1 中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院,浙江 杭州 310018
2 肯特大学工程学院,英国 肯特郡 CT2 7NZ
表面等离子共振(SPR)现象因其对表面折射率变化的敏感而受到广泛关注,相应的SPR传感器以其独特的无标记、高灵敏度和快速检测的优势,在生物标志物检测、食品过敏原筛查和环境监测等领域具有广阔的应用潜力。本文介绍了SPR生物传感器的3种主要结构类型:棱镜耦合结构、光栅耦合结构、光纤耦合结构;着重研究了3种结构的检测原理、典型结构等传感特性及其进展;重点论述了SPR生物传感技术中生物功能化的研究现状和技术难题以及不同材料表面特性的SPR传感器;分析了目前SPR生物传感实际应用遇到的问题以及探讨了未来的研究方向;最后,结合实际情况,从结构和材料等方面展望了新型生物传感器的发展趋势。
生物传感 表面等离子共振 生物敏感材料 生物功能化 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(11): 1106004
南京信息工程大学电子与信息工程学院,江苏 南京 210044
在过去的十几年中,衍射耦合超窄共振已经发展成为一个独立的、快速扩展的研究领域。这种共振模式通常被称为表面晶格共振,具有体积小、易集成、低功耗等特点。设计了一种性能优异且可规模化生产的表面晶格共振折射率传感器。利用时域有限差分法进行了仿真,对结构的光学性能进行了研究。采用纳米球光刻技术以及纳米压印技术,制备出大面积、高质量的银纳米环阵列,结构的灵敏度为663 nm/RIU,品质因数为9.2。通过改变结构的几何参数,不仅能实现对共振波的调谐,同时还能提高折射率灵敏度。所提传感器在生物传感领域具有潜在的应用前景。
传感器 表面等离激元 纳米环型阵列 自组装 纳米压印 生物传感
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
Optical biosensors with a high sensitivity and a low detection limit play a highly significant role in extensive scenarios related to our daily life. Combined with a specific numerical simulation based on the transfer matrix and resonance condition, the idea of novel single-waveguide-based microresonators with a double-spiral-racetrack (DSR) shape is proposed and their geometry optimizations and sensing characteristics are also investigated based on the Vernier effect. The devices show good sensing performances, such as a high quality factor of 1.23×105, a wide wavelength range of over 120 nm, a high extinction ratio (ER) over 62.1 dB, a high sensitivity of 698.5 nm/RIU, and a low detection limit of 1.8×10 5. Furthermore, single-waveguide-based resonators can also be built by cascading two DSR structures in series, called twin-DSRs, and the results show that the sensing properties are enhanced in terms of quasi free spectral range (FSR) and ER due to the double Vernier effect. Excellent features indicate that our novel single-waveguide-based resonators have the potential for future compact and highly integrated biosensors.
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 230.5750 Resonators 230.3990 Micro-optical devices 230.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 010006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Photonics Research Center, Department of Electrical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
The uses of optical fibers are numerous, and over the past few decades, they have extended from optical fiber communications to a wide variety of sensing applications. In particular, fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors inscribed in single-mode optical fibers offer significant advantages over more conventional electrical sensors and have been successfully deployed in many different industries. In this Review, we review the applications of intrinsic FBG pressure and flow sensors in oil and gas and the deployment of FBG sensing networks in railways. The promising prospect of using polymer FBGs in wearable medical devices is also described.
060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 280.4991 Passive remote sensing Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 120007

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 College of Physics and Energy, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
An ultrasensitive biosensor based on hybrid structure and composed of long-range surface plasmon polariton (LRSPP) and dielectric planar waveguide (PWG) modes is proposed. Both PWG and LRSPP modes have strong resonances to form strong coupling between the two modes, and the two modes can couple to enhance sensitivityof sensors. In the hybrid structure, PWG is composed of cytop–Si–cytop multilayers and the LRSPP configuration is composed of cytop–metal–sensing medium multilayer slabs. The highest imaging sensitivities of 2264 and 3619 RIU?1 were realized in the proposed sensors based on Au and Al-monolayer graphene, respectively, which are nearly 1.2 and 1.9 times larger than the 1910 RIU?1 sensitivity of the conventional LRSPR sensor (LRSPP sensor). Moreover, it is demonstrated that the PWG-coupled LRSPP biosensor is applicable to the sensing medium, with refractive index in the vicinity of 1.34.of Guangdong Province (2016B050501005); Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen (JCYJ20140828163633996, JCYJ20150324141711667); Natural Science Foundation ofSZU (201452, 201517, 827-000051, 827-000052, 827-000059).
Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Sensors Sensors Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000262
首都师范大学 物理系 北京市太赫兹波谱与成像重点实验室 太赫兹光电子学教育部重点实验室, 北京 100048
基于太赫兹金属光栅谐振传输现象, 利用金属光栅表面等离子体共振对周围介质敏感的特性, 设计了一种由金属光栅、样品池和高阻硅基底组成的免标记生物传感器.利用这种传感器在太赫兹时域光谱下测量了苏氨酸和精氨酸溶液的太赫兹透射光谱.结果表明:苏氨酸和精氨酸的共振频率随着溶液浓度改变在0.6~0.75 THz之间出现频移, 并且苏氨酸和精氨酸的混合样品的光谱并不是两者光谱的线性叠加.
生物传感 金属光栅 氨基酸溶液 太赫兹时域光谱 表面等离子增强 Biological sensing Metallic array Amino acid solutions THz time domain spectroscopy Surface plasmon-enhanced 光子学报
2016, 45(7): 070730003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems, Ministry of Education of China, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
3 Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 401122, China
4 Chongqing Engineering Research Center of Graphene Film Manufacturing, Chongqing 401329, China
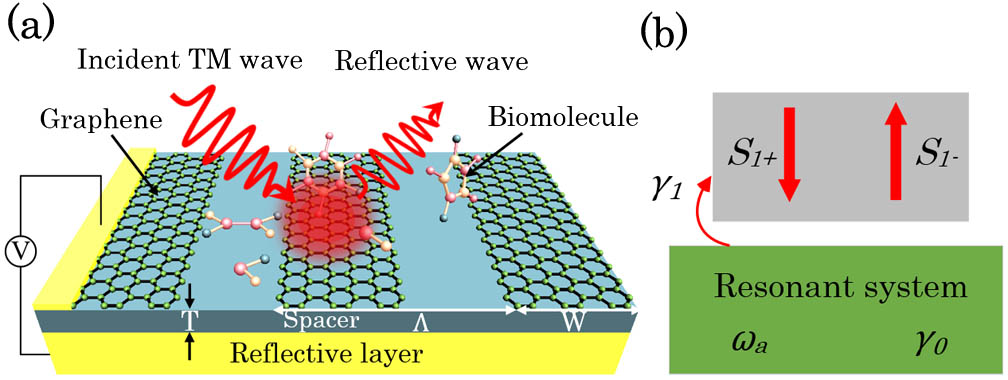
We propose a reflection-type infrared biosensor by exploiting localized surface plasmons in graphene ribbon arrays. By enhancing the coupling between the incident light and the resonant system, an asymmetric Fabry–Perot cavity formed by the ribbons and reflective layer is employed to reshape the reflection spectra. Simulation results demonstrate that the reflection spectra can be modified to improve the figure of merit (FOM) significantly by adjusting the electron relaxation time of graphene, the length of the Fabry–Perot cavity, and the Fermi energy level. The FOM of such a biosensor can achieve a high value of up to 36/refractive index unit (36/RIU), which is ~4 times larger than that of the traditional transmission-type one. Our study offers a feasible approach to develop biosensing devices based on graphene plasmonics with high precision.
280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.4236 Nanomaterials 260.3060 Infrared Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(8): 082801

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Measuring Technology and Instruments, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 School of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300387, China
3 Tianjin Nankai Hospital, Tianjin 300100, China
A CO2 sensor for capnography, based on a hollow waveguide (HWG) and tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS), is presented; the sensor uses direct absorption spectroscopy and requires neither frequent calibration nor optical filters, giving it a significant advantage over existing techniques. Because of the HWG, the CO2 measurement achieved a concentration resolution of 60 ppm at a measurement rate of 25 Hz, as characterized by Allan variance. The length of the HWG was selected to efficiently suppress the optical fringes. This setup is perfectly suited for the detection of CO2 by capnography, and shows promise for the potential detection of other breath gases.
120.3890 Medical optics instrumentation 300.6260 Spectroscopy, diode lasers 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(11): 111201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China
2 Laboratory for Microstructures, Shanghai University, Shanghai 00444, China
The optical fiber nanoprobe is prepared using spark fused taper and acid corrosion methods. With 3-ami-nopropyltrimethoxysilane coupling, gold nanoparticles are solidified onto the surface of fiber optic and then the optical fiber sensor is prepared using the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) measurement of the cell solution. The SERS of the esophageal cancer cell solution is measured by direct detection and fiber detection methods. Similar results are obtained by both detection methods. SERS measurement of tissues and organs is done using the optical fiber sensor.
170.5660 Raman spectroscopy 170.1530 Cell analysis 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S23002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
An optical fiber sensor for ultrathin layer sensing based on short-range surface plasmon polariton (SRSPP) is proposed, and the sensing characteristics are theoretically analyzed. Simulation results indicate that even for a detecting layer much thinner than the vacuum wavelength, a resolution as high as 3.7\times 10-6 RIU can be obtained. Moreover, an average thickness-detection sensitivity of 6.2 dB/nm is obtained, which enables the sensor to detect the thickness variation of the ultrathin layer up to tens of nanometers. The sensitive region of thickness could be adjusted by tuning the structure parameters.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 250.5403 Plasmonics 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(1): 010602





