华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
基于改进的化学气相沉积(MCVD)工艺,结合溶液掺杂技术,成功制备出11 µm/125 µm掺镱保偏光纤,并研究了其激光性能。该光纤的纤芯数值孔径为0.09,双折射系数值为3.0×10-4,915 nm和976 nm处的包层吸收系数分别为2.48 dB/m和7.05 dB/m。搭建了全光纤振荡器结构测试平台,当掺镱保偏光纤长度为2.25 m、976 nm泵浦功率为57 W时,实现了最大输出功率为48.9 W、斜率效率为85.5%的激光输出,输出光谱呈洛伦兹型。
激光光学 光纤光学 光纤激光振荡器 光纤测试 掺镱保偏光纤
苏州热工研究院有限公司材料力学研究所,江苏 苏州 215004
针对多向应变测量问题,采用凸台和圆环状基片结构设计了一种三向光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)应变传感器,实现了对结构三个方向应变的同步测量。通过振动试验台和不锈钢板进行了同电阻应变片的静态对比实验和振动监测实验。结果表明,FBG应变传感器和应变片在三个方向的静态应变曲线基本一致,相关系数分别为0.98、0.98和0.99。振动功率谱分析结果表明,FBG应变传感器和应变片均观察到了一次谐波和二次谐波,频率误差分别为2.77%和0.97%,且应变片还监测到了高次谐波信号。该传感器具有结构简单、尺寸小、测量精度高、定位准确等优点,在多向应变监测领域具有良好的应用前景。
传感器 光纤测量 三向应变 光纤布拉格光栅 振动实验 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(11): 1128001
苏州科技大学土木工程学院,江苏 苏州 215000
分析了光纤传感器应变传递率的影响因素,进行了粘贴式光纤传感器等强度梁试验。光纤传感器监测结构材料中应变分布的能力取决于材料与光纤之间的键合特性。取粘贴长度和胶体剪切模量两个参数,研究了分布式光纤传感器应变传递的顶端效应。结果表明:延长粘贴的光纤长度或提高胶体的剪切模量,可以使高应变传递段加长。工程应用中应选用剪切模量高的胶黏剂,粘贴长度应在粘贴测量段两端多粘贴5 cm,以保证测量段可以得到相对精确的应变结果。
光纤光学 光纤测量 光纤传感器 瑞利散射 光频域反射技术 应变传递率 等强度梁 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(19): 1906005
1 西南交通大学物理科学与技术学院,四川 成都 610031
2 国防科技大学气象海洋学院,湖南 长沙 410073
3 西南交通大学信息科学与技术学院,四川 成都 610031
布里渊光时域分析(BOTDA)在分布式光纤传感系统中展现出独特的优势并得到了广泛的关注,对BOTDA传感系统的温度分布信息进行快速且精确的提取至关重要。随着机器学习算法的快速发展,其在BOTDA传感系统的温度分布信息的提取中展现出巨大潜力。首先,阐述了BOTDA传感系统温度测量的原理。接着,介绍了几种基于机器学习的算法并分析了其在BOTDA传感系统温度提取中的应用和优势。最后,对未来的研究进行了展望。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(13): 1306022
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Lightwave Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
2 Key Laboratory of All Optical Network and Advanced Telecommunication Network of Ministry of Education, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
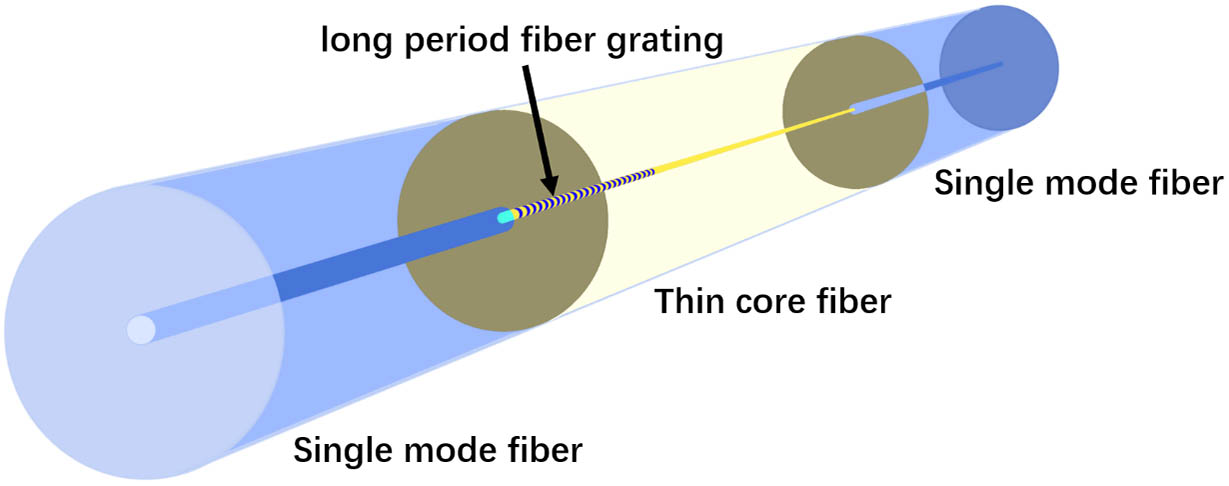
A refractive index intensity detecting sensor with long-period grating written in the single-mode–thin-core–single-mode fiber (STS) structure is proposed and optimized theoretically. The sensor is composed of two single-mode fibers connected by a section of long-period fiber grating fabricated on thin-core fiber. After optimization and benefitting from the phase matching point, the loss peak of the structure can reach 62.8 dB theoretically. The wavelength of the characteristic peak is fixed at the phase matching point, so intensity detection can be achieved. The sensitivity can reach 272.5 dB/RIU. The structural optimization in this Letter provides a reference for the fabrication of an easy-made all-fiber sensor without extra cladding.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2300 Fiber measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 070601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Radar Imaging and Microwave Photonics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
Optoelectronic components and subsystems such as optically controlled phased array antennas, distributed radar networks, interferometric optical fiber hydrophones, and high-speed optoelectronic chips demand high-accuracy optical time delay measurement with large measurement range and the capability for single-end and wavelength-dependent measurement. In this paper, the recent advances in the optical time delay measurement of a fiber link with high accuracy are reviewed. The general models of the typical time delay measurement technologies are established with the operational principle analyzed. The performance of these techniques is also discussed.
060.2300 Fiber measurements 120.5050 Phase measurement 280.3400 Laser range finder Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 060601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Engineering Laboratory for Fiber Optic Sensing Technology, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
2 Key Laboratory of Fiber Optic Sensing Technology and Information Processing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto M5S-3G4, Canada
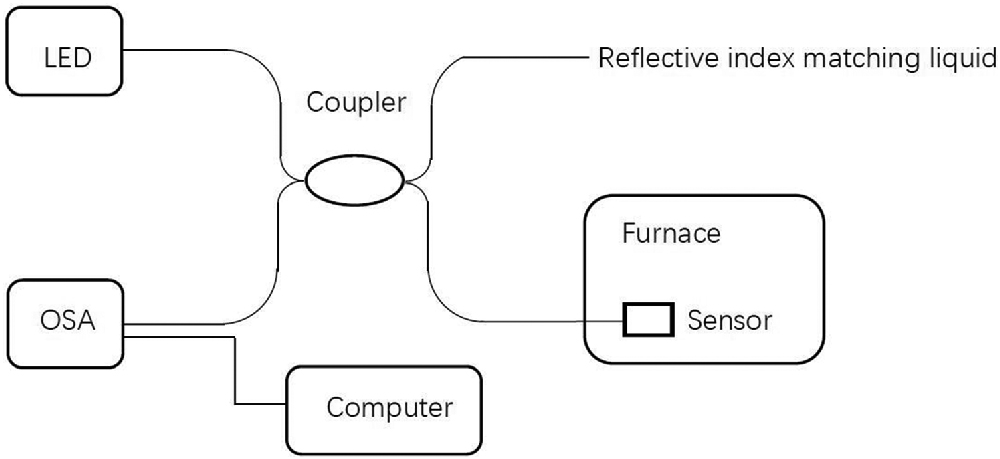
We propose a cavity length demodulation method that combines virtual reference interferometry (VRI) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) algorithm for fiber-optic Fabry–Perot (F-P) sensors. In contrast to the conventional demodulating method that uses fast Fourier transform (FFT) for cavity length estimation, our method employs the VRI technique to obtain a raw cavity length, which is further refined by the MMSE algorithm. As an experimental demonstration, a fiber-optic F-P sensor based on a sapphire wafer is fabricated for temperature sensing. The VRI-MMSE method is employed to interrogate cavity lengths of the sensor under different temperatures ranging from 28°C to 1000°C. It eliminates the “mode jumping” problem in the FFT-MMSE method and obtains a precision of 4.8 nm, corresponding to a temperature resolution of 2.0°C over a range of 1000°C. The experimental results reveal that the proposed method provides a promising, high precision alternative for demodulating fiber-optic F-P sensors.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2300 Fiber measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 010606
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 e-mail: fsy@siom.ac.cn
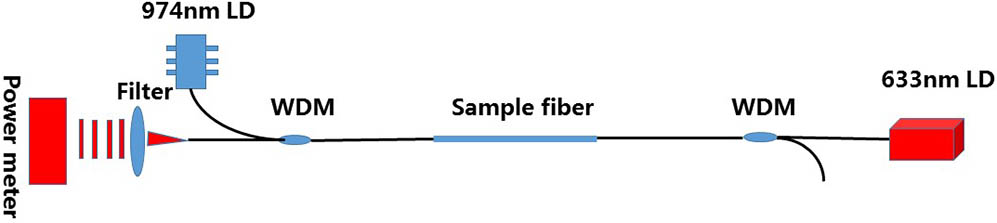
Induced loss at 633 nm is tested in Yb3+/Al3+ co-doped silica fiber by a core pumped with a 974 nm laser and probed with a 633 nm laser. The fiber is prepared by the modified chemical vapor deposition method combined with solution doping. Different power scales of pump light and probe light are used in the tests. It is found that there is a dynamic equilibrium between photobleaching induced by 633 nm probe light and photodarkening (PD) induced by 974 nm pump light. For the first time to our knowledge, the effect of 633 nm probe laser power on an induced loss test of Yb3+/Al3+ co-doped silica fiber is studied quantitatively. It suggests that as long as the 633 nm probe light power is less than 0.2 mW, the induced loss is mainly contributed by the PD effect of pumping light, and the deviation of induced loss is less than 5%.
060.2270 Fiber characterization 060.2290 Fiber materials 060.2300 Fiber measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 010603

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 Accelink Technologies Co., LTD, Wuhan 430074, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Optical Communication Technologies and Networks, Wuhan Research Institute of MPT, Wuhan 430074, China
A dual optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) system, which employs two different continuous waves at the optical line terminal and a pair of fiber Bragg gratings at the end of each optical network unit, is proposed in a time-division multiplexing passive optical network (PON). The proposed scheme accomplishes the fiber fault monitoring by comparing the different wavelength’s testing curves. Complete complementary code is utilized to measure multiple wavelength signals simultaneously with only one receiver and to improve the dynamic range of this system. The PON system consisting of 20 km feeding fiber and a 1:16 splitter is investigated by the experiments. The experimental results show that the faulty branch can be successfully identified by using our scheme. What is more, we also demonstrate that our scheme can be applied to the multi-stage PON.
120.4825 Optical time domain reflectometry 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 060.2300 Fiber measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(3): 031201





