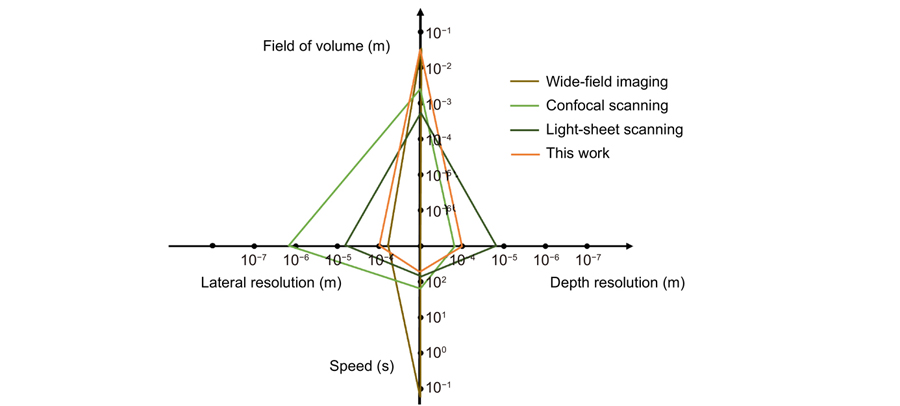
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 UTS-SUSTech Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
2 Institute for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Faculty of Science, University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, New South Wales 2007, Australia
3 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Biomaterials, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
Fluorescence imaging through the second near-infrared window (NIR-II,1000–1700 nm) allows in-depth imaging. However, current imaging systems use wide-field illumination and can only provide low-contrast 2D information, without depth resolution. Here, we systematically apply a light-sheet illumination, a time-gated detection, and a deep-learning algorithm to yield high-contrast high-resolution volumetric images. To achieve a large FoV (field of view) and minimize the scattering effect, we generate a light sheet as thin as 100.5 μm with a Rayleigh length of 8 mm to yield an axial resolution of 220 μm. To further suppress the background, we time-gate to only detect long lifetime luminescence achieving a high contrast of up to 0.45 Ιcontrast. To enhance the resolution, we develop an algorithm based on profile protrusions detection and a deep neural network and distinguish vasculature from a low-contrast area of 0.07 Ιcontrast to resolve the 100 μm small vessels. The system can rapidly scan a volume of view of 75 × 55 × 20 mm3 and collect 750 images within 6 mins. By adding a scattering-based modality to acquire the 3D surface profile of the mice skin, we reveal the whole volumetric vasculature network with clear depth resolution within more than 1 mm from the skin. High-contrast large-scale 3D animal imaging helps us expand a new dimension in NIR-II imaging.
NIR-II fluorescence time-gated light sheet illumination deep learning vessel enhancement 3D imaging Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(4): 220105
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering of Hainan Province, School of Biomedical Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan 570228, P. R. China
2 Britton Chance Center and MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics-Huazhong, University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, P. R. China
As the largest internal organ of the human body, the liver has an extremely complex vascular network and multiple types of immune cells. It plays an important role in blood circulation, material metabolism, and immune response. Optical imaging is an effective tool for studying fine vascular structure and immunocyte distribution of the liver. Here, we provide an overview of the structure and composition of liver vessels, the three-dimensional (3D) imaging of the liver, and the spatial distribution and immune function of various cell components of the liver. Especially, we emphasize the 3D imaging methods for visualizing fine structure in the liver. Finally, we summarize and prospect the development of 3D imaging of liver vessels and immune cells.
Liver blood vessel immune cell 3D imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(3): 2330006
College of Big Data and Internet, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, Guangdong, China
This paper presents a novel 3D measurement method for a light field camera (LFC) in which 3D information of object space is encoded by a microlens array (MLA). The light ray corresponding to each pixel of the LFC is calibrated. Once the matching points from at least two subviews exhibit sub-pixel accuracy, the 3D coordinates can be calculated optimally by intersecting light rays of these points matched through phase coding. Moreover, the proposed method obtains high-resolved results that exceed the subview resolution due to the virtual continuous phase search strategy. Finally, we combine the LFC and coaxial projection to solve the 3D data loss caused by shadowing and occlusion problems. Experimental results verify the feasibility of the proposed method, and the measurement error is about 30 μm in a depth range of 60 mm.
light field 3D imaging microlens array structured light 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(8): 0811017
1 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所光电探测技术研究部,吉林 长春 130033
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 吉林省智能波前传感与控制重点实验室,吉林 长春 130033
4 中国科学院空间目标与碎片观测重点实验室,江苏 南京 210008
单光子计数成像技术在暗弱目标探测、激光遥感、自动驾驶等领域均展现出了极大的应用潜力。为了探究如何利用该技术得到更多维度的目标信息,提出并验证了一种获取目标姿态的方法。将目标处于不同姿态时的单光子计数三维成像图(深度图)建成数据库,作为先验信息,通过求取库中图像与目标实际的单光子计数成像深度图(姿态未知)的相关系数,选取相关性最强的库中姿态作为目标实际姿态。采用单光子阵列探测器搭建实验系统,激光发散照明目标,以20°为单位构建数据库中的-60°至40°的目标深度图。结合库中数据与姿态分别处于-45°和25°时的目标深度图,利用所提方法估计目标姿态并验证其准确性。在该两种姿态下,分别做出光子计数为10,50,100时的深度图,以探究目标实际姿态与库中对应姿态的相似度和光子计数间的关系。以15°和20°为单位对目标进行多轴旋转,以探究目标进行多轴姿态变化时所提方法的可行性。改变背景噪声,在信号光子与背景光子数比值(SBR)分别为8.13,4.83,3.21,0.72的条件下对目标进行三维成像,探究背景噪声对估计成功率的影响。以木头人玩具为目标,以30°为单位建立数据库,对处于-20°和20°的木头人玩具进行成像并验证所提方法对复杂目标姿态估计的可行性。实验结果表明:所提方法可成功对目标实际姿态进行估计。目标实际姿态与库中对应姿态的相关性和光子计数成正相关,高SBR有利于准确估计目标姿态。
三维成像 激光雷达 姿态估计 时间相关单光子计数 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(8): 0811031
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi'an 710119, Shaanxi, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
In low-light conditions, the single-photon light detection and ranging (Lidar) technique based on time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) is suited for collecting a three-dimensional (3D) profile of the target. We present a rapid 3D reconstruction approach for single-photon Lidar with low signal-to-background ratio (SBR) and few photons based on a combination of short-duration range gate selection, photon accumulation of surrounding pixels, and photon efficiency algorithm in this paper. We achieve the best noise filtering and 3D image reconstruction by choosing the optimal combined order of simple methods. Experiments were carried out to validate the various depth estimation algorithms using simulated data and single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array data under varying SBR. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method can achieve high-quality 3D reconstruction with a faster processing speed compared to the existing algorithms. The proposed technology will encourage the use of single-photon Lidar to suit practical needs such as quick and noise-tolerant 3D imaging.In low-light conditions, the single-photon light detection and ranging (Lidar) technique based on time-correlated single-photon counting (TCSPC) is suited for collecting a three-dimensional (3D) profile of the target. We present a rapid 3D reconstruction approach for single-photon Lidar with low signal-to-background ratio (SBR) and few photons based on a combination of short-duration range gate selection, photon accumulation of surrounding pixels, and photon efficiency algorithm in this paper. We achieve the best noise filtering and 3D image reconstruction by choosing the optimal combined order of simple methods. Experiments were carried out to validate the various depth estimation algorithms using simulated data and single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array data under varying SBR. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method can achieve high-quality 3D reconstruction with a faster processing speed compared to the existing algorithms. The proposed technology will encourage the use of single-photon Lidar to suit practical needs such as quick and noise-tolerant 3D imaging.
Lidar 3D imaging photon counting few photons time-of-flight imaging low SBR 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(8): 0811033





