Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Integrated Service Networks, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
2 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
3 School of Electronic Engineering, Xidian University, Xi’an 710071, China
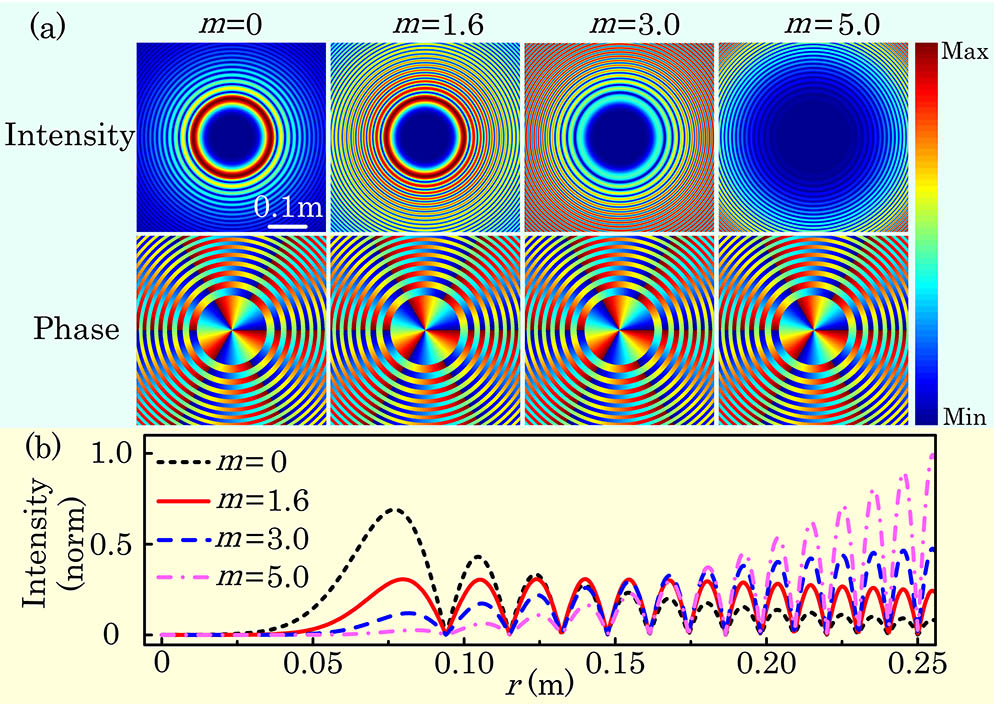
Vortex splitting is one of the main causes of instability in orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes transmission. Recent advances in OAM modes free-space propagation have demonstrated that abruptly autofocusing Airy vortex beams (AAVBs) can potentially mitigate the vortex splitting effect. However, different modes of vortex embedding will affect the intensity gradients of the background beams, leading to changes in the propagation characteristics of vortex beams. This study presents the unification of two common methods of coupling autofocusing Airy beams with vortices by introducing a parameter (m), which also controls the intensity gradients and focusing properties of the AAVBs. We demonstrate that vortex splitting can be effectively reduced by selecting an appropriate value of the parameter (m) according to different turbulence conditions. In this manner, the performance of OAM-based free-space optical systems can be improved.
010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(4): 040101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping, and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University,129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Geospatial Technology, 129 Luoyu Road, Wuhan 430079, China
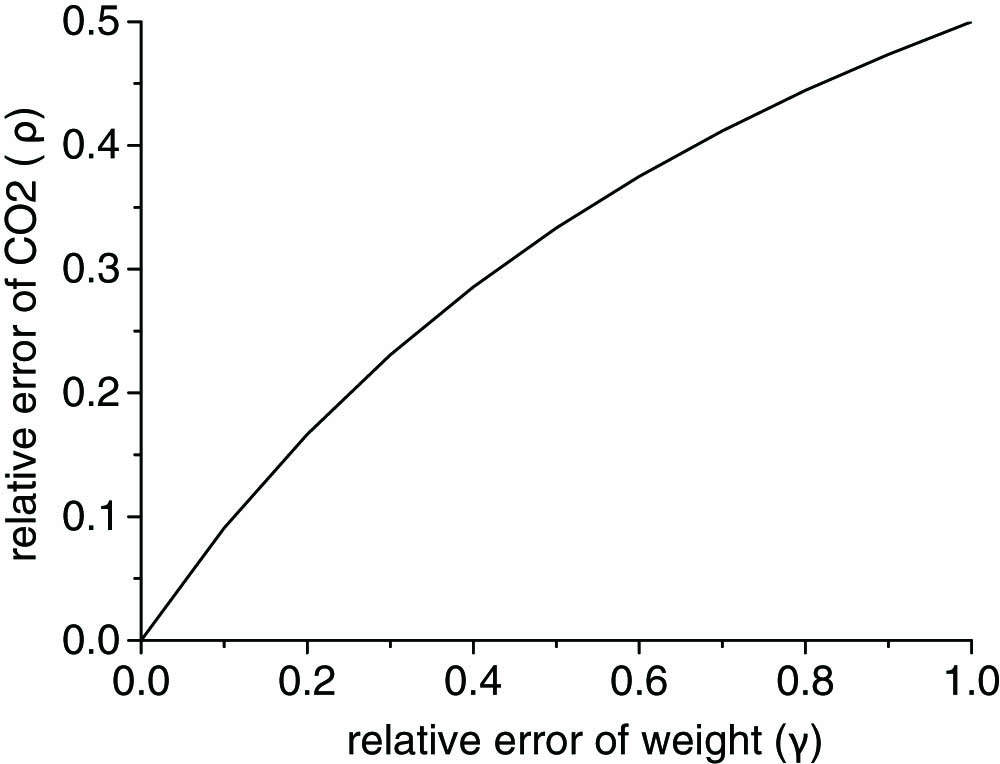
Accurately measuring the differential molecular absorption cross section is the key to obtaining a high-precision concentration of atmospheric trace gases in a differential absorption lidar (DIAL) system. However, the CO2 absorption line is meticulous at 1.6 μm, easily translating and broadening because of the change of temperature and pressure. Hence, measuring the vertical profile of atmospheric temperature and pressure to calculate the vertical profile of the CO2 weight parameter is necessary. In general, measuring atmospheric temperature and pressure has a certain amount of uncertainty. Therefore, this study proposes the concept of a balanced on-line wavelength, where the differential molecular absorption cross section is larger and the CO2 weight parameter is insensitive to the uncertainty of atmospheric temperature and pressure. In this study, we analyzed the influence of uncertainty on the CO2 weight parameter at every preselected wavelength, as well as determined an appropriate wavelength near one of the absorption peaks. Our result shows that 1572.023 nm should be one of the appropriate balanced online wavelengths. The measurement errors of the mixing ratio of CO2 molecule in this wavelength are only 0.23% and 0.25% and are caused by 1 K temperature error and 1 hPa pressure error, respectively. This achievement of a balanced on-line wavelength will not only depress the requirement of the laser’s frequency stabilization but also the demand for measurement precision of the atmospheric temperature and pressure profile. Furthermore, this study can achieve the exact measurement of the vertical profile of atmospheric CO2 based on an independent differential absorption laser.
Atmospheric optics Lidar Photonics Research
2015, 3(4): 04000146
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xian 710024, China
We simulate the integrated effects of atmospheric aberration, atmospheric turbulence, thermal blooming, random jitter of laser's intensity and phase, speed of wind, direction of wind, absorption of air, kinetic cooling of CO2 and N2, speed of target, output power and beam quality of laser, wavelength, focus length, and the launch altitude of laser to accurately simulate the transmission loss of the laser's energy, concentration of laser's power and other beam quality parameters of the laser propagating to the dynamic target. And we evaluate the efficiency of laser's irradiation on the target more accurately for the optical link of ground-to-airspace. We also investigate influences of characteristics of dynamic parameters (Strehl's ratio, RMS of wave-front, spatial distribution of intensity on the target, the real focus on the optical link and the peak intensity along the propagation path) including speed of wind, direction of wind, speed of target and the kinetic cooling effect of air, especially. We conclude that the higher speed of wind and target weakens the thermal blooming of atmosphere and improves the beam quality and efficiency of laser's irradiation on the target. The kinetic cooling effect of air is more remarkable to improve the beam quality irradiating on the target at the initial part of the propagation path of the laser. The changed direction of wind weakens the atmospheric aberration and directs to better beam quality and higher efficiency of laser's irradiation on the target.
010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s2): S20101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optical Calibration and Characterization, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
2 College of Atmospheric Physics, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
Remote measurements of Earth's surface from ground, airborne, and spaceborne instruments show that its albedo is highly variable and is sensitive to solar zenith angle (SZA) and atmospheric opacity. Using a vali-dated radiative transfer calculating toolbox, DISORT and a bidirectional reflectance distribution function library, AMBRALS, a land surface albedo (LSA) lookup table (LUT) is produced with respect to SZA and aerosol optical depth. With the LUT, spectral and broadband LSA can be obtained at any given illumination geometries and atmospheric conditions. It provides a fast and accurate way to simulate surface reflectance over large temporal and spatial scales for climate study.
010.1310 Atmospheric scattering 280.1310 Atmospheric scattering 240.5698 Reflectance anisotropy spectroscopy 350.5610 Radiation Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(11): 110101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Partially coherent vortex beams are generated by the illumination of high-power red-color light-emitting diodes. We investigate the influence of correlation property of partially coherent vortex beams on intensity distribution. The correlation property of partially coherent vortex beams are modulated by adjusting the propagation distance of the incident light. Effects of the topological charge and propagation distance of vortex beams on the intensity are also studied. Experiment results are consistent with theoretical simulations.
030.1640 Coherence 050.4865 Optical vortices 260.3160 Interference 110.4980 Partial coherence in imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S10301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
In this Letter, we investigate the packet error rate (PER) performance of digital pulse interval modulation (DPIM) for free-space optical (FSO) links under the combined effect of turbulence and pointing errors. The theoretical model is developed by considering the effect of some important parameters, including turbulence condition, beamwidth, receiver aperture size, jitter variance, data rate, transmitted optical power, etc. A closed-form average PER expression for DPIM is derived for this fading channel. The results of numerical simulation are further provided to verify the validation of our model. This work can be helpful for selecting DPIM in the FSO system design.
010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence 060.2605 Free-space optical communication 060.4080 Modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S10101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We establish a system to measure the functional absorption cross section of photosystem II (PSII) (\sigma PSII) and maximum quantum yield of photochemistry in PSII (Fv/Fm). The system utilizes a sequence of high-frequency excitation flashes at microsecond intervals to induce a microsecond-level fluorescence yield curve. Parameters \sigma PSII and Fv/Fm are calculated by fitting the curve using nonlinear regression. Experimental results show that the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the system is less than 3%, and the correlation coefficient of Fv/Fm values measured by this system and those measured by pulse amplitude modulation method is 0.950.
010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(8): 080101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
In the letter the polarization properties of quasi-homogenous (QH) beam propagating in Kolmogorov and non-Kolmogorov turbulence are studied. The results show that the polarization properties of QH beam undergoes three stages during the propagation in turbulence: in the “near field”, the degree of polarization (Dop) and the state of polarization (Sop) fluctuate with source parameters and transverse position; after that the beam come to the “middle field” where its properties are affected by source parameters and turbulence perturbation; in the final “far field”, the values come to constants which dependent only on source parameters.
010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 030.7060 Turbulence 260.2710 Inhomogeneous optical media Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(s2): S20102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A closed-form bit-error rate (BER) expression is derived for free-space optical (FSO) communication systems with circle polarization shift keying and spatial diversity receivers in the gamma-gamma (GG) distribution fading channel. This model can predict the performance without the need of lengthy simulation runs. The performance can be analyzed by some system parameters such as atmospheric conditions, link length, communication wavelength, receiver aperture size, and number of spatial diversity receivers. Numerical results demonstrate the influence of the above parameters on the FSO systems and show quantitatively the differences in behavior among various different parameters.
010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence 060.2605 Free-space optical communication 060.4080 Modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(s2): S20101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We propose and experimentally evaluate a novel approach to measure atmospheric turbulence, in which imaging of light column technology is integrated into a differential motion method. In the approach, a large acquisition scene of the light column and a narrow field of view of one pixel of the charge-coupled device respectively allow high temporal and spatial resolutions, which offer the possibility of path-integrated turbulence strength measurement with multiple paths. In addition, we describe the measurement principle of the approach. Lastly, comparative experiment is performed to verify the feasibility of the approach.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 010.3640 Lidar 120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(12): 120101





