
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Infrared Materials and Devices, Research Institute of Advanced Technologies, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2 Engineering Research Center for Advanced Infrared Photoelectric Materials and Devices of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
3 Department of Quantum Science and Technology, Research School of Physics, Australian National University, Canberra ACT 2601, Australia
4 School of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
Three-dimensional (3D) nonlinear photonic crystals have received intensive interest as an ideal platform to study nonlinear wave interactions and explore their applications. Periodic fork-shaped gratings are extremely important in this context because they are capable of generating second-harmonic vortex beams from a fundamental Gaussian wave, which has versatile applications in optical trapping and materials engineering. However, previous studies mainly focused on the normal incidence of the fundamental Gaussian beam, resulting in symmetric emissions of the second-harmonic vortices. Here we present an experimental study on second-harmonic vortex generation in periodic fork-shaped gratings at oblique incidence, in comparison with the case of normal incidence. More quasi-phase-matching resonant wavelengths have been observed at oblique incidence, and the second-harmonic emissions become asymmetric against the incident beam. These results agree well with theoretic explanations. The oblique incidence of the fundamental wave is also used for the generation of second-harmonic Bessel beams with uniform azimuthal intensity distributions. Our study is important for a deeper understanding of nonlinear interactions in a 3D periodic medium. It also paves the way toward achieving high-quality structured beams at new frequencies, which is important for manipulation of the orbital angular momentum of light.
second-harmonic generation nonlinear photonic crystal periodically poled ferroelectric crystal quasi-phase matching nonlinear wavefront shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041902

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 SwissFEL, Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen PSI, Switzerland
2 Photonics Institute, Technische Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria
3 Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
4 Institute for Quantum Electronics, Physics Department, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
We demonstrate the generation, spectral broadening and post-compression of second harmonic pulses using a thin beta barium borate (BBO) crystal on a fused-silica substrate as the nonlinear interaction medium. By combining second harmonic generation in the BBO crystal with self-phase modulation in the fused-silica substrate, we efficiently generate millijoule-level broadband violet pulses from a single optical component. The second harmonic spectrum covers a range from long wave ultraviolet (down to 310 nm) to visible (up to 550 nm) with a bandwidth of 65 nm. Subsequently, we compress the second harmonic beam to a duration of 4.8 fs with a pulse energy of 0.64 mJ (5 fs with a pulse energy of 1.05 mJ) using chirped mirrors. The all-solid free-space apparatus is compact, robust and pulse energy scalable, making it highly advantageous for generating intense second harmonic pulses from near-infrared femtosecond lasers in the sub-5 fs regime.
post-compression second harmonic generation self-phase modulation supercontinuum generation High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2024, 12(2): 02000e16
1 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院,湖北 武汉 430074
2 华中科技大学物理学院,湖北 武汉 430074
3 华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
4 湖北光谷实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
超短超强激光脉冲驱动的高次谐波是一种极紫外到软X射线波段的光源,具有指向性好、时空相干性高、亮度高等优点。高次谐波不但是在阿秒时间尺度上研究电子动力学的基础,而且其各类技术优点也使之成为一种有效的桌面型极紫外相干光源,在集成电路制造在线检测、材料科学、生物医药等领域中具有广泛应用。然而,受限于传统钛蓝宝石固体飞秒激光的平均功率和高次谐波传播过程中的转换效率,目前高次谐波极紫外光源的平均功率亟待提高。介绍了高重复频率、高平均功率高次谐波极紫外光源的产生方式及其应用。首先介绍了光纤、固体、啁啾光学参量放大器等新型高重复频率、高平均功率飞秒激光驱动源在高次谐波产生方面的研究进展,之后讨论了激光高次谐波在弱电离气体介质中的宏观传播效应和相位匹配条件。在此基础上,介绍了高平均功率高次谐波极紫外光源在成像检测方面的应用。
非线性光学 高次谐波 极紫外光源 飞秒激光器 极紫外成像检测
杭州电子科技大学通信工程学院,浙江 杭州 310018
研究了高重复频率的谐波自锁模Nd∶YVO4激光器。理论证明了当增益介质与谐振腔的光学长度的比值接近最简分数时,激光器的纵模模式间距可以被修改为增益介质自由光谱范围的整数倍,并对应谐波锁模脉冲输出。开展了相关实验,结果表明,当泵浦功率为6.57 W,增益介质和谐振腔的光学长度分别为11.0 mm和25.8 mm时,对应最简分数为3/7,获得了3倍增益介质自由光谱范围的模式间距纵模分布,对应谐波锁模脉冲的重复频率为40.92 GHz,平均输出功率为790.7 mW。实验还发现,当固定增益介质的光学长度时,获得的谐波锁模脉冲输出对应的谐振腔腔长存在锁定范围,进一步验证了谐振腔腔长锁定范围与增益介质的光学长度成正比。
激光器 激光技术 Nd∶YVO4晶体 高重复频率 谐波锁模
1 中国科学院物理研究所,北京凝聚态物理国家研究中心,北京 100190
2 松山湖材料实验室,广东 东莞 523808
高重复频率极紫外光源已被广泛应用于电子动力学研究,并且在阿秒谱学研究和显微成像中有广阔的应用前景。高重复频率极紫外光源正在朝更高重复频率、更高光子通量、更高光子能量和更短脉宽的方向发展。介绍了高重复频率极紫外光源的产生和调控,以及极紫外光源应用的分辨能力优化,并展望了高重复频率极紫外光源的未来发展趋势。
非线性光学 超快光学 高次谐波 极紫外光源
1 长春新产业光电技术有限公司, 吉林 长春 130103
2 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 吉林 长春 130033
紫外激光器是研究紫外共振拉曼光谱的重要工具,拉曼信号可以通过共振拉曼效应得到增强,从而降低拉曼测量的探测极限。本文研究了一种输出波长为228 nm的窄脉宽全固态紫外激光器。首先,以Nd:YVO4作为增益介质,采用电光调Q腔倒空技术,实现了纳秒量级914 nm基频光输出。然后,经过偏硼酸锂(LBO)晶体产生二次谐波,最终经偏硼酸钡(BBO)晶体获得四次谐波228 nm紫外激光。在此基础上,进一步研究了不同重复频率时基频光和倍频光功率的变化规律,优化了紫外激光器的输出效率。实验结果表明:当总抽运功率为30 W时,在10 kHz重复频率下,可获得最高平均功率为84 mW的228 nm紫外激光输出。228 nm激光在5~25 kHz重复频率范围内连续可调,脉冲宽度保持在2.8~2.9 ns,能够满足紫外光谱检测技术领域的应用需求。
228 nm激光器 紫外激光 腔倒空技术 二次谐波 228 nm laser ultraviolet laser cavity dumped laser second harmonic 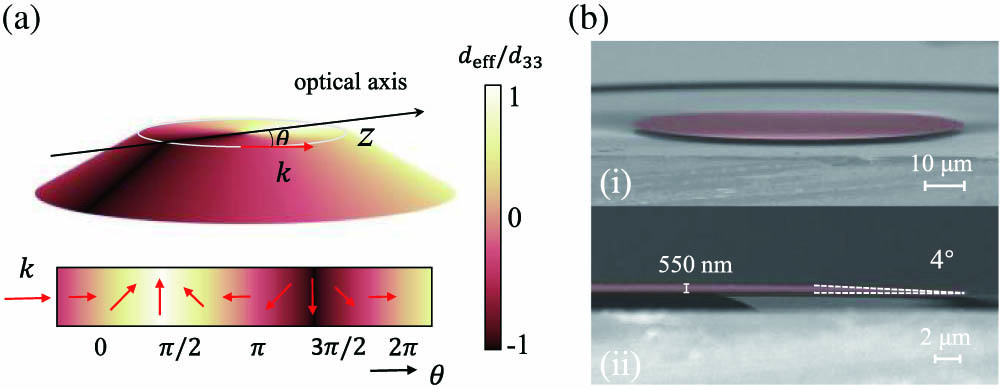
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai 201620, China
3 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai 201315, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microresonators can greatly enhance light–matter interaction, making them indispensable units for frequency conversion in nonlinear optics. Efficient nonlinear wave mixing in microresonators requires stringent simultaneous optical resonance and phase-matching conditions. Thus, it is challenging to achieve efficient frequency conversion over a broad bandwidth. Here, we demonstrate broadband second-harmonic generation (SHG) in the x-cut thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) microdisk with a quality factor above 107 by applying the cyclic quasi-phase-matching (CQPM) mechanism, which is intrinsically applicable for broadband operation. Broadband SHG of continuous-wave laser with a maximum normalized conversion efficiency of ∼15%/mW is achieved with a bandwidth spanning over 100 nm in the telecommunication band. Furthermore, broadband SHG of femtosecond lasers, supercontinuum lasers, and amplified spontaneous emission in the telecommunication band is also experimentally observed. The work is beneficial for integrated nonlinear photonics devices like frequency converters and optical frequency comb generator based on second-order nonlinearity on the TFLN platform.
lithium niobate whispering-gallery mode broadband second-harmonic generation cyclic quasi-phase matching Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031903

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Infrared Materials and Devices, Research Institute of Advanced Technologies, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2 Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Materials and Devices, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
3 Ningbo Institute of Oceanography, Ningbo 315832, China
4 Department of Quantum Science and Technology, Research School of Physics, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 2601, Australia
The design of nonlinear photonic Vogel’s spiral based on quasi-crystal theory was demonstrated. Two main parameters of Vogel’s spiral were arranged to obtain multi-reciprocal circles. Typical structure was fabricated by the near-infrared femtosecond laser poling technique, forming a nonlinear photonic structure, and multiple ring-like nonlinear Raman–Nath second-harmonic generation processes were realized and analyzed in detail. The structure for the cascaded third-harmonic generation process was predicted. The results could help deepen the understanding of Vogel’s spiral and quasi-crystal and pave the way for the combination of quasi-crystal theory with more aperiodic structures.
nonlinear photonic quasi-crystal second-harmonic generation Vogel’s spiral nonlinear Raman–Nath diffraction femtosecond laser poling Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices, and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060 P. R. China
Measurement of blood flow velocity is key to understanding physiology and pathology in vivo. While most measurements are performed at the middle of the blood vessel, little research has been done on characterizing the instantaneous blood flow velocity distribution. This is mainly due to the lack of measurement technology with high spatial and temporal resolution. Here, we tackle this problem with our recently developed dual-wavelength line-scan third-harmonic generation (THG) imaging technology. Simultaneous acquisition of dual-wavelength THG line-scanning signals enables measurement of blood flow velocities at two radially symmetric positions in both venules and arterioles in mouse brain in vivo. Our results clearly show that the instantaneous blood flow velocity is not symmetric under general conditions.
1700nm-Window third-harmonic generation imaging blood flow velocity Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(1): 2350011





