Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia
2 Faculty of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, 86400 Bt. Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
3 Industrial Biotechnology Research Centre, SIRIM Berhad, 40200 Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia
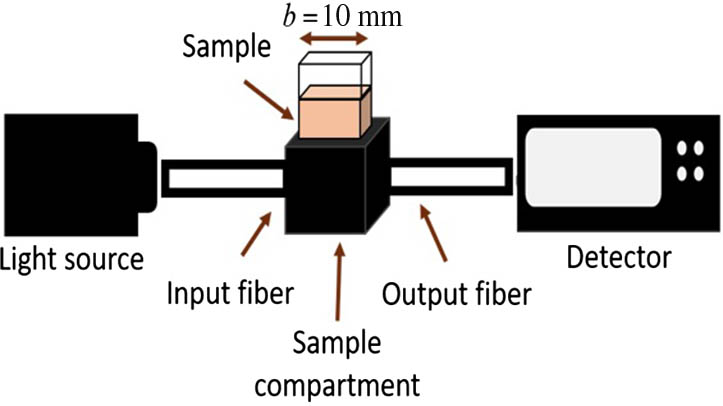
A spectrophotometer with an LED as the light source for uric acid detection is proposed in this work. The mechanism of uric acid detection is based on energy absorbed by sodium urate, which is a chemical product of uric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. For the performance validation, comparison between the spectrophotometer with an LED and halogen lamp is carried out. Measurement results suggest that the spectrophotometer system with LED light has better sensitivity than that with halogen light. At a 460 nm wavelength, the sensitivity for the spectrophotometer with an LED is 0.0046 dL/mg, which is 73% higher than that with halogen light that records 0.0012 dL/mg. This enhanced sensitivity is attributed to the higher luminous efficacy of the LED light beam. As a result, a larger amount of flux interacts with the sample, leading to the sensitivity enhancement. The spectrophotometer with an LED is also applied for the detection of uric acid in a real human urine sample. Based on the experimental data at a 460 nm wavelength, the method manages to achieve the sensitivity of 0.0016 dL/mg, accuracy of 96.01%, limit of detection of 4.79 mg/dL, and limit of quantification of 14.52 mg/dL. These findings show that the use of LED as the input light source is promising for the spectrophotometer.
170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6190 Spectrometers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Hefei University, Hefei 230601, China
2 State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Optical Monitoring Technology, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230031, China
Using a measurement system based on fluorescence induced by variable pulse light, photosynthesis parameters of
chlorella pyrenoidosa are obtained, employing single-turnover and multiple-turnover protocols under dark-adapted and light-adapted conditions. Under the light-adapted condition,
σPSII′ is larger, and
Fv′/Fm(ST)′ and
Fv′/Fm(MT)′ are smaller than those of the dark-adapted condition, but the corresponding parameters possess good linear correlations.
Fm(MT),
Fm(MT)′,
Fv/Fm(MT), and
Fv′/Fm(MT)′, which are measured using the multiple-turnover protocol, are larger than those of the single-turnover protocol. The linear correlation coefficient between
Fm(ST) and
300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 013001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
We demonstrate that the filamentation process is strongly influenced by the polarization state of the driver laser. When the laser polarization changes from linear to circular, the critical power for the self-focusing of a Ti:Sapphire laser (800 nm, 40 fs) in air increases from about 9.6±1.0 to 14.9±1.5 GW, while the second nonlinear refractive index n2 of air decreases from 9.9 × 10 20 to 6.4 × 10 20 cm2/W. We also demonstrate that the luminescence from the neutral nitrogen molecules at 337 nm is dependent on both the laser intensity and plasma density inside the filament.
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 260.5950 Self-focusing 260.5210 Photoionization Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(12): 120201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optical Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai Ultra-Precision Optical Manufacturing Engineering Center, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education), Shanghai 200433, China
3 College of Physical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
4 Department of Medical Physics, Weifang Medical University, Shandong 261053, China
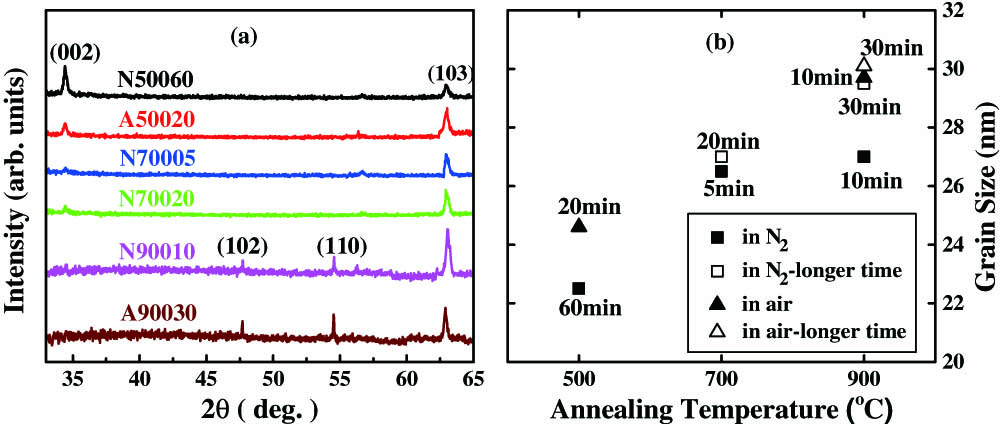
A number of zinc oxide (ZnO) films are deposited on silicon substrates using the magnetron sputtering method. After undergoing thermal treatment under different conditions, those films exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structures and different photoluminescent characteristics. Besides the notable ultraviolet emission, which is related to the free exciton effect, a distinct blue fluorescence around 475 nm is found in some special samples. The blue photoluminescence emission of the ZnO film is believed to be caused by oxygen vacancies.
310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 310.1860 Deposition and fabrication 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 260.3800 Luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 103101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We establish a system to measure the functional absorption cross section of photosystem II (PSII) (\sigma PSII) and maximum quantum yield of photochemistry in PSII (Fv/Fm). The system utilizes a sequence of high-frequency excitation flashes at microsecond intervals to induce a microsecond-level fluorescence yield curve. Parameters \sigma PSII and Fv/Fm are calculated by fitting the curve using nonlinear regression. Experimental results show that the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the system is less than 3%, and the correlation coefficient of Fv/Fm values measured by this system and those measured by pulse amplitude modulation method is 0.950.
010.4450 Oceanic optics 120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(8): 080101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Monovalent ions Li+, Na+, and K+, as charge compensators, are introduced into CaYAl3O7: M (M=Eu3+, Ce3+) in this letter. Their crystal phases and photoluminescence properties of different alkali metal ions doped in CaYAl3O7 are investigated. In addition, the influence of charge compensation ion Li+ which has a more obvious role in improving luminescence intensity on CaYAl3O7: Eu3+ phosphor is intentionally discussed in detail and a possible mechanism of charge compensation is given. The enhancement of red emission centered at 618 nm belonging to Eu3+ is achieved by adding alkali metal ion Li+ under 393-nm excitation.
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(5): 051602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institut d’Electronique Fondamentale, CNRS—Univ. Paris Sud 11, Batiment 220, F-91405 Orsay, France
2 Institut d’Electronique Fondamentale, CNRS—Univ. Paris Sud 11, Batiment 220, F-91405 Orsay, France
3 Laboratoire de Photonique et de Nanostructures, CNRS—UPR 20, Route de Nozay 91460 Marcoussis, France
4 Laboratoire de Physique des Interfaces et des Couches Minces, CNRS—Ecole polytechnique, F-91128 Palaiseau, France
The optical properties of germanium can be tailored by combining strain engineering and -type doping. In this paper, we review the recent progress that has been reported in the study of germanium light emitters for silicon photonics. We discuss the different approaches that were implemented for strain engineering and the issues associated with -type doping. We show that compact germanium emitters can be obtained by processing germanium into tensile-strained microdisks.
Semiconductor materials Optoelectronics Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence Photonics Research
2013, 1(3): 03000102
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Aiming at the crosstalk problem caused by small spectral intervals between fluorescent reagents in fourplex fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection analysis system, we calculate and analyse the effect of cut-off steepness, central wavelength positioning, and bandwidth of filters on crosstalk. Design and prepare four sets of fluorescence excitation and emission filters with proper shape cut-off steepness (optical density (OD) from OD 0.3 to OD 6 is less than 8 nm) and bandwidth (9–11 nm). In fourplex PCR instrument, crosstalk coefficient in all four channels are less than 0.3%.
230.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(s1): S10402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Noninvasive technology for measuring instantaneously two-dimensional (2D) temperature distributions of flame using two-color planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) of OH is investigated. A calibration method is researched and developed. This method is based on the calibration experiments with a laminar premixed flame and thermocouple, and avoids complex calculation and uncertainty of the spectrum parameters. Measurements for a flat burner at ambient temperature under atmospheric pressure are also presented; calibration results are used to diagnose a supersonic combustion in scramjet combustor. The conclusion indicates that this method is useful, and a better precision of calibration can be acquired by correcting the line shapes of the spectral lines and lasers.
300.2530 Fluorescence, laser-induced 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6360 Spectroscopy, laser 300.6540 Spectroscopy, ultraviolet Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(5): 053001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
The effects of Nd3+ concentration on the visible fluorescence spectroscopic properties of Nd:(Y0.9La0.1)2O3 transparent ceramics are investigated. Under 270 nm excitation, three emission peaks are observed at 396, 426, and 633 nm. When the Nd3+ concentration is increased, intensities of the peaks at 396 and 426 nm increase while the 633 nm peak become weak due to the fluorescence re-absorption effect. Broad luminescence band centered at 426 nm is observed from the fluorescence spectrum stimulated at 358 nm. The emission intensity increases with the increase of Nd3+ ion content firstly, then decreases owing to the concentration quenching of Nd3+ ions.
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 160.4670 Optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s2): S21604





