
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Dalian University of Technology, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dalian 116024, China
Control of chirality using metamaterials plays a critical role in a diverse set of advanced photonics applications, such as polarization control, bio-sensing, and polarization-sensitive imaging devices. However, this poses a major challenge, as it primarily involves the geometrical reconfiguration of metamolecules that cannot be adjusted dynamically. Real-world applications require active tuning of the chirality, which can easily manipulate the magnitude, handedness, and spectral range of chiroptical response. Here, enabled by graphene, we theoretically reveal a tunable/switchable achiral metasurface in the near-infrared region. In the model, the achiral metasurface consists of an array of circular holes embedded through a metal/dielectric/metal trilayer incorporated with the graphene sheet, where holes occupy the sites of a rectangular lattice. Circular conversion dichroism (CCD) originates from the mutual orientation between the achiral metasurface and oblique incident wave. The achiral metasurface possesses dual-band sharp features in the CCD spectra, which are tuned over a broad bandwidth by electrically modulating the graphene’s Fermi level. By selecting aluminium as the metal materials, we numerically achieved strong CCD and considerably reduced materials costs with our nanostructures compared with the typically used noble metals such as gold and silver.
(160.3918) Metamaterials (160.1585) Chiral media (240.6680) Surface plasmons. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000441
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China
2 Key Laboratory for High Energy Density Physics and Technology, Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China
3 e-mail: jian-hun.123@163.com
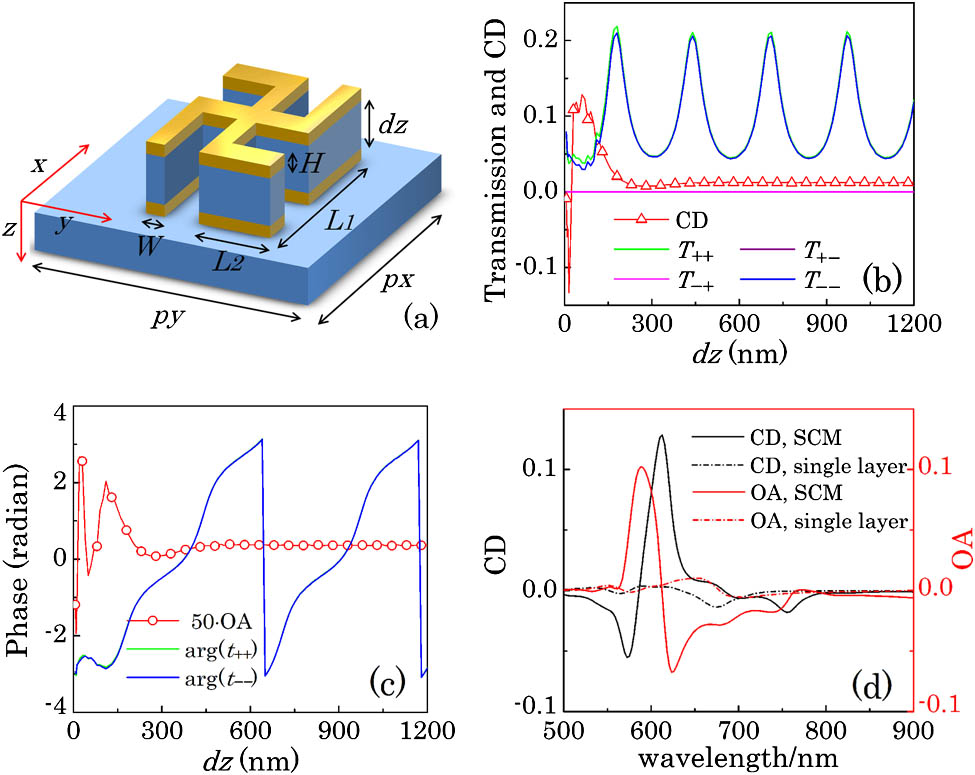
Cavity-coupled plasmonic structure is demonstrated to be a simple and effective tool to manipulatelight, enhance the biosensing figure of merit, and control the polarization state. In this Letter, we demonstrate the tunability of the chiroptical effect of cavity-coupled chiral structure, i.e., sandwich chiral metamaterials (SCMs), in whichradiation coupling dominates the interaction between particles. Two types of SCMs whose building blocks are 3D chiral and 2D chiral, respectively, are numerically studied. Distinct responses are observed in these two materials. The chiroptical effect can be effectively manipulated and enhanced in the 2D case, while the SCMs consisting of 3D chiral layers keep the chiroptical effecta constant. A theoretical analysis based on matrix optics is developed to explain the corresponding phenomena, which gives a reasonable agreement with numerical simulations.
160.1585 Chiral media 160.4760 Optical properties 160.3918 Metamaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 061602
1 西安电子科技大学物理与光电工程学院, 陕西 西安 710071
2 西安电子科技大学信息感知技术协同创新中心, 陕西 西安 710071
利用复源点方法将厄米-高斯光束展开为球矢量波函数的形式。基于广义洛伦兹米氏理论,应用手征介质球与自由空间分界面处电磁场切向连续的边界条件以及球矢量波函数的正交性,得到手征介质球远区散射场展开系数。研究了厄米-高斯光束对手征介质球的散射特性。数值计算了厄米-高斯光束对手征介质球的远区散射场分布,分析了波束模式、手征参数和手征球尺寸等对散射特性的影响。
激光光学 手征介质 厄米高斯模 散射

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Information Sensing and Understanding at Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
Research on light scattering from a large chiral sphere shows that the rainbow phenomenon is different from that of an isotropic sphere. A chiral sphere with certain chirality generates three first-order rainbows. In this Letter, we present a geometric optics interpretation for the phenomenon and make a calculation of the rainbow angles. The ray traces inside the sphere are determined by the reflection and refraction laws of light at the achiral–chiral interface and the chiral–achiral interface. The calculated rainbow angles achieve good agreements with those obtained by the analytical solutions. The effects of chirality and the refractive index of the sphere on rainbow angles are analyzed.
160.1585 Chiral media 080.0080 Geometric optics 290.5850 Scattering, particles Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 121602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Liquid Crystal Institute, Kent State University, Kent, Ohio 44242, USA
Cholesteric liquid crystals, consisting of chiral molecules, form self-assembled periodic structures exhibiting a photonic bandgap. Their selective reflectivity makes them well suited for a variety of applications; their optical response is therefore of considerable interest. The reflectance and transmittance of finite cholesteric cells is usually calculated numerically. Evanescent modes in the bandgap make the calculations challenging; existing matrix propagation methods cannot describe the reflection and transmission coefficients of thick cholesteric cells accurately. Here we present analytic solutions for the electromagnetic fields in cholesteric cells of finite thickness, and use them to calculate the transmission and reflection spectra. The use of analytic solutions allows for the accurate description of arbitrarily thick cholesteric cells, which would not be possible with only direct numerical methods.
Liquid crystals Photonic bandgap materials Birefringence Anisotropic optical materials Chiral media Photonics Research
2013, 1(1): 01000058
Author Affiliations
Abstract
TiO2 chiral sculptured thin films (CSTFs) prepared using glancing angle deposition (GLAD) method based on electron beam evaporation are studied. The relationship between structural parameters and circular Bragg phenomenon (CBP) is investigated. Results demonstrate that, the central wavelength of Bragg regime red-shifts with the increasing pitch of helix, and peak value of selective transmittance will increase after adding more turns to the helix. After annealing, the central wavelength blue-shifts and the peak value rises. Tuning CBP by modulating the deposition parameters and annealing can optimize the performance of circularly polarized devices fabricated from CSTFs.
310.1860 Deposition and fabrication 310.5448 Polarization, other optical properties 160.1585 Chiral media Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(s1): S10102
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, College of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Hunan Electric Power Company Dispatches & Communication Center, Changsha 410007, China
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2012, 5(3): 248
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Based on the optical rotatory dispersion and zero reflection of the p-polarization light at the Brewster angle, a novel optical filter that employs only one NaBrO3 crystal and one polarizer are proposed and demonstrated. Performance of the optical filter is studied both theoretically and experimentally. Results show that the green light is becomes nearly extinct when the angles of the polarizer are set at 80o and 260o, whereas the red light becomes nearly extinct when the angles of the polarizer are set at 116o and 296o. Isolation of more than 8 dB can be achieved. The measured extinction ratios are 12.3 and 12.6 dB for green and red lights, respectively.
230.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 160.1585 Chiral media 260.5430 Polarization Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(6): 062301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Optical Fiber Communication and Network Technology, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
A new concept to realize negative refractive index in non-resonance spectrum using chiral metamaterial is proposed. A low-index metamaterial is added to diminish the effective refractive index of the combined structure. Simulation and material parameter retrieval procedures are carried out to determine material performances. Results show evidence of negative refractive index and strong optical activity in the new chiral metamaterial.
负折射 手征 RCP LCP 160.3918 Metamaterials 160.1585 Chiral media 160.4670 Optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(11): 1067
给出了方便实用的计算非线性旋光角Δθ的公式,在理论上分析了非线性旋光角随椭圆特征参量改变的变化规律,给出了数值模拟的结果,并针对具体手性材料与入射光强估算了非线性旋光角的量级。
手性介质 非线性旋光 椭圆偏振光





