1 之江实验室智能芯片与器件研究中心,浙江 杭州 311121
2 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院极端光学技术与仪器全国重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310027
3 上海电力大学电子与信息工程学院,上海 200090
4 浙江大学杭州国际科创中心, 浙江 杭州 311200
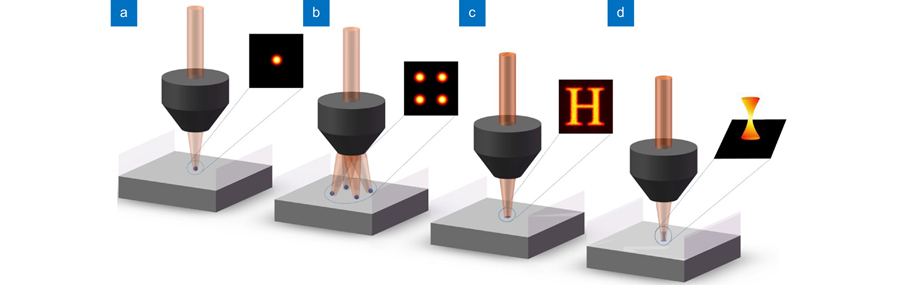
Overview: Two-photon lithography (TPL) has been a research hotspot in 3D micro/nano writing technology due to its characteristics of high resolution, low thermal influence, a wide range of processed materials, low environmental requirements, and 3D processing capability. It has shown unique advantages in the fields of life science, material engineering, micro/nano optics, microfluidic, micro machinery, and so on. This paper summarizes the research works done by researchers on different writing methods to improve TPL processing efficiency. Single-beam writing is the main method for TPL, which mainly depends on the speed of the scanning device. Single-beam writing has the advantages of simple system and high-quality beam, and it is easy to combine various effects to improve writing results. It mainly includes scanning modes based on the translation stage, galvo, polygon laser scanner, and acousto-optic deflector (AOD) (Fig. 2). All these modes have advantages and disadvantages. As for the scanning speed comparison, polygon laser scanner and AOD have relatively faster writing rates (faster than m/s). Multi-foci parallel lithography can obviously promote efficiency, elevating the speed by dozens or even hundreds of thousands of times, mainly based on spatial light modulator (SLM), digital micromirror device (DMD), microlens array (MLA), diffractive optical elements (DOE), multi-beam interference, and so on (Figs. 3-15). Multi-foci parallel lithography based on SLM is most widely used owing to its high efficiency and ability to flexible and independent control of each single beam, but the refresh rate is still insufficient. DMD has a higher refreshing rate (32 kHz), but the state-of-the-art beam parallelism realized by DMD is severely limited. More parallel beams are further required for improving the processing efficiency. The 2D pattern exposure method based on SLM or DMD can further improve the TPL efficiency with the superiority of generating flexibly designed pattern (Figs. 16-18). However, the 2D projection exposure technology is still difficult to achieve high writing precision, especially the axial resolution. An available method to improve the axial precision is spatially and temporally focusing an ultrafast laser to implement a strong intensity gradient at the spatial focal plane that restricts polymerization within a thin layer. The 3D projection method will be the most efficient writing method in the future, especially in 3D device processing (Figs. 19-20). Researchers used this technique to make hollow tubular and conical helices structures, increasing the processing speed by 600 times. However, the research results show that the current 3D projection can only process simple 3D structures. Further researches on 3D exposure processing of complex structures are expected, which will effectively expand its application in various fields. Authors believe that with the effort of researchers on efficiency improvement gradually, TPL can further highlight its advantages to promote the development of life science, materials engineering, micro-nano optics, and many other fields.
飞秒激光直写 双光子光刻 单光束扫描 多焦点并行 面曝光 体曝光 femtosecond laser direct writing two-photon lithography single-beam scanning multi-focus parallelism pattern projection 3D projection exposure
1 中国科学院大学 光电学院, 北京 100049
2 中国科学院 光电研究院, 北京 100094
3 西京学院 理学院, 陕西 西安 710123
传统单光束多强度重建(SBMIR)系统中, 多次平移图像传感器所积累的误差导致光电成像系统的成像效果及有效分辨率降低, 为了解决这一问题。本文提出基于平行平晶的三步相干衍射成像系统, 采取插入或抽取 2块平行平晶的方法获取 3个不同的衍射面, 实现了对复振幅型物体的成像及恢复重建。数值模拟及实验表明, 系统有效克服了SBMIR系统中数次平移的误差积累问题, 且仅需记录 3个衍射面, 避免过采样。而且光学系统实现简便、可重复性高。
单光束多强度 相干衍射成像 平行平晶 复振幅 the single-beam multiple-intensity coherent diffraction imaging parallel plates complex amplitude
华南理工大学化学化工学院, 广东 广州 510640
为扣除溶剂或其他背景组分的干扰, 测量红外光谱时常常需要获得期望强度的高质量背景单光束谱。 通常, 实验上获得期望强度的背景谱是极其困难的。 为实现这一重要且十分困难的目标, 引进了杂化单光束谱的概念。 同一溶液但不同厚度的b1和b2的两样品的单光束谱分别为b1和b2, 则定义它们的线性组合α=αb1+(1-α)b2为杂化单光束谱, 其中α(0≤α≤1)称为组分因子。 调整组分因子α数值, 就可以精确调控杂化谱的强度。 在合适的条件下, 杂化谱α与厚度为b2-αb2+αb1的真实样品的光谱高度类似, 即b2-αb2+αb1≈α。 因此, 不用制备厚度为b2-αb2+αb1的样品, 其单光束谱可以用α来替代。 随着α变化, 可以得到不同的α, 厚度在b1和b2间的真实样品的单光束谱都可用相应的α来替代。 实验结果证实, 杂化谱提供了一种简单和易操作的扣除背景干扰的高效方法。
红外光谱 杂化单光束谱 光谱失真 背景扣除 光谱类似性 Infrared spectroscopy Hybrid single-beam spectrum Spectral distortion Background elimination Spectral similarity 光谱学与光谱分析
2017, 37(5): 1581
华南理工大学化学与化工学院, 广东 广州 510640
同一样品不同厚度(b1和b2)的两单光束谱b1和b2经线性组合得到杂化单光束谱α=αb1+(1-α)b2=α0e-Kb1+(1-α)0e-Kb2, α为杂化系数。 通过改变杂化系数α, 就可获得任意强度的杂化谱α。 系统研究了杂化光谱α的性质。 研究表明, 只要控制合适的条件, 则厚度为(b2-αb2+αb1)的真实样品的单光束谱b(b=b2-αb2+αb1)与杂化谱α高度相似, α的失真程度可忽略不计。 也就是说, 厚度在b1~b2间任一厚度b的真实样品的单光束谱都可用杂化谱α来表达, α≈b。 因此, 不需制备厚度为b的样品, 通过改变杂化系数α就可获得研究者所希望强度的单光束谱b。 杂化谱方法有望在扣除背景干扰等方面得到广泛应用。
红外光谱 杂化单光束谱 性质 光谱失真 期望的强度 Infrared spectroscopy Hybrid single-beam spectrum Property Spectral distortion Desired intensity
南京理工大学 智能弹药技术国防重点学科实验室, 江苏 南京 210094
针对水下单光束扫描探测系统探测水中近场目标的需求, 为抑制海水后向散射干扰, 提高系统信噪比, 对系统光路参数进行了优化设计。通过推导系统盲区距离公式、水中目标回波和后向散射功率方程, 分析了系统探测区域和信噪比同光路参数的关系。在不同水质条件下, 基于粒子群算法(PSO)对光路参数进行了优化计算。结果表明: 对探测区域为6-10 m的系统, 当发射光束与接收视场平行, 接收视场半角为9 mrad, 收发间距为10.6 cm时, 系统信噪比达到最佳。为验证理论模型的正确性, 设计了水下激光探测光路模拟系统, 测试不同光路参数下系统信噪比, 实验结果与理论值一致。优化结果可为水下单光束扫描探测系统光路设计提供理论依据。
单光束扫描 光路参数 探测区域 信噪比 single-beam scanning optical parameters detecting field SNR 红外与激光工程
2016, 45(6): 0612001
1 中南大学 物理与电子学院, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 中南大学 物理与电子学院 超微超快过程湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
基于核(金属)/壳(介质)微球的单光束梯度阱模型, 计算了外面包覆较厚聚苯乙烯的铜微球在聚焦光场中的轴向散射力、梯度力以及合力, 分析了表面被高度氧化的铜微球的轴向捕获力。不同于纯金属米氏粒子, 外层包覆较厚介质材料的金属粒子在聚焦光场中容易被捕获但不能被捕获在聚焦光束的高强度区域。光学微操作实验显示: 高度氧化的铜微球能被聚焦的高斯光束捕获并可以在平面内移动。理论和实验结果便于研究核壳结构金属微粒的光学特性, 进一步拓展了光镊技术的应用范围。
单光束梯度阱 微球 光学捕获 single-beam gradient trap microsphere optical trapping 红外与激光工程
2016, 45(6): 0621002
南京理工大学 智能弹药技术国防重点学科实验室,南京 210094
受常规弹药空间及功耗限制,无法采用多个激光接收器实现大视场探测,且系统结构应简单易实现,故传统的四种大视场光束布局方式无法直接应用.为此,本文设计了一种新型的光学大视场旋转扫描接收方案,根据激光引信光学接收系统结构特点,应用Zemax光学软件,在非球面光学设计理论基础上,设计出多级光学聚焦整形接收透镜组.仿真结果显示相对于传统单级聚焦透镜,多级接收透镜组将光斑中心辐照亮度提高了近8倍,使光斑能量集中,尺寸减小.加工了非球面透镜组并进行了实验.结果表明该接收光学系统可有效汇聚激光回波能量,提高系统探测距离,实现目标周向360°大视场探测.
激光引信 新型接收技术 光学设计 单光束 Laser fuze New receiving technology Optical design Single beam
1 新疆大学信息科学与工程学院,乌鲁木齐,830046
2 山东科技大学工程物理研究所,山东,泰安,271019
采用物理吸附方法制备出多孔硅和偶氮化合物染料分散红(DR1)的复合薄膜.用单光束扫描法研究了多孔硅/DR1复合膜的三阶非线性光学性质,测量了在1064 nm处多孔硅/DR1复合膜的双光子吸收系数和非线性折射率.实验结果表明,同多孔硅相比,多孔硅/DR1复合膜三阶非线性光学效应明显得到了增强.
多孔硅 分散红1 单光束扫描法 三阶非线性光学 Porous Silicon Disperse red 1 ( DR1) Single beam technique( Z-scan) Third order optical Nonlinearities
1 Laboratory for Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, The Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Department of Physics, Suzhou University, Suzhou 215006, China
Chinese Journal of Lasers B
2000, 9(3): 255





