1 湖北大学计算机与信息工程学院,湖北 武汉 430062
2 华中科技大学计算机科学与技术学院,湖北 武汉 430074
为了全面且针对性地研究水下湍流成像的退化因素,同时优化相应图像恢复算法,搭建了一个可控湍流条件和重复使用的水下成像实验系统,利用循环水泵控制实验水箱中湍流的强度,气泡发生器制造微气泡,图像传感器获取不同条件下的正弦条纹目标板的成像结果。研究了流速场、程辐射和流体介质对水下成像的影响,结合图像复原和超分辨率重建技术,比较了基于三种退化因素的调制传递函数(MTF)的差异和适用性。结果表明,湍流流速场在低空间频率段造成MTF 快速下降,程辐射和流体介质则会导致高空间频率的调制对比度减小;在水下湍流退化图像恢复中,湍流流速场的MTF 适合图像复原,程辐射和流体介质的MTF 适合图像重建。
海洋光学 调制传递函数 图像复原重建 超分辨率 oceanic optics modulation transfer function image reconstruction-restoration superresolution
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100039, China
3 Institute of Opto-electronics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
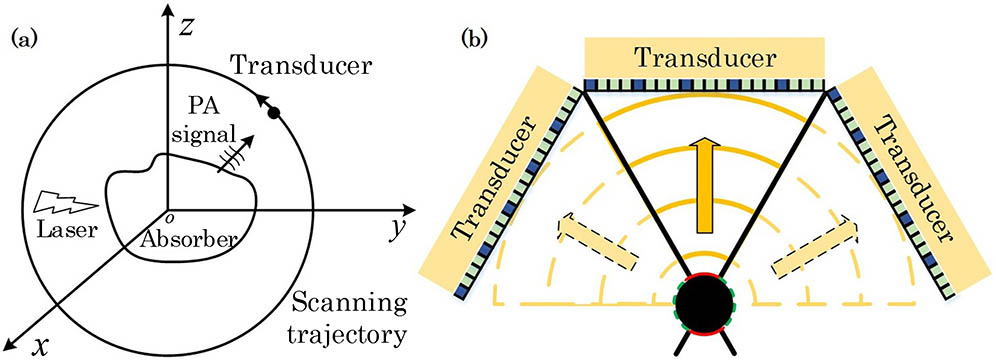
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has the unique capability of visualizing optical absorption inside several centimeters-deep biological tissue with a high spatial resolution. However, single linear-array transducer-based PAT suffers from the limited-view challenge, and thus the synthetic aperture configuration is designed that still requires multichannel data acquisition hardware. Herein, a feasible synthetic aperture PAT based on compressed sensing reconstruction is proposed. Both the simulation and experimental results tested the theoretical model and validated that this approach can improve the image resolution and address the limited-view problem while preserving the target information with a fewer number of measurements.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Photoacoustic tomography is a noninvasive and nonionized biomedical imaging modality but it cannot reveal the inner structure and sideward boundary information of blood vessels in the linear array detection mode. In contrast, Monte Carlo (MC) light transport could provide the optical fluence distribution around the entire vascular area. This research explores the combination of linear array transducer-based photoacoustic tomography and MC light transport in the blood vessel quantification. Simulation, phantom, and in vivo experiments are in good correlation with the ultrasound imaging, validating this approach can clearly visualize the internal region of blood vessels from background tissue.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
As a high-resulotion biological imaging technology, photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) is difficult to use in real-time imaging due to the long data acquisition time. Herein, a fast data acquisition and image recovery method named sparse PAM based on a low-rank matrix approximation is proposed. Specifically, the process to recover the final image from incomplete data is formulated into a low-rank matrix completion framework, and the “Go Decomposition” algorithm is utilized to solve the problem. Finally, both simulated and real PAM experiments are conducted to verify the performance of the proposed method and demonstrate clinical potential for many biological diseases.
100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 170.0110 Imaging systems Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(9): 091701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130033, China
Phase diversity (PD) is a kind of wavefront sensing technology based on image collecting and post-processing. We apply the PD technology to align an off-axis three-mirror reflecting anastigmatic system precisely. It can be concluded that the wavefront error obtained by PD agrees well with the interferometric result. The focused images are also restored according to the testing results of PD, and the qualities of restored images are improved.
100.5070 Phase retrieval 010.7350 Wave-front sensing 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.6770 Telescopes Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(s1): S11003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Microsoft Research, Redmond 98052, USA
Photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) is recognized as a powerful tool for various microcirculation system studies. To improve the spatial resolution for the PAM images, the requirements of the system will always be increased correspondingly. Without additional cost of the system, we address the problem of improving the resolution of PAM images by integrating a deconvolution model with a directional total variation regularization. Additionally, we present a primal-dual-based algorithm to solve the associated optimization problem efficiently. Results from both test images and some PAM images studies validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing the spatial resolution. We expect the proposed technique to be an alternativeresolution enhancement tool for some important biomedical applications.
100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 330.6130 Spatial resolution Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 121701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
A new photoacoustic (PA) signal sampling and image reconstruction method, called compressive sampling PA tomography (CSPAT), is recently proposed to make low sampling rate and high-resolution PA tomography possible. A key problem within the CSPAT framework is the design of optic masks. We propose to use edge expander codes-based masks instead of the conventional random distribution masks, and efficient total variation (TV) regularization-based model to formulate the associated problem. The edge expander codes-based masks, corresponding to non-uniform sampling schemes, are validated by both theoretical analysis and results from computer simulations. The proposed method is expected to enhance the capability of CSPAT for reducing the number of measurements and fast data acquisition.
100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Wavefront coding (WFC) is kind of computational imaging technique that controls misfocus and misfocus-related aberrations of optical systems by appending a specially designed phase distribution to the pupil function. This technology has been applied in many fields to increase the performance or/and reduce the cost of imaging systems. The application of WFC technology on an off-axis three-mirror anastigmatic (TMA) system has been proposed in our previous work. In this letter, we describe the alignment, the imaging experiment and image restoration of an actual TMA system with WFC technology.
220.1140 Alignment 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.1758 Computational imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S12201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The resolution of astronomical imaging from large optical telescopes is usually limited by the blurring effects of refractive index fluctuations in the Earth’s atmosphere. In this letter, we develop a lucky imaging system to restore astronomical images through atmosphere turbulence on large telescope. Our system takes very short exposures, on the order of the atmospheric coherence time. The rapidly changing turbulence leads to a very variable point spread function (PSF), and the variability of the PSF leads to some frames having better quality than the rest. Only the best frames are selected, aligned and co-added to give a final image with much improved angular resolution. Our lucky imaging system is successfully applied to restore the astronomical images taken by a 1.23 m telescope. We get clear images of moon surface, Jupiter, and Saturn, and our system can be demonstrated to greatly improve the imaging resolution through atmospheric turbulence.
100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.7060 Turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S21004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
The photoacoustic tomography (PAT) method, based on compressive sensing (CS) theory, requires that, for the CS reconstruction, the desired image should have a sparse representation in a known transform domain. However, the sparsity of photoacoustic signals is destroyed because noises always exist. Therefore, the original sparse signal cannot be effectively recovered using the general reconstruction algorithm. In this study, Bayesian compressive sensing (BCS) is employed to obtain highly sparse representations of photoacoustic images based on a set of noisy CS measurements. Results of simulation demonstrate that the BCS-reconstructed image can achieve superior performance than other state-of-the-art CS-reconstruction algorithms.
光声层析成像 压缩感知 贝叶斯压缩感知 图像重建 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(6): 061002





