Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 College of Science, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai 201418, China
3 Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102, China
We develop an improved region growing method to realize automatic retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell segmentation for photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) imaging. The minimum bounding rectangle of the segmented region is used in this method to dynamically update the growing threshold for optimal segmentation. Phantom images and PAM imaging results of normal porcine RPE are applied to demonstrate the effectiveness of the segmentation. The method realizes accurate segmentation of RPE cells and also provides the basis for quantitative analysis of cell features such as cell area and component content, which can have potential applications in studying RPE cell functions for PAM imaging.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 110.0180 Microscopy 100.2000 Digital image processing 170.1530 Cell analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 051101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Beijing 100039, China
3 Institute of Opto-electronics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
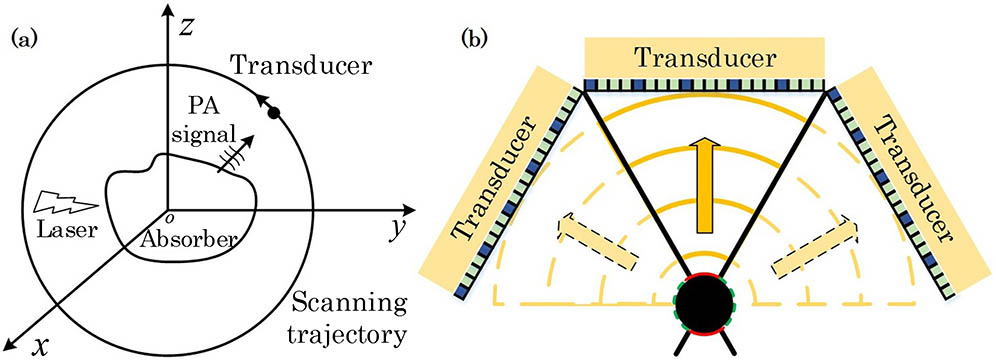
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has the unique capability of visualizing optical absorption inside several centimeters-deep biological tissue with a high spatial resolution. However, single linear-array transducer-based PAT suffers from the limited-view challenge, and thus the synthetic aperture configuration is designed that still requires multichannel data acquisition hardware. Herein, a feasible synthetic aperture PAT based on compressed sensing reconstruction is proposed. Both the simulation and experimental results tested the theoretical model and validated that this approach can improve the image resolution and address the limited-view problem while preserving the target information with a fewer number of measurements.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Photoacoustic tomography is a noninvasive and nonionized biomedical imaging modality but it cannot reveal the inner structure and sideward boundary information of blood vessels in the linear array detection mode. In contrast, Monte Carlo (MC) light transport could provide the optical fluence distribution around the entire vascular area. This research explores the combination of linear array transducer-based photoacoustic tomography and MC light transport in the blood vessel quantification. Simulation, phantom, and in vivo experiments are in good correlation with the ultrasound imaging, validating this approach can clearly visualize the internal region of blood vessels from background tissue.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 111701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
University of Michigan-Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
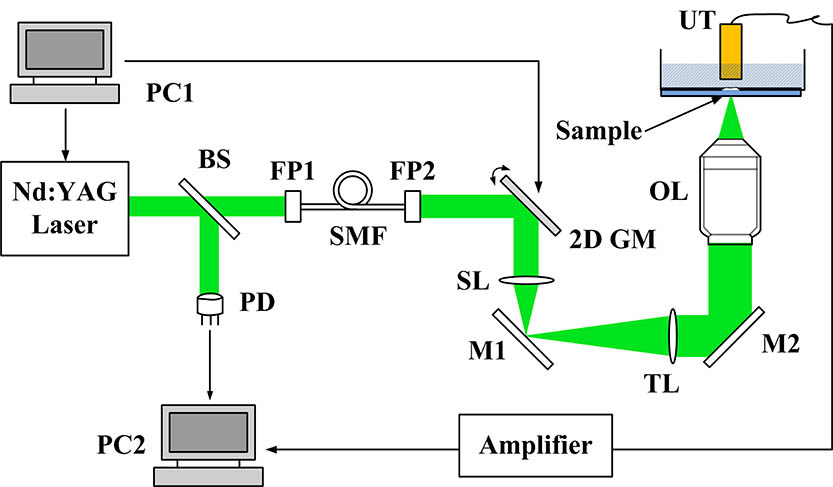
Photoacoustic imaging with a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) is an effective method to improve the lateral resolution for out-of-focus regions in scanning microscopy systems, which commonly require a decent motorized scanning stage for a lateral scan of a transducer to obtain a cross-sectional image. In this study, we propose and test a photoacoustic imaging system with a scanning mirror-based SAFT (SM-SAFT) for simple and fast data acquisition, without the need for a physical scan of the transducer. Photoacoustic images of hair phantoms acquired by SM-SAFT are demonstrated, serving as a proof-of-concept experiment to show the feasibility and potential of the proposed approach.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 180.5810 Scanning microscopy 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 101101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Key Laboratory of Medical Imaging Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Shanghai 200433, China
We propose a novel method by combining the total variation (TV) with the high-degree TV (HDTV) to improve the reconstruction quality of sparse-view sampling photoacoustic imaging (PAI). A weighing function is adaptively updated in an iterative way to combine the solutions of the TV and HDTV minimizations. The fast iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithm is implemented to solve both the TV and the HDTV minimizations with better convergence rate. Numerical results demonstrate the superiority and efficiency of the proposed method on sparse-view PAI. In vitro experiments also illustrate that the method can be used in practical sparse-view PAI.
110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(11): 111703
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
A new photoacoustic (PA) signal sampling and image reconstruction method, called compressive sampling PA tomography (CSPAT), is recently proposed to make low sampling rate and high-resolution PA tomography possible. A key problem within the CSPAT framework is the design of optic masks. We propose to use edge expander codes-based masks instead of the conventional random distribution masks, and efficient total variation (TV) regularization-based model to formulate the associated problem. The edge expander codes-based masks, corresponding to non-uniform sampling schemes, are validated by both theoretical analysis and results from computer simulations. The proposed method is expected to enhance the capability of CSPAT for reducing the number of measurements and fast data acquisition.
100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(10): 101102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Combining photoacoustic (PA) imaging with laser speckle (LS) imaging (LSI) can simultaneously determine total hemoglobin concentration (HbT), hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SO2), and blood flow rates. Thus, the co-registration of PA and LS images is important in physiological studies and pathological diagnosis. This letter presents a co-registration algorithm combining mutual information with the maximum between-class variance segmentation method (Otsu method). The mutual information and Otsu method are used to provide the registration measure criterion and image feature recognition, respectively. The evaluation results show that the registration function possesses a single maximum peak and high smoothness across the global co-registration district, indicating a robust behavior. Moreover, this method has good registration accuracy, and the fusion result simultaneously visualizes the separate functional information of two kinds of images.
110.6150 Speckle imaging 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 100.2000 Digital image processing 170.2655 Functional monitoring and imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(6): 061101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
The photoacoustic tomography (PAT) method, based on compressive sensing (CS) theory, requires that, for the CS reconstruction, the desired image should have a sparse representation in a known transform domain. However, the sparsity of photoacoustic signals is destroyed because noises always exist. Therefore, the original sparse signal cannot be effectively recovered using the general reconstruction algorithm. In this study, Bayesian compressive sensing (BCS) is employed to obtain highly sparse representations of photoacoustic images based on a set of noisy CS measurements. Results of simulation demonstrate that the BCS-reconstructed image can achieve superior performance than other state-of-the-art CS-reconstruction algorithms.
光声层析成像 压缩感知 贝叶斯压缩感知 图像重建 100.3020 Image reconstruction-restoration 110.5120 Photoacoutic imaging 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(6): 061002





