Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Beijing Key Lab. for Precision Optoelectronic Measurement Instrument and Technology, School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Institute of Microelectronics, Peking University, Beijing 100087, China
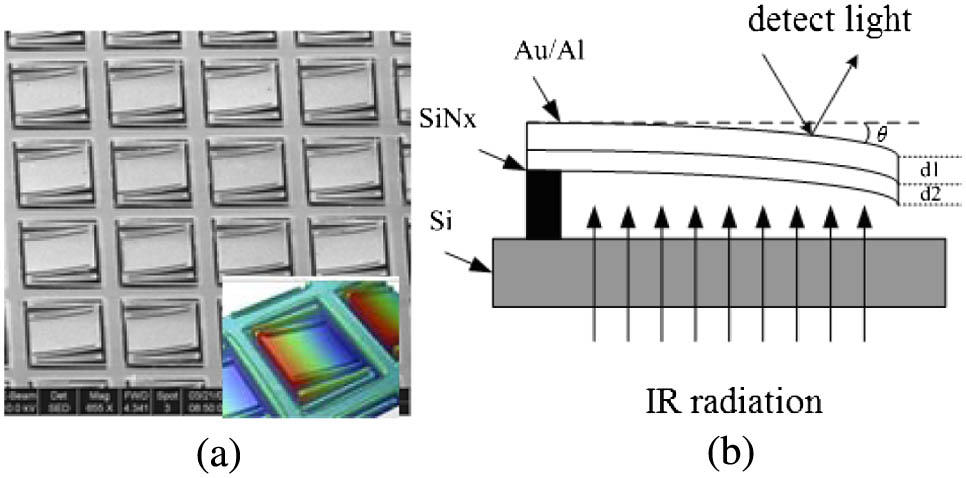
Noise and the resonance characteristics of the focal plane array (FPA) are the most important factors that affect the performance of the optical readout infrared (IR) FPA imaging system. This Letter presents a time-discrete modulation technology that eliminates the background and restrain noise, which effectively improves the image quality of the optical readout IR FPA imaging system. The comparative experiments show that this technology can reduce the noise equivalent temperature difference greatly and make the images sharper. Moreover, when the imaging system is influenced by the environment vibration, the images obtained from the imaging system with time-discrete modulation restore twice as fast as without time-discrete modulation.
110.3080 Infrared imaging 110.2970 Image detection systems 040.6808 Thermal (uncooled) IR detectors, arrays and imaging 100.2550 Focal-plane-array image processors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Lab, School of Electronic Engineering and Optoelectronic Techniques, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
Scene-based adaptive nonuniformity correction (NUC) is currently being applied to achieve higher performance in infrared imaging systems. However, almost all scene-based NUC algorithms cause the production of ghosting artifacts over output images. Based on constant-statistics theory, we propose a novel threshold self-adaptive ghosting reduction algorithm to improve the space low-pass and temporal high-pass (SLPTHP) NUC technique. The correction parameters of the previous frame are regarded as thresholds to compute new correction parameters. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can obtain a satisfactory performance in reducing unwanted ghosting artifacts.
红外成像 场景非均匀性校正 鬼影抑制 040.3060 Infrared 100.2550 Focal-plane-array image processors 100.2960 Image analysis 100.2980 Image enhancement Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(12): 1113
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Gunma University, Gunma 376-8515, Japan
3 Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Engineering, Gunma University, Gunma 376-8515, Japan
4 Medical Operations, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), JAXA Houston Office, Houston 77058, USA
A practical method for evaluating the three-dimensional (3D) position and velocity of a moving object used in the parabolic flight experiment is developed by using the binocular stereo vision measurement theory. The camera calibration mathematic model without considering the lens distortion is introduced. The direct linear transformation (DLT) algorithm is improved to accomplish the camera calibration. The camera calibration result and optimization algorithm are used to calculate the object's world coordinate from image coordinate. The 3D position and the velocity of the moving object are obtained. The standard uncertainty in estimating the velocity is 0.0024 m/s, which corresponds to 1% level of the velocity of the object in the experiment. The results show that this method is very useful for the parabolic flight experiments.
立体视觉 摄像机标定 微重力 三维位置 100.2550 Focal-plane-array image processors 150.1488 Calibration 150.6910 Three-dimensional sensing Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(6): 601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laboratory of Infrared Technology, School of Information Science and Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081
The striping pattern nonuniformity of the infrared line scanner (IRLS) severely limits the system performance. An adaptive nonuniformity correction (NUC) algorithm for IRLS using neural network is proposed. It uses a one-dimensional median filter to generate ideal output of network and can complete NUC by a single frame with a high correction level. Applications to both simulated and real infrared images show that the algorithm can obtain a satisfactory result with low complexity, no need of scene diversity or global motion between consecutive frames. It has the potential to realize real-time hardware-based applications.
图像处理 非均匀性校正 扫描型 红外热像仪 神经网络 自适应 040.3060 Infrared 100.2550 Focal-plane-array image processors 100.2980 Image enhancement 200.4260 Neural networks Chinese Optics Letters
2007, 5(2): 74
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Information Optics Laboratory, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
2 Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100039
Determination of the energy range is an important precondition of focus calibration using alignment procedure (FOCAL) test. A new method to determine the energy range of FOCAL off-lined is presented in this paper. Independent of the lithographic tool, the method is time-saving and effective. The influences of some process factors, e.g. resist thickness, post exposure bake (PEB) temperature, PEB time and development time, on the energy range of FOCAL are analyzed.
050.0050 diffraction and gratings 100.2550 focal-plane-array image processors 120.0120 instrumentation measurement and metrology 230.0230 optical devices Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(10): 10589





