强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(10): 102001
强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(5): 052002
强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(8): 082203
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Graduate School of Engineering, Utsunomiya University, Utsunomiya 321-8585, Japan
2 Institute of Physics of the ASCR, ELI-Beamlines, Na Slovance 2, 18221 Prague, Czech Republic
3 Institute of Plasma Physics of the CAS, Za Slovankou 1782/3, 18200 Prague, Czech Republic
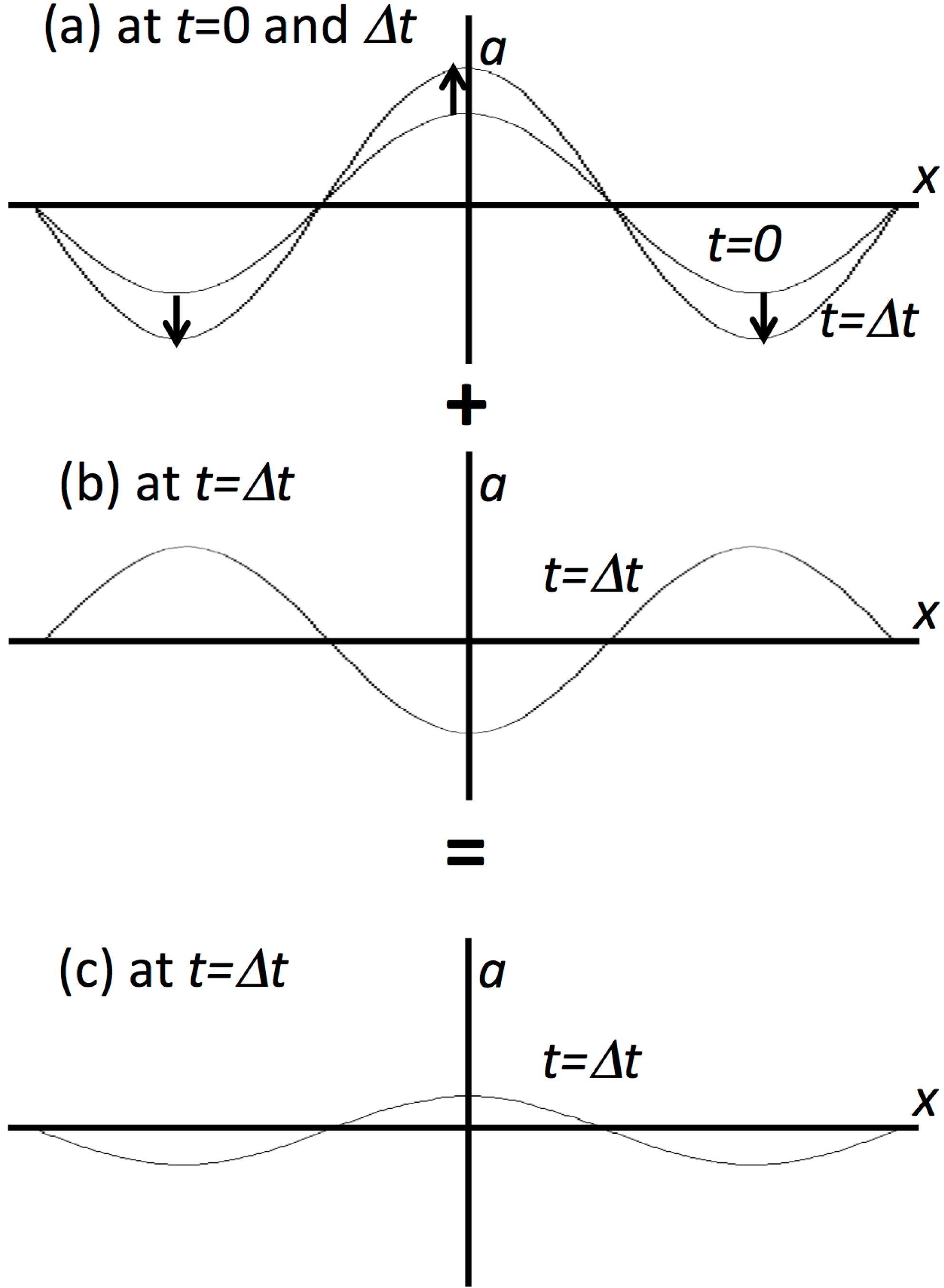
The paper presents a review of dynamic stabilization mechanisms for plasma instabilities. One of the dynamic stabilization mechanisms for plasma instability was proposed in the paper [Kawata, Phys. Plasmas 19, 024503 (2012)], based on a perturbation phase control. In general, instabilities emerge from the perturbations. Normally the perturbation phase is unknown, and so the instability growth rate is discussed. However, if the perturbation phase is known, the instability growth can be controlled by a superimposition of perturbations imposed actively. Based on this mechanism we present the application results of the dynamic stabilization mechanism to the Rayleigh–Taylor instability (RTI) and to the filamentation instability as typical examples in this paper. On the other hand, in the paper [Boris, Comments Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 3, 1 (1977)] another mechanism was proposed to stabilize RTI, and was realized by the pulse train or the laser intensity modulation in laser inertial fusion [Betti et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3131 (1993)]. In this latter mechanism, an oscillating strong force is applied to modify the basic equation, and consequently the new stabilization window is created. Originally the latter was proposed by Kapitza. We review the two stabilization mechanisms, and present the application results of the former dynamic stabilization mechanism.
dynamic instability stabilization filamentation instability plasma instability Rayleigh–Taylor instability stabilization of instability High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(1): 010000e3
中国工程物理研究院 流体物理研究所, 四川 绵阳 621999
为了研究物质弹塑性对磁驱动实验运动过程、不稳定性发展等的影响, 在MDSC2程序的基础上, 增加了弹塑性模块, 研制了包括弹塑性的磁流体力学程序, 并进行了弹塑性项影响的数值模拟和分析。数值模拟表明: 没有初始扰动时, 弹塑性项几乎不影响套筒内外半径的运动轨迹; 有初始扰动时, 弹塑性项对磁驱动固体套筒的Rayleigh-Tayor不稳定性有明显的抑制作用。
弹塑性 磁流体力学 磁驱动数值模拟程序 RT不稳定性 固体套筒 elastoplasticity magnetohydrodynamic two-dimensional magnetically driven simulation cod Rayleigh-Taylor instability solid liner 强激光与粒子束
2018, 30(6): 065002
1 中国工程物理研究院 流体物理研究所, 四川 绵阳 621999
2 中国科学技术大学 近代物理系, 合肥 230026
提出采用方向时变(旋转)的驱动磁场(交替Θ-Z箍缩构型)或者多级嵌套Θ-Z箍缩构型来抑制动态Z箍缩的MRT不稳定性的概念, 介绍了对交替/嵌套Θ-Z箍缩MRT不稳定性的最新研究进展, 结果表明适当优化的交替/嵌套Θ-Z箍缩的MRT不稳定性明显远低于标准Θ箍缩或者Z箍缩的, 一定厚度时甚至被完全致稳, 这表明交替/嵌套Θ-Z箍缩构型具有潜力应用于Θ-Z箍缩套筒惯性聚变。
磁-瑞利-泰勒不稳定性 动态Z箍缩 磁场方向旋转 Θ-Z箍缩套筒惯性聚变 交替/嵌套Θ-Z箍缩 惯性约束聚变 磁惯性约束聚变 magneto-Rayleigh-Taylor instability dynamic Z-pinch rotating magnetic field theta-Z liner inertial fusion alternant/nested theta-Z-pinch inertial confinement fusion magneto-inertial fusion 强激光与粒子束
2018, 30(2): 020101
中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
面向背光照相技术是诊断惯性约束聚变(ICF)中瑞利-泰勒(RT)不稳定性的重要方法,讨论了利用该技术对球形靶丸扰动幅度测量时由于收缩几何效应带来的影响。通过计算,分析了一个简化模型下扰动振幅的实际值和测量值,讨论了偏移距离、靶丸外半径、扰动波长和扰动振幅等因素对实验结果相对误差的影响。计算表明,合理选择这些参数能使诊断的系统误差小于3%,而且可通过计算模型对测量结果进行修正。研究结果可为即将开展的神光III激光装置上的收缩几何烧蚀RT不稳定性实验参数设计和结果分析提供依据。
激光光学 惯性约束聚变 瑞利-泰勒不稳定性 面向背光照相技术 收缩几何
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Graduate School of Engineering, Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya, 321-8585, Japan
2 CORE (Center for Optical Research and Education), Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya, 321-8585, Japan
3 Department of Physics, Technical University of Varna, Ulitska, Studentska 1, Varna, Bulgaria
In this review paper on heavy ion inertial fusion (HIF), the state-of-the-art scientific results are presented and discussed on the HIF physics, including physics of the heavy ion beam (HIB) transport in a fusion reactor, the HIBs-ion illumination on a direct-drive fuel target, the fuel target physics, the uniformity of the HIF target implosion, the smoothing mechanisms of the target implosion non-uniformity and the robust target implosion. The HIB has remarkable preferable features to release the fusion energy in inertial fusion: in particle accelerators HIBs are generated with a high driver efficiency of ~30%-40%, and the HIB ions deposit their energy inside of materials. Therefore, a requirement for the fusion target energy gain is relatively low, that would be ~50-70 to operate a HIF fusion reactor with the standard energy output of 1 GWof electricity. The HIF reactor operation frequency would be ~10-15 Hz or so. Several-MJ HIBs illuminate a fusion fuel target, and the fuel target is imploded to about a thousand times of the solid density. Then the DT fuel is ignited and burned. The HIB ion deposition range is defined by the HIB ions stopping length, which would be ~1 mm or so depending on the material. Therefore, a relatively large density-scale length appears in the fuel target material. One of the critical issues in inertial fusion would be a spherically uniform target compression, which would be degraded by a non-uniform implosion. The implosion non-uniformity would be introduced by the Rayleigh-Taylor (R-T) instability, and the large densitygradient- scale length helps to reduce the R-T growth rate. On the other hand, the large scale length of the HIB ions stopping range suggests that the temperature at the energy deposition layer in a HIF target does not reach a very-high temperature: normally about 300 eV or so is realized in the energy absorption region, and that a direct-drive target would be appropriate in HIF. In addition, the HIB accelerators are operated repetitively and stably. The precise control of the HIB axis manipulation is also realized in the HIF accelerator, and the HIB wobbling motion may give another tool to smooth the HIB illumination non-uniformity. The key issues in HIF physics are also discussed and presented in the paper.
Heavy ion inertial fusion Heavy ion inertial fusion Heavy ion fusion reactor system Heavy ion fusion reactor system Fusion fuel target implosion Fusion fuel target implosion Implosion dynamics Implosion dynamics Heavy ion beam transport Heavy ion beam transport Rayleigh- Taylor instability stabilization Rayleigh- Taylor instability stabilization Robust fusion system Robust fusion system Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2016, 1(2): 89
1 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100094
3 中国工程物理研究院, 四川 绵阳 621900
在神光Ⅱ装置上开展了辐射驱动RT不稳定性的一系列实验, 获得了不同初始扰动幅度、不同扰动波长、不同材料样品等条件下辐射烧蚀RT不稳定性增长的高时空分辨背光图像, 特别是在大初始扰动幅度样品实验中获得了扰动增长的清晰图像, 观察到了扰动增长从线性区到非线性区的过渡过程, 二次和三次谐波的产生和发展清楚可见。充实了数值模拟程序考核的实验数据库, 对间接驱动ICF点火靶设计和研究具有重要作用。
惯性约束聚变 激光间接驱动 内爆 RT不稳定性 辐射驱动 inertial confinement fusion laser indirect-driven implosion Rayleigh-Taylor instability radiation-driven 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032016
北京应用物理与计算数学研究所, 北京 100088
激光等离子体相互作用(LPI)和瑞利-泰勒流体不稳定性(RTI)是影响间接驱动惯性约束聚变成功的两个主要不确定性因素。点火黑腔内环激光通道在靠近黑腔壁的区域是内环激光SRS背反产生与发展的主要区域。内环通道在该区域满足通道内外压力平衡和能量平衡条件。据此提出了间接驱动惯性约束聚变点火黑腔等离子体定标关系。结合描述靶丸内爆飞行阶段物理以及内爆性能的两个定标关系, 提出了描述稳定性相对性能的指标。该指标可以指导点火靶设计, 为LPI和RTI提供需要的裕量空间, 是点火阈值因子(ITF)的补充。
惯性约束聚变 激光等离子体相互作用 瑞利-泰勒不稳定性 等离子体定标关系 点火靶设计 inertial confinement fusion laser and plasma interaction Rayleigh-Taylor instability plasma scaling ignition target design 强激光与粒子束
2015, 27(3): 032012





