Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 UTS-SUSTech Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
2 Institute for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Faculty of Science, University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, New South Wales 2007, Australia
3 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Biomaterials, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
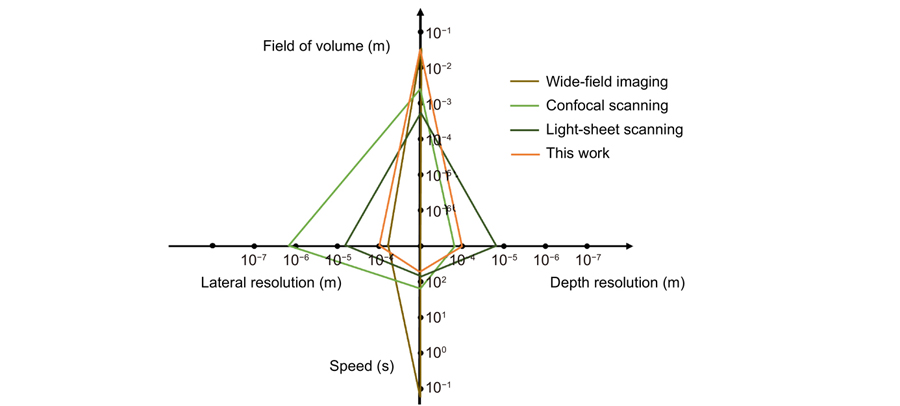
Fluorescence imaging through the second near-infrared window (NIR-II,1000–1700 nm) allows in-depth imaging. However, current imaging systems use wide-field illumination and can only provide low-contrast 2D information, without depth resolution. Here, we systematically apply a light-sheet illumination, a time-gated detection, and a deep-learning algorithm to yield high-contrast high-resolution volumetric images. To achieve a large FoV (field of view) and minimize the scattering effect, we generate a light sheet as thin as 100.5 μm with a Rayleigh length of 8 mm to yield an axial resolution of 220 μm. To further suppress the background, we time-gate to only detect long lifetime luminescence achieving a high contrast of up to 0.45 Ιcontrast. To enhance the resolution, we develop an algorithm based on profile protrusions detection and a deep neural network and distinguish vasculature from a low-contrast area of 0.07 Ιcontrast to resolve the 100 μm small vessels. The system can rapidly scan a volume of view of 75 × 55 × 20 mm3 and collect 750 images within 6 mins. By adding a scattering-based modality to acquire the 3D surface profile of the mice skin, we reveal the whole volumetric vasculature network with clear depth resolution within more than 1 mm from the skin. High-contrast large-scale 3D animal imaging helps us expand a new dimension in NIR-II imaging.
NIR-II fluorescence time-gated light sheet illumination deep learning vessel enhancement 3D imaging Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(4): 220105
浙江大学光电科学与工程学院, 浙江杭州 310007
为了提高医用电子内窥镜所获图像的血管与组织的对比度, 针对内窥镜血管图像的特点, 提出了一种基于多颜色空间非线性对比度拉伸的血管增强处理方法。首先在 RGB颜色空间利用非线性映射函数对绿色(G)分量进行自适应对比度拉伸; 接着依据 G分量的拉伸结果, 相应地调整红色 (R)和蓝色(B)两个分量的灰度值; 然后将图像转换到 HSV颜色空间, 并对图像的饱和度(S)分量进行自适应对比度拉伸; 最后将图像转换回 RGB颜色空间, 最终达到血管增强的目的。在本文中, 利用所提出的算法对多幅电子内窥镜图像进行处理, 结果表明, 算法对于原始特征不明显的细小血管也具有较好的增强效果。通过与其它的增强方法相对比, 增强后图像的细节方差 (DV)显著大于其它方法。将算法嵌入到分辨率为 1280×800的内窥镜软件中, 其处理速度可达 26 f/s。
对比度 血管增强 颜色空间 电子内窥镜 contrast vessel enhancement color space electronic endoscope
浙江大学现代光学仪器国家重点实验室, 浙江 杭州 310027
内窥镜图像质量在医生对早期病灶、异型增生复发的诊断中至关重要。因此本文根据血管对光谱的吸收特性, 提出了一种基于光谱变换的血管增强算法。首先, 该算法对图像RGB通道进行导向滤波, 将各通道分为亮度层和细节层; 接着, 将各通道的细节层进行基于信噪比的自适应增强, 并将亮度层进行拉伸, 使得GB通道的信息增强, R通道信息降低; 最后, 将各通道合并生成增强图像。本文应用该算法对大量内窥镜图像进行增强, 并且与Spectra B增强技术相比较。本文方法在DV-BV指标和韦伯对比度指标均优于Spectra B。
内窥镜 导向滤波 血管增强 光谱变换 endoscope guided filter vessel enhancement spectral enhancement





