中国海洋大学物理与光电工程学院,山东 青岛 266100
通过涡旋光束的轨道角动量的叠加态的识别研究,提出了一种在水下无线光通信中运用涡旋光束进行高维信息调制与解调的方法。给出了两种涡旋光束的叠加态的识别方法和流程,并对水信道传输后的叠加态的光强分布图进行了识别,得出叠加态中的拓扑荷数,以此通过实验论证了轨道角动量叠加态可在低拓扑荷数情况下实现16维信息的调制与解调,为涡旋光束在水下无线光通信中的应用提供了一种可行方案。
大气光学与海洋光学 水下无线光通信 涡旋光束 轨道角动量 空间光调制器 图像识别 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(9): 0901001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
CAS Key Laboratory of Wireless-Optical Communications, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
The received signal intensity fluctuation and communication performance of an underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC) system under the air bubble effects are experimentally investigated. For different bubble density and size, lognormal, gamma, Weibull, and generalized extreme value distributions are tested to fit the fluctuation of the signal intensity at the receiving end. The best fitting distribution is found to vary with bubble parameters. The communication system performance with on–off keying and pulse position modulation is further studied.
060.4510 Optical communications 010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100008
1 空军工程大学航空航天工程学院, 陕西 西安 710038
2 中国人民解放军95084部队, 广东 佛山 528226
机载光电雷达随着使用频次的增加,其探测距离会与出厂时的指标产生严重偏差。为此,分析了机载光电雷达的工作原理,以及光电雷达的最大探测距离受目标辐射强度、大气条件、光学系统等影响;根据光电雷达的探测原理,提出了新型便携式光电雷达测试系统的设计思路,利用黑体和特制平行光管模拟无穷远目标红外辐射强度,将衰减片与步进电机、传动齿轮结合来模拟不同的大气条件,最终确定其样机,并完成了红外衰减片的计量测试;阐明了新型便携式光电雷达测试系统的使用方法及测试结果。该测试系统便于携带,测试效率较高,适用于极端恶劣的环境条件,并可推广至各种类型的红外探测系统的性能测试中。
大气与海洋光学 光电雷达测试系统 黑体 组合式衰减片 伺服系统 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(1): 010101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Technology Innovation, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
2 Center of Medical Physics and Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
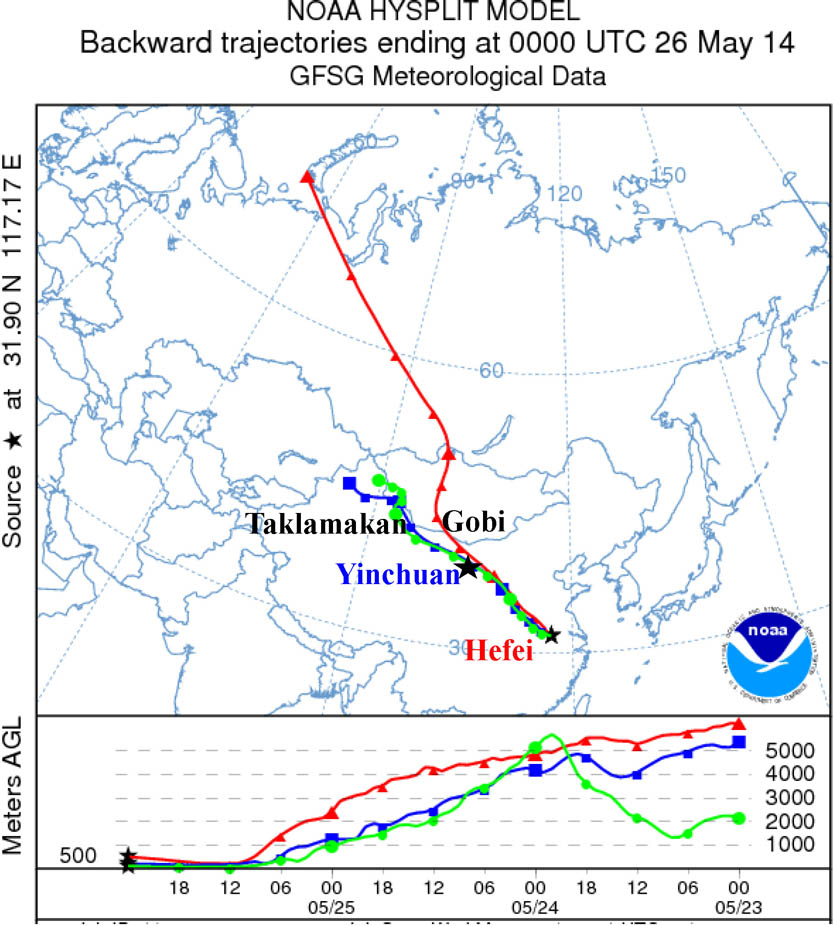
As an extension of the Mie lidar technique to measure the extinction coefficient of the surface particles, a horizontally pointing Mie lidar is used for determining the optical properties of Asian dust, which is an approach without knowing the actual lidar ratio. A long lasting dust event is observed based on this approach in May 2014. The “no dust,” “pure dust,” and “polluted dust” stage is observed during this event, and their optical and hygroscopic properties are discussed. Some new optical and hygroscopic features are observed, which benefit from the quantitative, multi-wavelength, and continuous measurement of the extinction related optical properties of dust particles.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 290.2200 Extinction Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020102
1 中国科学院安徽光学精密机械研究所 中国科学院大气成分与光学重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230031
2 中国科学技术大学研究生院 科学岛分院, 安徽 合肥230031
为研究海洋大气气溶胶粒子数浓度时空分布和粒径谱分布特征, 2014年8月至2016年3月期间, 利用光学粒子计数器和自动气象站等设备在广州茂名海边、东海和南海海域、三亚近海海域以及太平洋和印度洋海域对海洋大气气溶胶粒子数密度谱及大气温度、湿度、气压、风速等进行了测量。对不同海域不同气象条件下的谱分布特征进行了统计分析, 并对谱分布进行了拟合。结果表明海洋大气气溶胶粒子谱分布是由一个细粒模和一个中间模组成, 但近海的粒子数浓度大于远海。远海气溶胶粒子谱型稳定, 海面风力是引起粒子数浓度变化的主要原因。东海和南海的粒子谱分为二段, 小于0.5 ?滋m时用Junge谱的指数分布来描述, 0.5~4 ?滋m段用对数正态分布来描述。大风天气下海洋气溶胶的消光系数明显增加, 且在1~3 ?滋m波段的消光特征基本不受波长的影响。
海洋大气光学 大气气溶胶 粒子谱分布 消光系数 粒子数浓度 atmospheric and oceanic optics atmospheric aerosol particle size distribution extinction coefficient particle number density 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(12): 1211002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Environmental Optics and Technology, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
2 University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Air Pollution Prevention and Control, Tianjin Academy of Environmental Sciences, Tianjin 300191, China
A mobile vehicle lidar system has been developed and applied to detect urban air quality. On September 21 and 22, 2015, particulate matter observation with mobile vehicle lidar was carried out in the Binhai New Area of Tianjin. Combined with the latitude and longitude information acquired by a GPS, the three-dimensional distribution of the aerosol extinction coefficient was presented in the experimental area. Furthermore, the source, distribution, and the transportation path of the aerosols in the area were investigated based on lidar data, local meteorological data, and backward trajectory analysis. The results show that mobile vehicle lidar can detect the atmospheric aerosols and reflect the stereoscopic distribution properties of aerosols. The potential of this vehicle lidar system provides a new scientific basis for the study of the source, distribution, and transportation of atmospheric particles.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 290.0290 Scattering Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 060101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Air and Missile Defense College, Air Force Engineering University, Xi’an 710051, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves, Nanjing 210096, China
3 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
Mathematical models for the superimposed orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode of multiple Hankel–Bessel (HB) beams in anisotropic non-Kolmogorov turbulence are developed. The effects of anisotropic turbulence and source parameters on the mode detection spectrum of the superimposed OAM mode are analyzed. Anisotropic characteristics of the turbulence in the free atmosphere can enhance the performance of OAM-based communication. The HB beam is a good source for mitigating the turbulence effects due to its nondiffraction and self-focusing properties. Turbulence effects on the superimposed OAM mode can be effectively reduced by the appropriate allocation of OAM modes at the transmitter based on the reciprocal features of the mode cross talk.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence 010.3310 Laser beam transmission 270.5585 Quantum information and processing Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(8): 080102
中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学院, 山东 青岛 266100
为研究正交偏振云气溶胶激光雷达(CALIOP)最新Version 4(V4)版产品与Version 3(V3)版产品全球大气气溶胶和云衰减后向散射特征的差异及其对以往研究可能造成的影响,利用2011年1、4、7、10月CALIOP 这两个版本的数据,对20.2 km海拔高度内全球范围云和气溶胶样本点的532 nm总衰减后向散射、1064 nm衰减后向散射、总衰减颜色比进行了概率分布统计,并对两个不同版本相应数据的相对偏差做出统计分析。结果表明,云或气溶胶V4版与V3版散射数据的相对偏差趋于正值,夜间数据的变化比日间数据明显。V4版与V3版云的日间532 nm总衰减后向散射、1064 nm衰减后向散射及总衰减颜色比的相对偏差均值分别为3.40%、4.66%和1.18%,而夜间的则分别为2.80%、8.00%和5.33%。气溶胶的532 nm总衰减后向散射、1064 nm衰减后向散射及总衰减颜色比的相对偏差均值日间分别为1.14%、6.94%和5.62%,夜间分别为3.33%、10.92%和7.64%。
大气海洋光学 衰减后向散射 总衰减颜色比 云 气溶胶 激光与光电子学进展
2016, 53(6): 060102
西安理工大学自动化与信息工程学院, 陕西 西安 710048
大气分子的吸收、散射和大气湍流等因素引起的光强闪烁严重影响无线光通信系统的性能,导致激光束能量衰减、信噪比下降,而分集接收技术能有效地克服这种影响。采用开关键控(OOK)调制,建立了强湍流模型-K 分布模型下无线光通信空间接收分集系统模型,在不同信道参数和接收天线数下,分别对比分析了最大比合并(MRC)、等增益合并(EGC)和选择合并(SC)的差错性能。仿真结果表明,分集接收能在很大程度上改善大气激光通信的性能,具有较强的抗大气信道衰落能力。三种合并算法中,MRC 性能最优,EGC 次之,SC性能最差。
大气和海洋光学 无线光通信 强湍流信道 K 分布模型 分集合并 差错性能
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We propose and experimentally evaluate a novel approach to measure atmospheric turbulence, in which imaging of light column technology is integrated into a differential motion method. In the approach, a large acquisition scene of the light column and a narrow field of view of one pixel of the charge-coupled device respectively allow high temporal and spatial resolutions, which offer the possibility of path-integrated turbulence strength measurement with multiple paths. In addition, we describe the measurement principle of the approach. Lastly, comparative experiment is performed to verify the feasibility of the approach.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 010.3640 Lidar 120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(12): 120101





